Simeng Liu
LinguaLinked: A Distributed Large Language Model Inference System for Mobile Devices
Dec 01, 2023



Abstract:Deploying Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on mobile devices presents a significant challenge due to their extensive memory requirements. In this paper, we introduce LinguaLinked, a system for decentralized, distributed LLM inference on mobile devices. LinguaLinked enables collaborative execution of the inference task across multiple trusted devices. LinguaLinked ensures data privacy by processing information locally. LinguaLinked uses three key strategies. First, an optimized model assignment technique segments LLMs and uses linear optimization to align segments with each device's capabilities. Second, an optimized data transmission mechanism ensures efficient and structured data flow between model segments while also maintaining the integrity of the original model structure. Finally, LinguaLinked incorporates a runtime load balancer that actively monitors and redistributes tasks among mobile devices to prevent bottlenecks, enhancing the system's overall efficiency and responsiveness. We demonstrate that LinguaLinked facilitates efficient LLM inference while maintaining consistent throughput and minimal latency through extensive testing across various mobile devices, from high-end to low-end Android devices. In our evaluations, compared to the baseline, LinguaLinked achieves an inference performance acceleration of $1.11\times$ to $1.61\times$ in single-threaded settings, $1.73\times$ to $2.65\times$ with multi-threading. Additionally, runtime load balancing yields an overall inference acceleration of $1.29\times$ to $1.32\times$.
Matrix Variate RBM Model with Gaussian Distributions
Sep 27, 2016



Abstract:Restricted Boltzmann Machine (RBM) is a particular type of random neural network models modeling vector data based on the assumption of Bernoulli distribution. For multi-dimensional and non-binary data, it is necessary to vectorize and discretize the information in order to apply the conventional RBM. It is well-known that vectorization would destroy internal structure of data, and the binary units will limit the applying performance due to fickle real data. To address the issue, this paper proposes a Matrix variate Gaussian Restricted Boltzmann Machine (MVGRBM) model for matrix data whose entries follow Gaussian distributions. Compared with some other RBM algorithm, MVGRBM can model real value data better and it has good performance in image classification.
Mixture of Bilateral-Projection Two-dimensional Probabilistic Principal Component Analysis
Jan 07, 2016

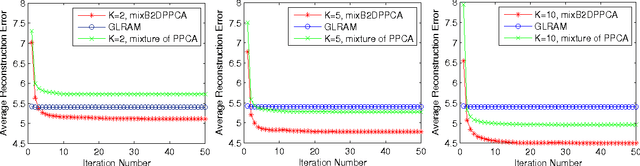

Abstract:The probabilistic principal component analysis (PPCA) is built upon a global linear mapping, with which it is insufficient to model complex data variation. This paper proposes a mixture of bilateral-projection probabilistic principal component analysis model (mixB2DPPCA) on 2D data. With multi-components in the mixture, this model can be seen as a soft cluster algorithm and has capability of modeling data with complex structures. A Bayesian inference scheme has been proposed based on the variational EM (Expectation-Maximization) approach for learning model parameters. Experiments on some publicly available databases show that the performance of mixB2DPPCA has been largely improved, resulting in more accurate reconstruction errors and recognition rates than the existing PCA-based algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge