Bjørk Antoniussen
Aalborg University
Language-Driven Active Learning for Diverse Open-Set 3D Object Detection
Apr 19, 2024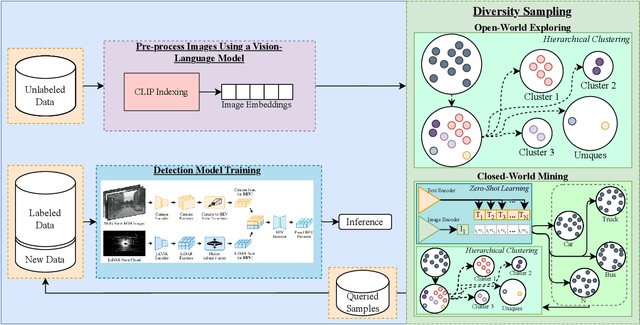
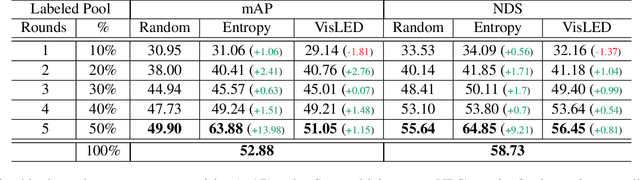
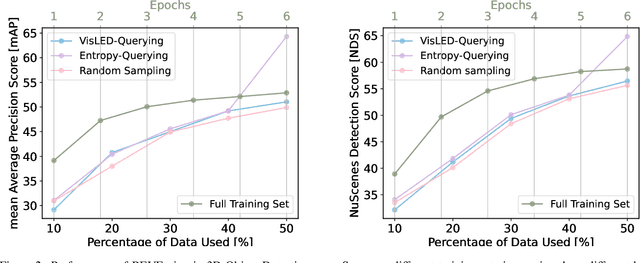
Abstract:Object detection is crucial for ensuring safe autonomous driving. However, data-driven approaches face challenges when encountering minority or novel objects in the 3D driving scene. In this paper, we propose VisLED, a language-driven active learning framework for diverse open-set 3D Object Detection. Our method leverages active learning techniques to query diverse and informative data samples from an unlabeled pool, enhancing the model's ability to detect underrepresented or novel objects. Specifically, we introduce the Vision-Language Embedding Diversity Querying (VisLED-Querying) algorithm, which operates in both open-world exploring and closed-world mining settings. In open-world exploring, VisLED-Querying selects data points most novel relative to existing data, while in closed-world mining, it mines new instances of known classes. We evaluate our approach on the nuScenes dataset and demonstrate its effectiveness compared to random sampling and entropy-querying methods. Our results show that VisLED-Querying consistently outperforms random sampling and offers competitive performance compared to entropy-querying despite the latter's model-optimality, highlighting the potential of VisLED for improving object detection in autonomous driving scenarios.
Raw Instinct: Trust Your Classifiers and Skip the Conversion
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:Using RAW-images in computer vision problems is surprisingly underexplored considering that converting from RAW to RGB does not introduce any new capture information. In this paper, we show that a sufficiently advanced classifier can yield equivalent results on RAW input compared to RGB and present a new public dataset consisting of RAW images and the corresponding converted RGB images. Classifying images directly from RAW is attractive, as it allows for skipping the conversion to RGB, lowering computation time significantly. Two CNN classifiers are used to classify the images in both formats, confirming that classification performance can indeed be preserved. We furthermore show that the total computation time from RAW image data to classification results for RAW images can be up to 8.46 times faster than RGB. These results contribute to the evidence found in related works, that using RAW images as direct input to computer vision algorithms looks very promising.
* https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/mathiasviborg/raw-instinct
ActiveAnno3D -- An Active Learning Framework for Multi-Modal 3D Object Detection
Feb 05, 2024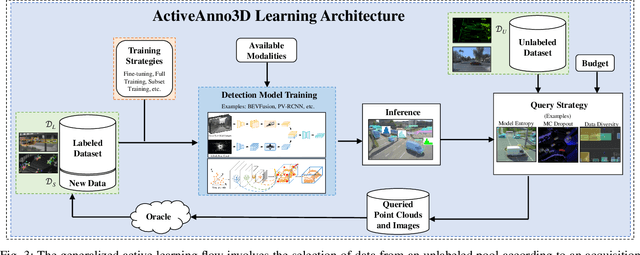
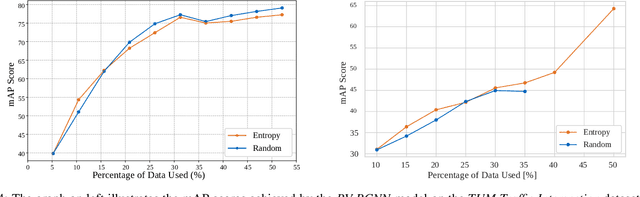
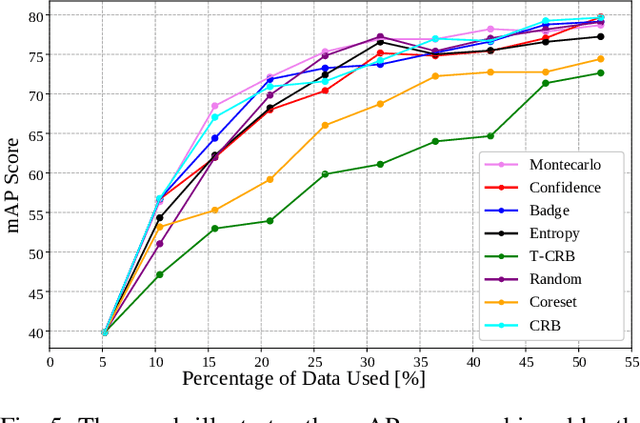

Abstract:The curation of large-scale datasets is still costly and requires much time and resources. Data is often manually labeled, and the challenge of creating high-quality datasets remains. In this work, we fill the research gap using active learning for multi-modal 3D object detection. We propose ActiveAnno3D, an active learning framework to select data samples for labeling that are of maximum informativeness for training. We explore various continuous training methods and integrate the most efficient method regarding computational demand and detection performance. Furthermore, we perform extensive experiments and ablation studies with BEVFusion and PV-RCNN on the nuScenes and TUM Traffic Intersection dataset. We show that we can achieve almost the same performance with PV-RCNN and the entropy-based query strategy when using only half of the training data (77.25 mAP compared to 83.50 mAP) of the TUM Traffic Intersection dataset. BEVFusion achieved an mAP of 64.31 when using half of the training data and 75.0 mAP when using the complete nuScenes dataset. We integrate our active learning framework into the proAnno labeling tool to enable AI-assisted data selection and labeling and minimize the labeling costs. Finally, we provide code, weights, and visualization results on our website: https://active3d-framework.github.io/active3d-framework.
The Why, When, and How to Use Active Learning in Large-Data-Driven 3D Object Detection for Safe Autonomous Driving: An Empirical Exploration
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:Active learning strategies for 3D object detection in autonomous driving datasets may help to address challenges of data imbalance, redundancy, and high-dimensional data. We demonstrate the effectiveness of entropy querying to select informative samples, aiming to reduce annotation costs and improve model performance. We experiment using the BEVFusion model for 3D object detection on the nuScenes dataset, comparing active learning to random sampling and demonstrating that entropy querying outperforms in most cases. The method is particularly effective in reducing the performance gap between majority and minority classes. Class-specific analysis reveals efficient allocation of annotated resources for limited data budgets, emphasizing the importance of selecting diverse and informative data for model training. Our findings suggest that entropy querying is a promising strategy for selecting data that enhances model learning in resource-constrained environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge