Simiao Lai
Exploring Enhanced Contextual Information for Video-Level Object Tracking
Dec 15, 2024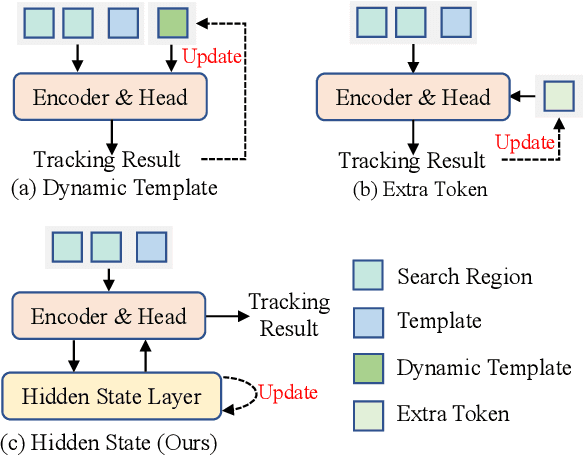
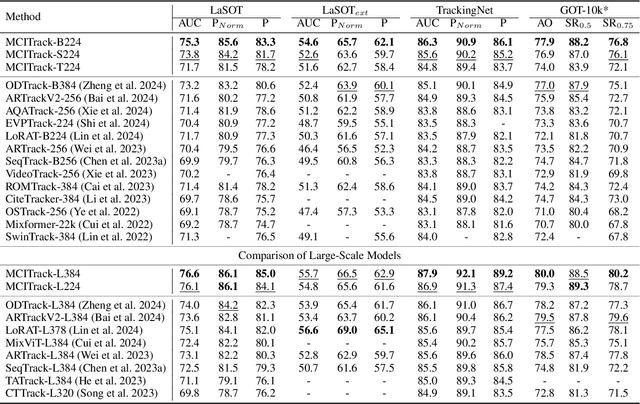
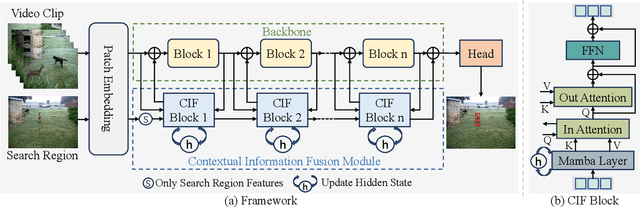
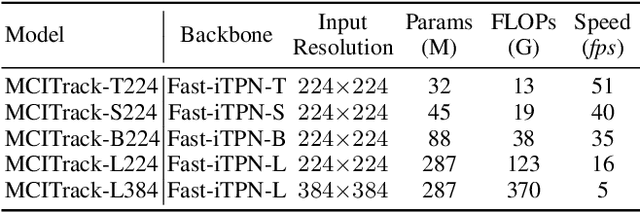
Abstract:Contextual information at the video level has become increasingly crucial for visual object tracking. However, existing methods typically use only a few tokens to convey this information, which can lead to information loss and limit their ability to fully capture the context. To address this issue, we propose a new video-level visual object tracking framework called MCITrack. It leverages Mamba's hidden states to continuously record and transmit extensive contextual information throughout the video stream, resulting in more robust object tracking. The core component of MCITrack is the Contextual Information Fusion module, which consists of the mamba layer and the cross-attention layer. The mamba layer stores historical contextual information, while the cross-attention layer integrates this information into the current visual features of each backbone block. This module enhances the model's ability to capture and utilize contextual information at multiple levels through deep integration with the backbone. Experiments demonstrate that MCITrack achieves competitive performance across numerous benchmarks. For instance, it gets 76.6% AUC on LaSOT and 80.0% AO on GOT-10k, establishing a new state-of-the-art performance. Code and models are available at https://github.com/kangben258/MCITrack.
MambaVT: Spatio-Temporal Contextual Modeling for robust RGB-T Tracking
Aug 15, 2024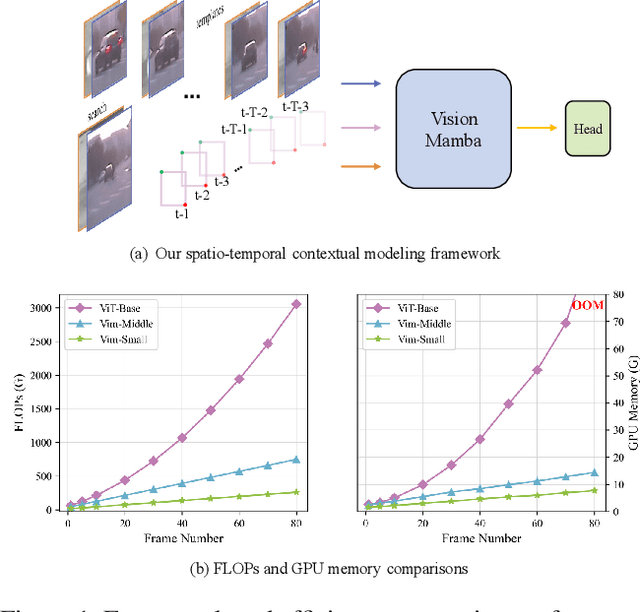
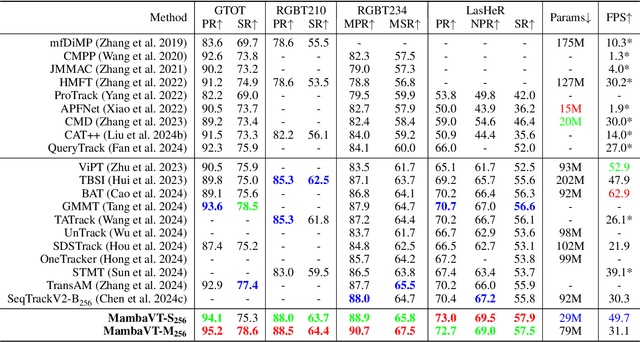
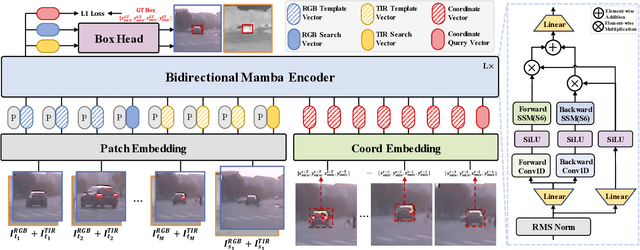
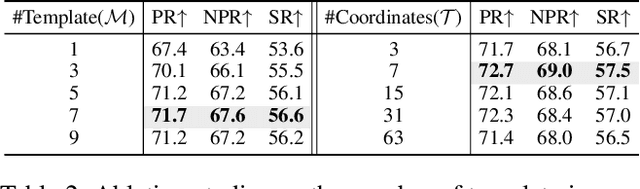
Abstract:Existing RGB-T tracking algorithms have made remarkable progress by leveraging the global interaction capability and extensive pre-trained models of the Transformer architecture. Nonetheless, these methods mainly adopt imagepair appearance matching and face challenges of the intrinsic high quadratic complexity of the attention mechanism, resulting in constrained exploitation of temporal information. Inspired by the recently emerged State Space Model Mamba, renowned for its impressive long sequence modeling capabilities and linear computational complexity, this work innovatively proposes a pure Mamba-based framework (MambaVT) to fully exploit spatio-temporal contextual modeling for robust visible-thermal tracking. Specifically, we devise the long-range cross-frame integration component to globally adapt to target appearance variations, and introduce short-term historical trajectory prompts to predict the subsequent target states based on local temporal location clues. Extensive experiments show the significant potential of vision Mamba for RGB-T tracking, with MambaVT achieving state-of-the-art performance on four mainstream benchmarks while requiring lower computational costs. We aim for this work to serve as a simple yet strong baseline, stimulating future research in this field. The code and pre-trained models will be made available.
Visual Prompt Multi-Modal Tracking
Mar 25, 2023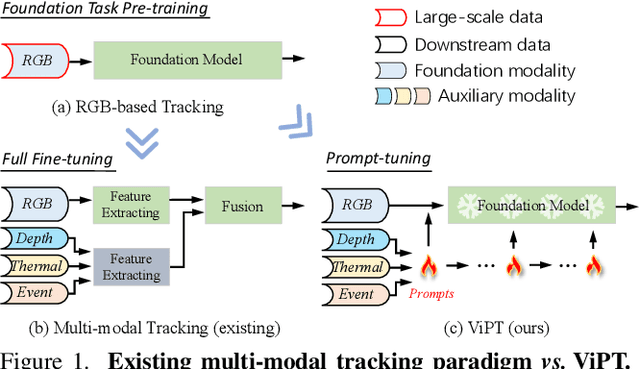
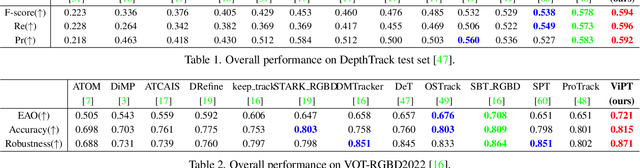
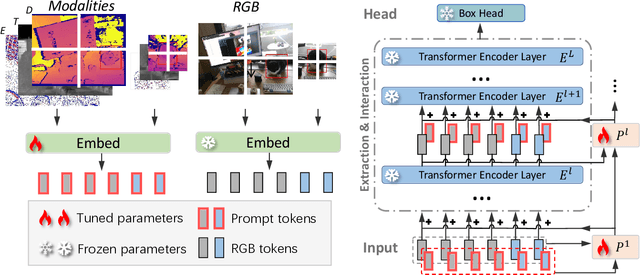
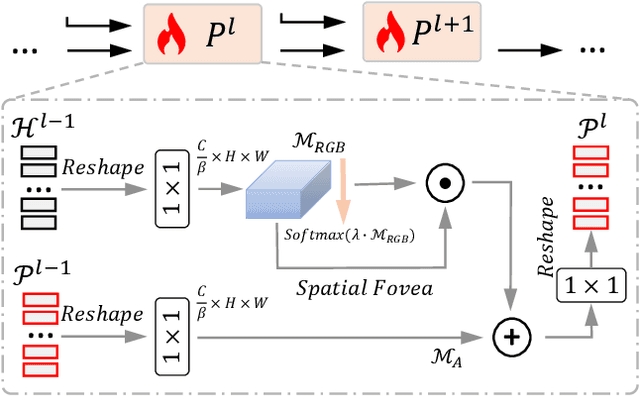
Abstract:Visible-modal object tracking gives rise to a series of downstream multi-modal tracking tributaries. To inherit the powerful representations of the foundation model, a natural modus operandi for multi-modal tracking is full fine-tuning on the RGB-based parameters. Albeit effective, this manner is not optimal due to the scarcity of downstream data and poor transferability, etc. In this paper, inspired by the recent success of the prompt learning in language models, we develop Visual Prompt multi-modal Tracking (ViPT), which learns the modal-relevant prompts to adapt the frozen pre-trained foundation model to various downstream multimodal tracking tasks. ViPT finds a better way to stimulate the knowledge of the RGB-based model that is pre-trained at scale, meanwhile only introducing a few trainable parameters (less than 1% of model parameters). ViPT outperforms the full fine-tuning paradigm on multiple downstream tracking tasks including RGB+Depth, RGB+Thermal, and RGB+Event tracking. Extensive experiments show the potential of visual prompt learning for multi-modal tracking, and ViPT can achieve state-of-the-art performance while satisfying parameter efficiency. Code and models are available at https://github.com/jiawen-zhu/ViPT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge