Multi-modal classification of forest biodiversity potential from 2D orthophotos and 3D airborne laser scanning point clouds
Paper and Code
Jan 03, 2025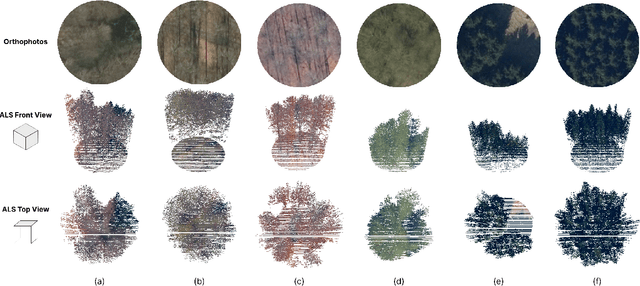
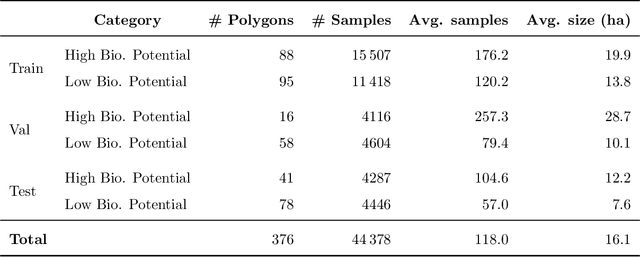
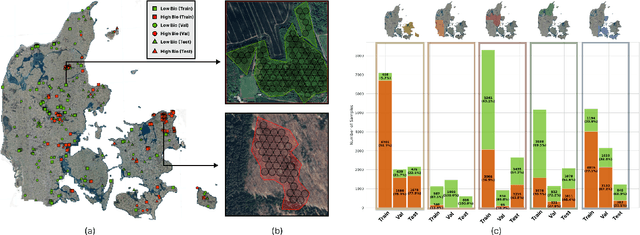
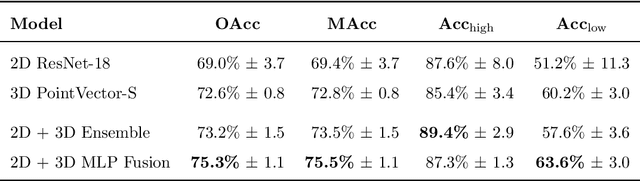
Accurate assessment of forest biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem management and conservation. While traditional field surveys provide high-quality assessments, they are labor-intensive and spatially limited. This study investigates whether deep learning-based fusion of close-range sensing data from 2D orthophotos (12.5 cm resolution) and 3D airborne laser scanning (ALS) point clouds (8 points/m^2) can enhance biodiversity assessment. We introduce the BioVista dataset, comprising 44.378 paired samples of orthophotos and ALS point clouds from temperate forests in Denmark, designed to explore multi-modal fusion approaches for biodiversity potential classification. Using deep neural networks (ResNet for orthophotos and PointVector for ALS point clouds), we investigate each data modality's ability to assess forest biodiversity potential, achieving mean accuracies of 69.4% and 72.8%, respectively. We explore two fusion approaches: a confidence-based ensemble method and a feature-level concatenation strategy, with the latter achieving a mean accuracy of 75.5%. Our results demonstrate that spectral information from orthophotos and structural information from ALS point clouds effectively complement each other in forest biodiversity assessment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge