Sicong Cao
ICON: Intent-Context Coupling for Efficient Multi-Turn Jailbreak Attack
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Multi-turn jailbreak attacks have emerged as a critical threat to Large Language Models (LLMs), bypassing safety mechanisms by progressively constructing adversarial contexts from scratch and incrementally refining prompts. However, existing methods suffer from the inefficiency of incremental context construction that requires step-by-step LLM interaction, and often stagnate in suboptimal regions due to surface-level optimization. In this paper, we characterize the Intent-Context Coupling phenomenon, revealing that LLM safety constraints are significantly relaxed when a malicious intent is coupled with a semantically congruent context pattern. Driven by this insight, we propose ICON, an automated multi-turn jailbreak framework that efficiently constructs an authoritative-style context via prior-guided semantic routing. Specifically, ICON first routes the malicious intent to a congruent context pattern (e.g., Scientific Research) and instantiates it into an attack prompt sequence. This sequence progressively builds the authoritative-style context and ultimately elicits prohibited content. In addition, ICON incorporates a Hierarchical Optimization Strategy that combines local prompt refinement with global context switching, preventing the attack from stagnating in ineffective contexts. Experimental results across eight SOTA LLMs demonstrate the effectiveness of ICON, achieving a state-of-the-art average Attack Success Rate (ASR) of 97.1\%. Code is available at https://github.com/xwlin-roy/ICON.
Federated Unlearning in the Wild: Rethinking Fairness and Data Discrepancy
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Machine unlearning is critical for enforcing data deletion rights like the "right to be forgotten." As a decentralized paradigm, Federated Learning (FL) also requires unlearning, but realistic implementations face two major challenges. First, fairness in Federated Unlearning (FU) is often overlooked. Exact unlearning methods typically force all clients into costly retraining, even those uninvolved. Approximate approaches, using gradient ascent or distillation, make coarse interventions that can unfairly degrade performance for clients with only retained data. Second, most FU evaluations rely on synthetic data assumptions (IID/non-IID) that ignore real-world heterogeneity. These unrealistic benchmarks obscure the true impact of unlearning and limit the applicability of current methods. We first conduct a comprehensive benchmark of existing FU methods under realistic data heterogeneity and fairness conditions. We then propose a novel, fairness-aware FU approach, Federated Cross-Client-Constrains Unlearning (FedCCCU), to explicitly address both challenges. FedCCCU offers a practical and scalable solution for real-world FU. Experimental results show that existing methods perform poorly in realistic settings, while our approach consistently outperforms them.
A Systematic Literature Review on Explainability for Machine/Deep Learning-based Software Engineering Research
Jan 26, 2024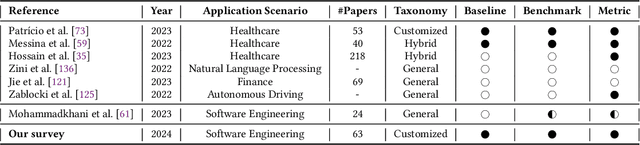
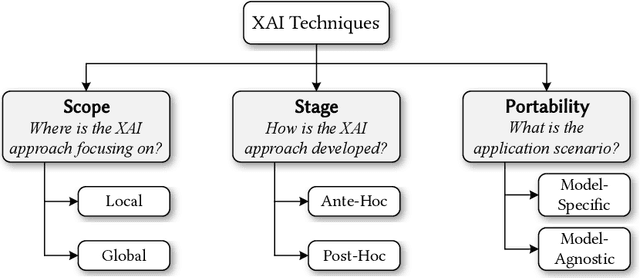
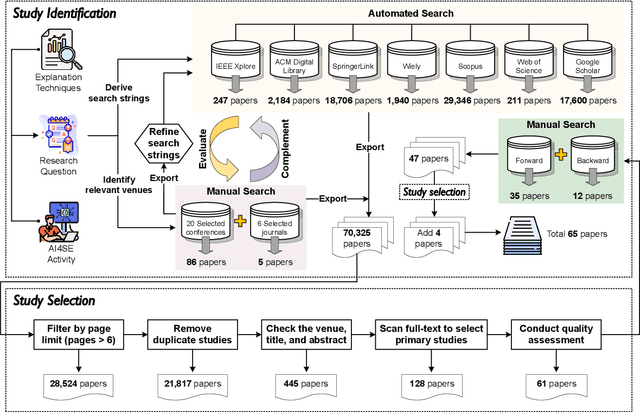
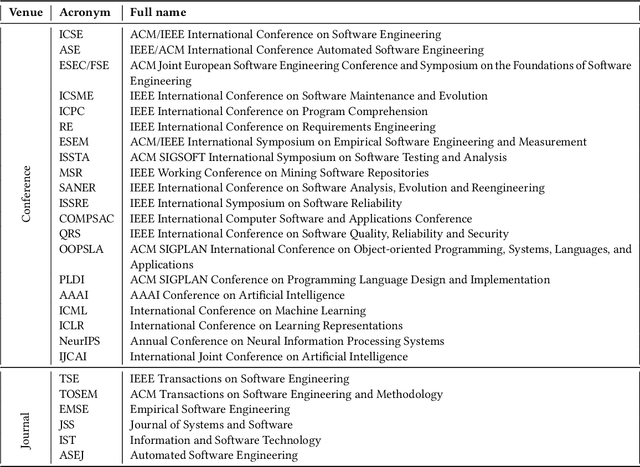
Abstract:The remarkable achievements of Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms, particularly in Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), have fueled their extensive deployment across multiple sectors, including Software Engineering (SE). However, due to their black-box nature, these promising AI-driven SE models are still far from being deployed in practice. This lack of explainability poses unwanted risks for their applications in critical tasks, such as vulnerability detection, where decision-making transparency is of paramount importance. This paper endeavors to elucidate this interdisciplinary domain by presenting a systematic literature review of approaches that aim to improve the explainability of AI models within the context of SE. The review canvasses work appearing in the most prominent SE & AI conferences and journals, and spans 63 papers across 21 unique SE tasks. Based on three key Research Questions (RQs), we aim to (1) summarize the SE tasks where XAI techniques have shown success to date; (2) classify and analyze different XAI techniques; and (3) investigate existing evaluation approaches. Based on our findings, we identified a set of challenges remaining to be addressed in existing studies, together with a roadmap highlighting potential opportunities we deemed appropriate and important for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge