How does overparametrization affect performance on minority groups?
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2022
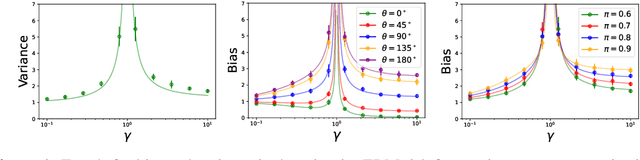
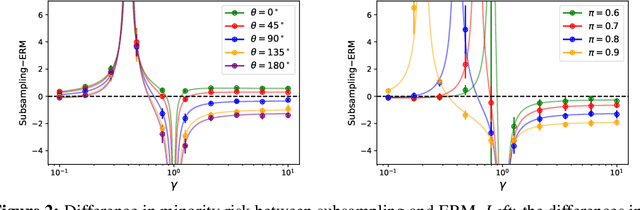
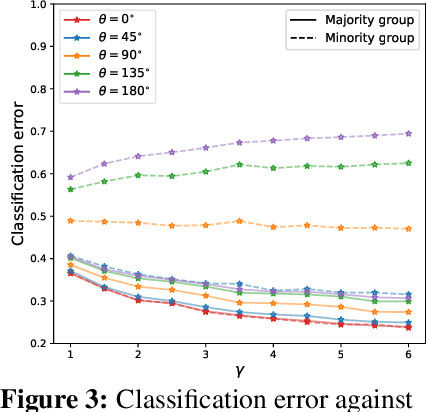
The benefits of overparameterization for the overall performance of modern machine learning (ML) models are well known. However, the effect of overparameterization at a more granular level of data subgroups is less understood. Recent empirical studies demonstrate encouraging results: (i) when groups are not known, overparameterized models trained with empirical risk minimization (ERM) perform better on minority groups; (ii) when groups are known, ERM on data subsampled to equalize group sizes yields state-of-the-art worst-group-accuracy in the overparameterized regime. In this paper, we complement these empirical studies with a theoretical investigation of the risk of overparameterized random feature models on minority groups. In a setting in which the regression functions for the majority and minority groups are different, we show that overparameterization always improves minority group performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge