Rohini Srihari
ESC-Judge: A Framework for Comparing Emotional Support Conversational Agents
May 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) increasingly power mental-health chatbots, yet the field still lacks a scalable, theory-grounded way to decide which model is most effective to deploy. We present ESC-Judge, the first end-to-end evaluation framework that (i) grounds head-to-head comparisons of emotional-support LLMs in Clara Hill's established Exploration-Insight-Action counseling model, providing a structured and interpretable view of performance, and (ii) fully automates the evaluation pipeline at scale. ESC-Judge operates in three stages: first, it synthesizes realistic help-seeker roles by sampling empirically salient attributes such as stressors, personality, and life history; second, it has two candidate support agents conduct separate sessions with the same role, isolating model-specific strategies; and third, it asks a specialized judge LLM to express pairwise preferences across rubric-anchored skills that span the Exploration, Insight, and Action spectrum. In our study, ESC-Judge matched PhD-level annotators on 85 percent of Exploration, 83 percent of Insight, and 86 percent of Action decisions, demonstrating human-level reliability at a fraction of the cost. All code, prompts, synthetic roles, transcripts, and judgment scripts are released to promote transparent progress in emotionally supportive AI.
A Recipe For Building a Compliant Real Estate Chatbot
Oct 07, 2024Abstract:In recent years, there has been significant effort to align large language models with human preferences. This work focuses on developing a chatbot specialized in the real estate domain, with an emphasis on incorporating compliant behavior to ensure it can be used without perpetuating discriminatory practices like steering and redlining, which have historically plagued the real estate industry in the United States. Building on prior work, we present a method for generating a synthetic general instruction-following dataset, along with safety data. Through extensive evaluations and benchmarks, we fine-tuned a llama-3-8B-instruct model and demonstrated that we can enhance it's performance significantly to match huge closed-source models like GPT-4o while making it safer and more compliant. We open-source the model, data and code to support further development and research in the community.
Steering Conversational Large Language Models for Long Emotional Support Conversations
Feb 16, 2024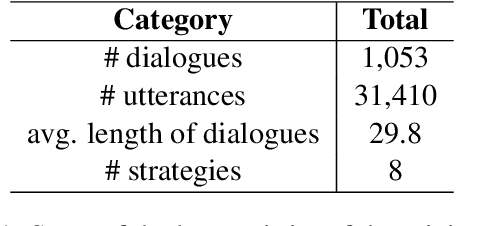
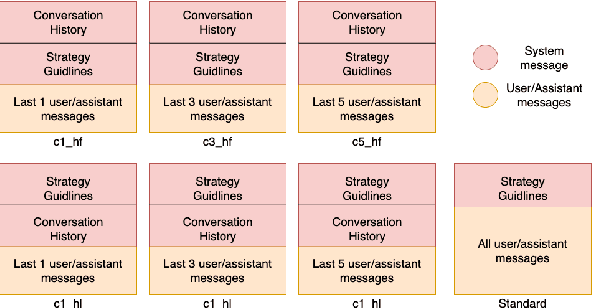
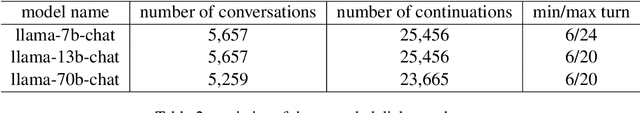
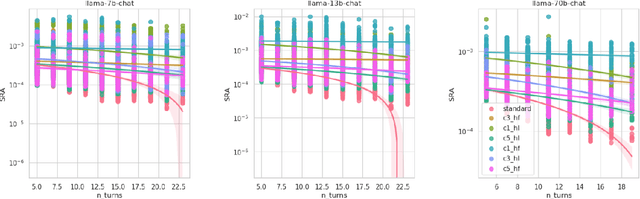
Abstract:In this study, we address the challenge of consistently following emotional support strategies in long conversations by large language models (LLMs). We introduce the Strategy-Relevant Attention (SRA) metric, a model-agnostic measure designed to evaluate the effectiveness of LLMs in adhering to strategic prompts in emotional support contexts. By analyzing conversations within the Emotional Support Conversations dataset (ESConv) using LLaMA models, we demonstrate that SRA is significantly correlated with a model's ability to sustain the outlined strategy throughout the interactions. Our findings reveal that the application of SRA-informed prompts leads to enhanced strategic adherence, resulting in conversations that more reliably exhibit the desired emotional support strategies over longer conversations. Furthermore, we contribute a comprehensive, multi-branch synthetic conversation dataset for ESConv, featuring a variety of strategy continuations informed by our optimized prompting method. The code and data are publicly available on our Github.
Consolidating Strategies for Countering Hate Speech Using Persuasive Dialogues
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:Hateful comments are prevalent on social media platforms. Although tools for automatically detecting, flagging, and blocking such false, offensive, and harmful content online have lately matured, such reactive and brute force methods alone provide short-term and superficial remedies while the perpetrators persist. With the public availability of large language models which can generate articulate synthetic and engaging content at scale, there are concerns about the rapid growth of dissemination of such malicious content on the web. There is now a need to focus on deeper, long-term solutions that involve engaging with the human perpetrator behind the source of the content to change their viewpoint or at least bring down the rhetoric using persuasive means. To do that, we propose defining and experimenting with controllable strategies for generating counter-arguments to hateful comments in online conversations. We experiment with controlling response generation using features based on (i) argument structure and reasoning-based Walton argument schemes, (ii) counter-argument speech acts, and (iii) human characteristics-based qualities such as Big-5 personality traits and human values. Using automatic and human evaluations, we determine the best combination of features that generate fluent, argumentative, and logically sound arguments for countering hate. We further share the developed computational models for automatically annotating text with such features, and a silver-standard annotated version of an existing hate speech dialog corpora.
Rudolf Christoph Eucken at SemEval-2023 Task 4: An Ensemble Approach for Identifying Human Values from Arguments
May 09, 2023Abstract:The subtle human values we acquire through life experiences govern our thoughts and gets reflected in our speech. It plays an integral part in capturing the essence of our individuality and making it imperative to identify such values in computational systems that mimic human actions. Computational argumentation is a field that deals with the argumentation capabilities of humans and can benefit from identifying such values. Motivated by that, we present an ensemble approach for detecting human values from argument text. Our ensemble comprises three models: (i) An entailment-based model for determining the human values based on their descriptions, (ii) A Roberta-based classifier that predicts the set of human values from an argument. (iii) A Roberta-based classifier to predict a reduced set of human values from an argument. We experiment with different ways of combining the models and report our results. Furthermore, our best combination achieves an overall F1 score of 0.48 on the main test set.
ArgU: A Controllable Factual Argument Generator
May 09, 2023Abstract:Effective argumentation is essential towards a purposeful conversation with a satisfactory outcome. For example, persuading someone to reconsider smoking might involve empathetic, well founded arguments based on facts and expert opinions about its ill-effects and the consequences on one's family. However, the automatic generation of high-quality factual arguments can be challenging. Addressing existing controllability issues can make the recent advances in computational models for argument generation a potential solution. In this paper, we introduce ArgU: a neural argument generator capable of producing factual arguments from input facts and real-world concepts that can be explicitly controlled for stance and argument structure using Walton's argument scheme-based control codes. Unfortunately, computational argument generation is a relatively new field and lacks datasets conducive to training. Hence, we have compiled and released an annotated corpora of 69,428 arguments spanning six topics and six argument schemes, making it the largest publicly available corpus for identifying argument schemes; the paper details our annotation and dataset creation framework. We further experiment with an argument generation strategy that establishes an inference strategy by generating an ``argument template'' before actual argument generation. Our results demonstrate that it is possible to automatically generate diverse arguments exhibiting different inference patterns for the same set of facts by using control codes based on argument schemes and stance.
Similarity Based Label Smoothing For Dialogue Generation
Jul 23, 2021
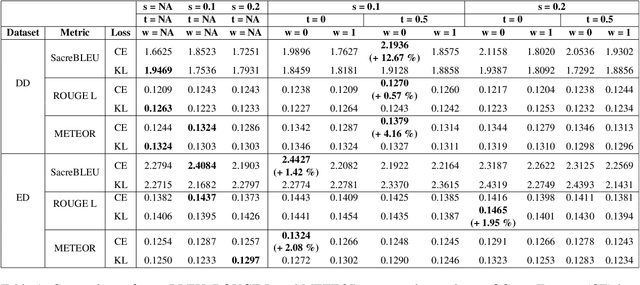
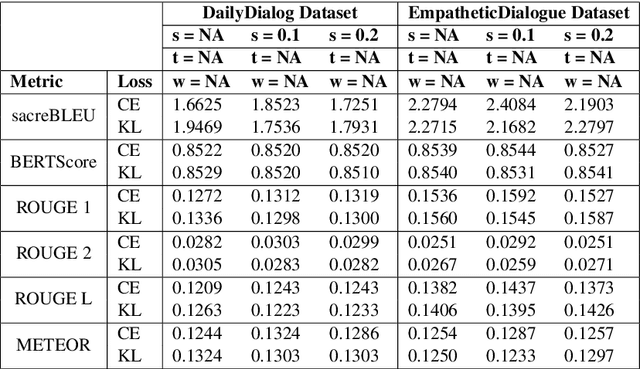
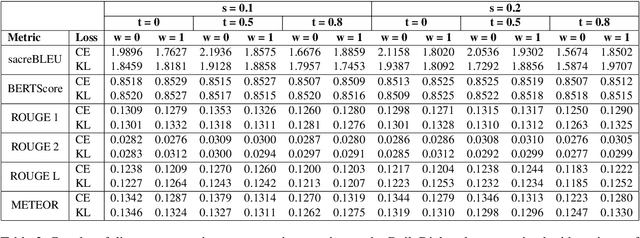
Abstract:Generative neural conversational systems are generally trained with the objective of minimizing the entropy loss between the training "hard" targets and the predicted logits. Often, performance gains and improved generalization can be achieved by using regularization techniques like label smoothing, which converts the training "hard" targets to "soft" targets. However, label smoothing enforces a data independent uniform distribution on the incorrect training targets, which leads to an incorrect assumption of equi-probable incorrect targets for each correct target. In this paper we propose and experiment with incorporating data dependent word similarity based weighing methods to transforms the uniform distribution of the incorrect target probabilities in label smoothing, to a more natural distribution based on semantics. We introduce hyperparameters to control the incorrect target distribution, and report significant performance gains over networks trained using standard label smoothing based loss, on two standard open domain dialogue corpora.
Self-Supervised Claim Identification for Automated Fact Checking
Feb 03, 2021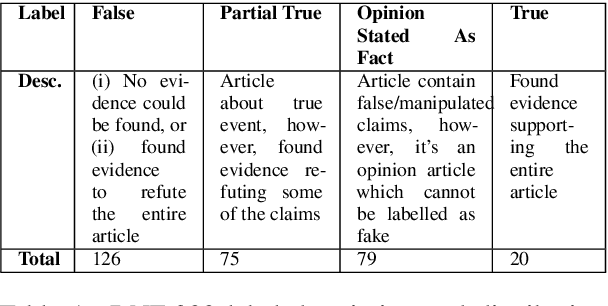
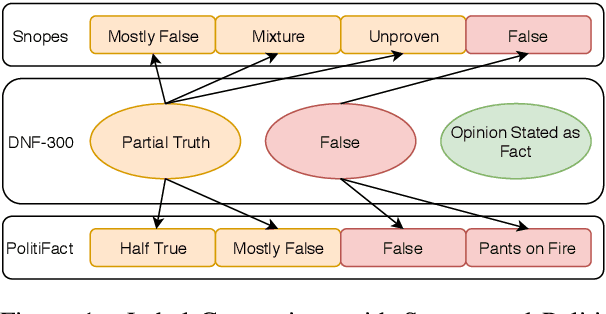


Abstract:We propose a novel, attention-based self-supervised approach to identify "claim-worthy" sentences in a fake news article, an important first step in automated fact-checking. We leverage "aboutness" of headline and content using attention mechanism for this task. The identified claims can be used for downstream task of claim verification for which we are releasing a benchmark dataset of manually selected compelling articles with veracity labels and associated evidence. This work goes beyond stylistic analysis to identifying content that influences reader belief. Experiments with three datasets show the strength of our model. Data and code available at https://github.com/architapathak/Self-Supervised-ClaimIdentification
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge