Simon B. Jensen
Aalborg University
Multi-modal classification of forest biodiversity potential from 2D orthophotos and 3D airborne laser scanning point clouds
Jan 03, 2025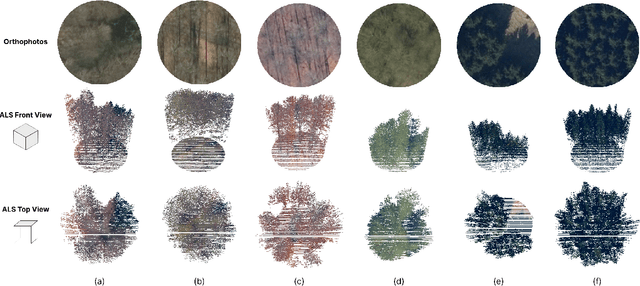
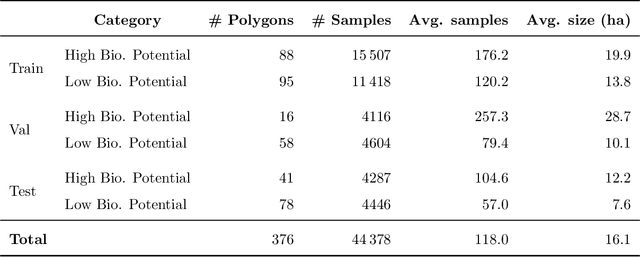
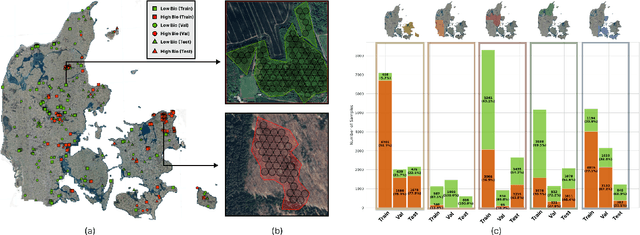
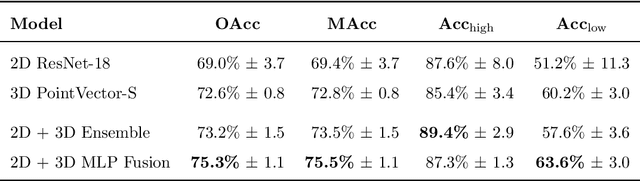
Abstract:Accurate assessment of forest biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem management and conservation. While traditional field surveys provide high-quality assessments, they are labor-intensive and spatially limited. This study investigates whether deep learning-based fusion of close-range sensing data from 2D orthophotos (12.5 cm resolution) and 3D airborne laser scanning (ALS) point clouds (8 points/m^2) can enhance biodiversity assessment. We introduce the BioVista dataset, comprising 44.378 paired samples of orthophotos and ALS point clouds from temperate forests in Denmark, designed to explore multi-modal fusion approaches for biodiversity potential classification. Using deep neural networks (ResNet for orthophotos and PointVector for ALS point clouds), we investigate each data modality's ability to assess forest biodiversity potential, achieving mean accuracies of 69.4% and 72.8%, respectively. We explore two fusion approaches: a confidence-based ensemble method and a feature-level concatenation strategy, with the latter achieving a mean accuracy of 75.5%. Our results demonstrate that spectral information from orthophotos and structural information from ALS point clouds effectively complement each other in forest biodiversity assessment.
OpenTrench3D: A Photogrammetric 3D Point Cloud Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Underground Utilities
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:Identifying and classifying underground utilities is an important task for efficient and effective urban planning and infrastructure maintenance. We present OpenTrench3D, a novel and comprehensive 3D Semantic Segmentation point cloud dataset, designed to advance research and development in underground utility surveying and mapping. OpenTrench3D covers a completely novel domain for public 3D point cloud datasets and is unique in its focus, scope, and cost-effective capturing method. The dataset consists of 310 point clouds collected across 7 distinct areas. These include 5 water utility areas and 2 district heating utility areas. The inclusion of different geographical areas and main utilities (water and district heating utilities) makes OpenTrench3D particularly valuable for inter-domain transfer learning experiments. We provide benchmark results for the dataset using three state-of-the-art semantic segmentation models, PointNeXt, PointVector and PointMetaBase. Benchmarks are conducted by training on data from water areas, fine-tuning on district heating area 1 and evaluating on district heating area 2. The dataset is publicly available. With OpenTrench3D, we seek to foster innovation and progress in the field of 3D semantic segmentation in applications related to detection and documentation of underground utilities as well as in transfer learning methods in general.
Raw Instinct: Trust Your Classifiers and Skip the Conversion
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:Using RAW-images in computer vision problems is surprisingly underexplored considering that converting from RAW to RGB does not introduce any new capture information. In this paper, we show that a sufficiently advanced classifier can yield equivalent results on RAW input compared to RGB and present a new public dataset consisting of RAW images and the corresponding converted RGB images. Classifying images directly from RAW is attractive, as it allows for skipping the conversion to RGB, lowering computation time significantly. Two CNN classifiers are used to classify the images in both formats, confirming that classification performance can indeed be preserved. We furthermore show that the total computation time from RAW image data to classification results for RAW images can be up to 8.46 times faster than RGB. These results contribute to the evidence found in related works, that using RAW images as direct input to computer vision algorithms looks very promising.
* https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/mathiasviborg/raw-instinct
Deep Learning-based Anomaly Detection on X-ray Images of Fuel Cell Electrodes
Feb 15, 2022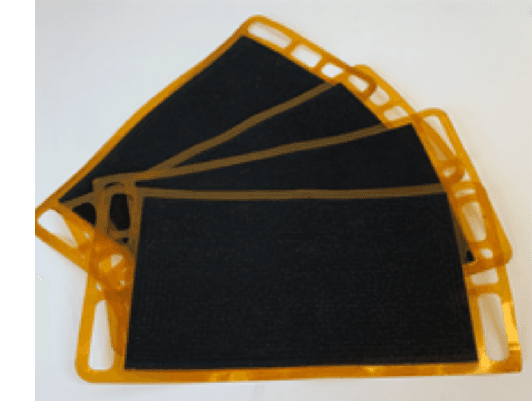
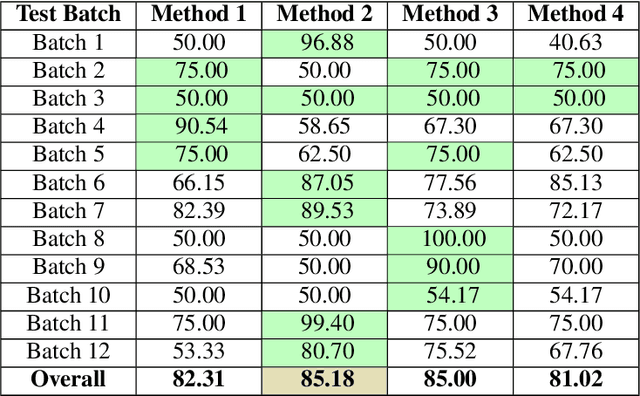

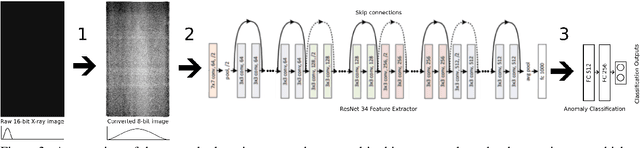
Abstract:Anomaly detection in X-ray images has been an active and lasting research area in the last decades, especially in the domain of medical X-ray images. For this work, we created a real-world labeled anomaly dataset, consisting of 16-bit X-ray image data of fuel cell electrodes coated with a platinum catalyst solution and perform anomaly detection on the dataset using a deep learning approach. The dataset contains a diverse set of anomalies with 11 identified common anomalies where the electrodes contain e.g. scratches, bubbles, smudges etc. We experiment with 16-bit image to 8-bit image conversion methods to utilize pre-trained Convolutional Neural Networks as feature extractors (transfer learning) and find that we achieve the best performance by maximizing the contrasts globally across the dataset during the 16-bit to 8-bit conversion, through histogram equalization. We group the fuel cell electrodes with anomalies into a single class called abnormal and the normal fuel cell electrodes into a class called normal, thereby abstracting the anomaly detection problem into a binary classification problem. We achieve a balanced accuracy of 85.18\%. The anomaly detection is used by the company, Serenergy, for optimizing the time spend on the quality control of the fuel cell electrodes
* 10 pages, 9 figures, VISAPP2022
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge