Sihua Shao
ABODE-Net: An Attention-based Deep Learning Model for Non-intrusive Building Occupancy Detection Using Smart Meter Data
Dec 21, 2022Abstract:Occupancy information is useful for efficient energy management in the building sector. The massive high-resolution electrical power consumption data collected by smart meters in the advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) network make it possible to infer buildings' occupancy status in a non-intrusive way. In this paper, we propose a deep leaning model called ABODE-Net which employs a novel Parallel Attention (PA) block for building occupancy detection using smart meter data. The PA block combines the temporal, variable, and channel attention modules in a parallel way to signify important features for occupancy detection. We adopt two smart meter datasets widely used for building occupancy detection in our performance evaluation. A set of state-of-the-art shallow machine learning and deep learning models are included for performance comparison. The results show that ABODE-Net significantly outperforms other models in all experimental cases, which proves its validity as a solution for non-intrusive building occupancy detection.
Backhaul-Aware Drone Base Station Placement and Resource Management for FSO based Drone Assisted Mobile Networks
Dec 24, 2021



Abstract:In drone assisted mobile networks, drones mounted small cell base stations (DBSs) are responsively and flexibly deployed over any Places of Interest (PoI), such as sporadic hotspots and disaster-struck areas, where the existing mobile network infrastructure is unable to provide wireless coverage. Here, a DBS is a relay node to relay traffic between a nearby macro base station (MBS) and the users. In addition, Free-space optics (FSO) is applied as the backhauling solution to significantly increase the capacity of the backhaul link between an MBS and a DBS in a drone assisted mobile network. Most of the existing DBS placement solutions assume the FSO based backhaul link provides sufficient link capacity, which may not be true, especially when a DBS is placed far away from an MBS (e.g., > 10 km in disaster-struck areas) or in a bad weather condition. In this paper, we formulate a problem to jointly optimize bandwidth allocation and DBS placement by considering the FSO based backhaul link capacity constraint. A Backhaul awaRe bandwidth allOcAtion and DBS placement (BROAD) algorithm is designed to efficiently solve the problem, and the performance of the algorithm is demonstrated via extensive simulations.
Optimal Discrete Constellation Inputs for Aggregated LiFi-WiFi Networks
Nov 04, 2021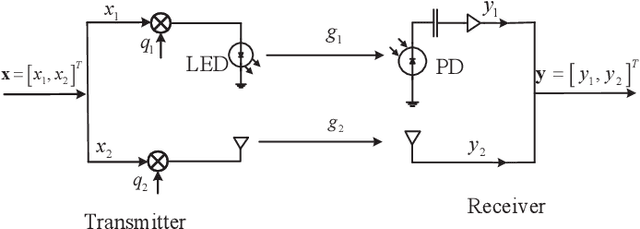
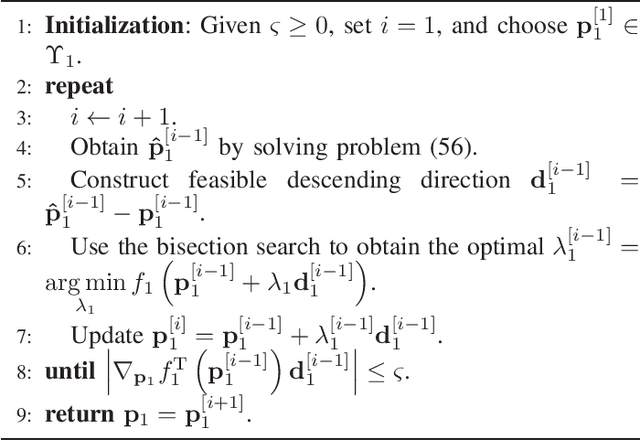

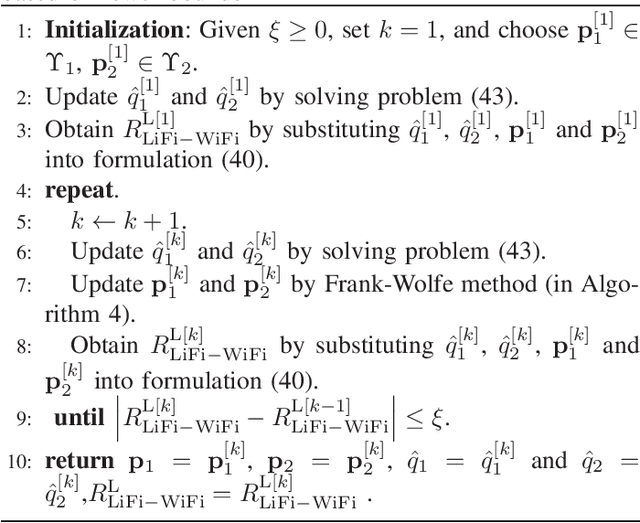
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the performance of a practical aggregated LiFi-WiFi system with the discrete constellation inputs from a practical view. We derive the achievable rate expressions of the aggregated LiFi-WiFi system for the first time. Then, we study the rate maximization problem via optimizing the constellation distribution and power allocation jointly. Specifically, a multilevel mercy-filling power allocation scheme is proposed by exploiting the relationship between the mutual information and minimum mean-squared error (MMSE) of discrete inputs. Meanwhile, an inexact gradient descent method is proposed for obtaining the optimal probability distributions. To strike a balance between the computational complexity and the transmission performance, we further develop a framework that maximizes the lower bound of the achievable rate where the optimal power allocation can be obtained in closed forms and the constellation distributions problem can be solved efficiently by Frank-Wolfe method. Extensive numerical results show that the optimized strategies are able to provide significant gains over the state-of-the-art schemes in terms of the achievable rate.
Indoor Localization Using Visible Light Via Fusion Of Multiple Classifiers
Dec 20, 2017



Abstract:A multiple classifiers fusion localization technique using received signal strengths (RSSs) of visible light is proposed, in which the proposed system transmits different intensity modulated sinusoidal signals by LEDs and the signals received by a Photo Diode (PD) placed at various grid points. First, we obtain some {\emph{approximate}} received signal strengths (RSSs) fingerprints by capturing the peaks of power spectral density (PSD) of the received signals at each given grid point. Unlike the existing RSSs based algorithms, several representative machine learning approaches are adopted to train multiple classifiers based on these RSSs fingerprints. The multiple classifiers localization estimators outperform the classical RSS-based LED localization approaches in accuracy and robustness. To further improve the localization performance, two robust fusion localization algorithms, namely, grid independent least square (GI-LS) and grid dependent least square (GD-LS), are proposed to combine the outputs of these classifiers. We also use a singular value decomposition (SVD) based LS (LS-SVD) method to mitigate the numerical stability problem when the prediction matrix is singular. Experiments conducted on intensity modulated direct detection (IM/DD) systems have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms. The experimental results show that the probability of having mean square positioning error (MSPE) of less than 5cm achieved by GD-LS is improved by 93.03\% and 93.15\%, respectively, as compared to those by the RSS ratio (RSSR) and RSS matching methods with the FFT length of 2000.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge