Songkai Xue
Textual Data Bias Detection and Mitigation -- An Extensible Pipeline with Experimental Evaluation
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Textual data used to train large language models (LLMs) exhibits multifaceted bias manifestations encompassing harmful language and skewed demographic distributions. Regulations such as the European AI Act require identifying and mitigating biases against protected groups in data, with the ultimate goal of preventing unfair model outputs. However, practical guidance and operationalization are lacking. We propose a comprehensive data bias detection and mitigation pipeline comprising four components that address two data bias types, namely representation bias and (explicit) stereotypes for a configurable sensitive attribute. First, we leverage LLM-generated word lists created based on quality criteria to detect relevant group labels. Second, representation bias is quantified using the Demographic Representation Score. Third, we detect and mitigate stereotypes using sociolinguistically informed filtering. Finally, we compensate representation bias through Grammar- and Context-Aware Counterfactual Data Augmentation. We conduct a two-fold evaluation using the examples of gender, religion and age. First, the effectiveness of each individual component on data debiasing is evaluated through human validation and baseline comparison. The findings demonstrate that we successfully reduce representation bias and (explicit) stereotypes in a text dataset. Second, the effect of data debiasing on model bias reduction is evaluated by bias benchmarking of several models (0.6B-8B parameters), fine-tuned on the debiased text dataset. This evaluation reveals that LLMs fine-tuned on debiased data do not consistently show improved performance on bias benchmarks, exposing critical gaps in current evaluation methodologies and highlighting the need for targeted data manipulation to address manifested model bias.
Distributionally Robust Performative Prediction
Dec 05, 2024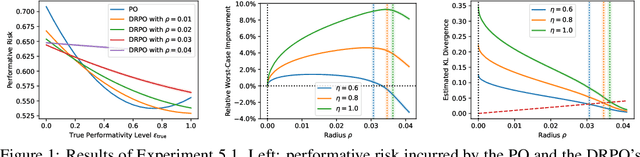
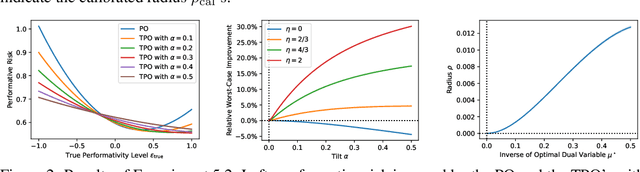
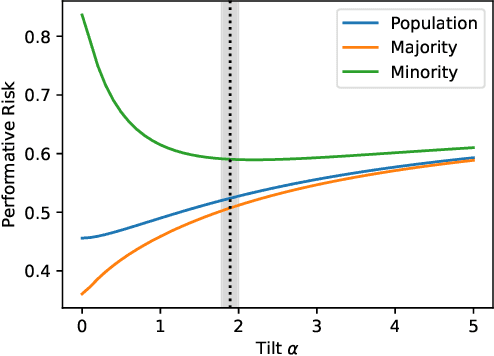
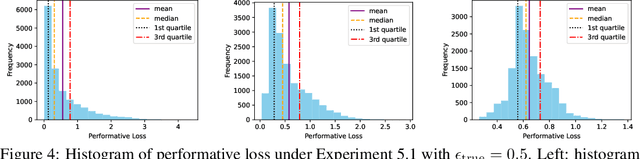
Abstract:Performative prediction aims to model scenarios where predictive outcomes subsequently influence the very systems they target. The pursuit of a performative optimum (PO) -- minimizing performative risk -- is generally reliant on modeling of the distribution map, which characterizes how a deployed ML model alters the data distribution. Unfortunately, inevitable misspecification of the distribution map can lead to a poor approximation of the true PO. To address this issue, we introduce a novel framework of distributionally robust performative prediction and study a new solution concept termed as distributionally robust performative optimum (DRPO). We show provable guarantees for DRPO as a robust approximation to the true PO when the nominal distribution map is different from the actual one. Moreover, distributionally robust performative prediction can be reformulated as an augmented performative prediction problem, enabling efficient optimization. The experimental results demonstrate that DRPO offers potential advantages over traditional PO approach when the distribution map is misspecified at either micro- or macro-level.
Minimax Regret Learning for Data with Heterogeneous Subgroups
May 02, 2024Abstract:Modern complex datasets often consist of various sub-populations. To develop robust and generalizable methods in the presence of sub-population heterogeneity, it is important to guarantee a uniform learning performance instead of an average one. In many applications, prior information is often available on which sub-population or group the data points belong to. Given the observed groups of data, we develop a min-max-regret (MMR) learning framework for general supervised learning, which targets to minimize the worst-group regret. Motivated from the regret-based decision theoretic framework, the proposed MMR is distinguished from the value-based or risk-based robust learning methods in the existing literature. The regret criterion features several robustness and invariance properties simultaneously. In terms of generalizability, we develop the theoretical guarantee for the worst-case regret over a super-population of the meta data, which incorporates the observed sub-populations, their mixtures, as well as other unseen sub-populations that could be approximated by the observed ones. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through extensive simulation studies and an application to kidney transplantation data from hundreds of transplant centers.
Calibrated Data-Dependent Constraints with Exact Satisfaction Guarantees
Jan 15, 2023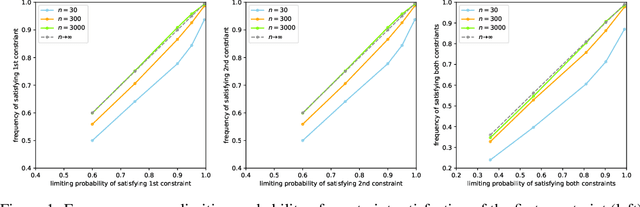
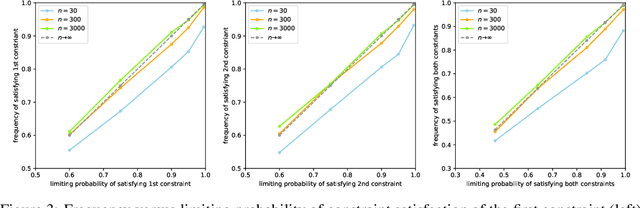
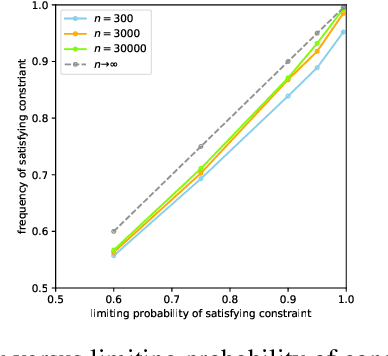
Abstract:We consider the task of training machine learning models with data-dependent constraints. Such constraints often arise as empirical versions of expected value constraints that enforce fairness or stability goals. We reformulate data-dependent constraints so that they are calibrated: enforcing the reformulated constraints guarantees that their expected value counterparts are satisfied with a user-prescribed probability. The resulting optimization problem is amendable to standard stochastic optimization algorithms, and we demonstrate the efficacy of our method on a fairness-sensitive classification task where we wish to guarantee the classifier's fairness (at test time).
How does overparametrization affect performance on minority groups?
Jun 07, 2022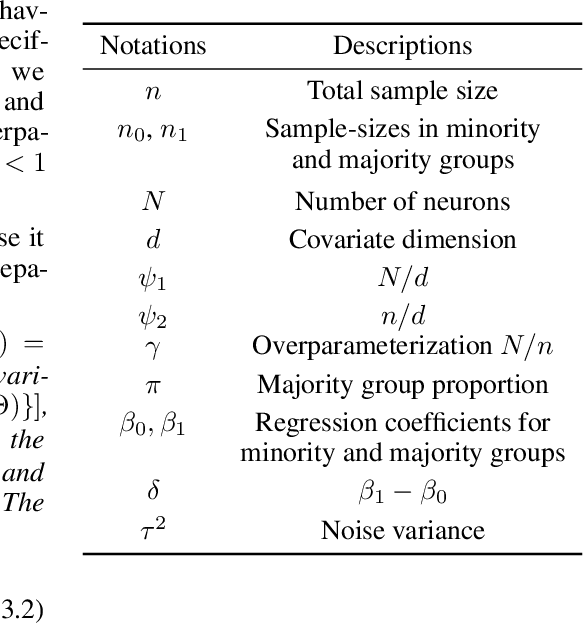
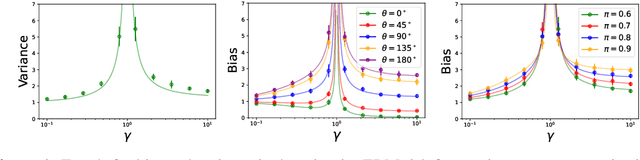
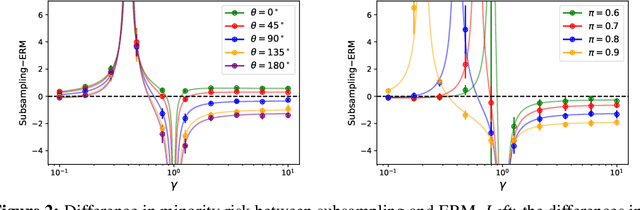
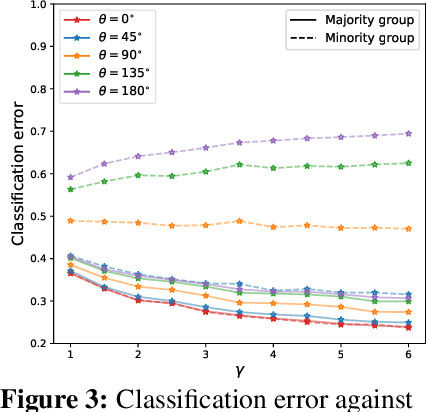
Abstract:The benefits of overparameterization for the overall performance of modern machine learning (ML) models are well known. However, the effect of overparameterization at a more granular level of data subgroups is less understood. Recent empirical studies demonstrate encouraging results: (i) when groups are not known, overparameterized models trained with empirical risk minimization (ERM) perform better on minority groups; (ii) when groups are known, ERM on data subsampled to equalize group sizes yields state-of-the-art worst-group-accuracy in the overparameterized regime. In this paper, we complement these empirical studies with a theoretical investigation of the risk of overparameterized random feature models on minority groups. In a setting in which the regression functions for the majority and minority groups are different, we show that overparameterization always improves minority group performance.
Statistical inference for individual fairness
Mar 30, 2021



Abstract:As we rely on machine learning (ML) models to make more consequential decisions, the issue of ML models perpetuating or even exacerbating undesirable historical biases (e.g., gender and racial biases) has come to the fore of the public's attention. In this paper, we focus on the problem of detecting violations of individual fairness in ML models. We formalize the problem as measuring the susceptibility of ML models against a form of adversarial attack and develop a suite of inference tools for the adversarial cost function. The tools allow auditors to assess the individual fairness of ML models in a statistically-principled way: form confidence intervals for the worst-case performance differential between similar individuals and test hypotheses of model fairness with (asymptotic) non-coverage/Type I error rate control. We demonstrate the utility of our tools in a real-world case study.
Auditing ML Models for Individual Bias and Unfairness
Mar 11, 2020



Abstract:We consider the task of auditing ML models for individual bias/unfairness. We formalize the task in an optimization problem and develop a suite of inferential tools for the optimal value. Our tools permit us to obtain asymptotic confidence intervals and hypothesis tests that cover the target/control the Type I error rate exactly. To demonstrate the utility of our tools, we use them to reveal the gender and racial biases in Northpointe's COMPAS recidivism prediction instrument.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge