Shuangkang Fang
WaterClear-GS: Optical-Aware Gaussian Splatting for Underwater Reconstruction and Restoration
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Underwater 3D reconstruction and appearance restoration are hindered by the complex optical properties of water, such as wavelength-dependent attenuation and scattering. Existing Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)-based methods struggle with slow rendering speeds and suboptimal color restoration, while 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) inherently lacks the capability to model complex volumetric scattering effects. To address these issues, we introduce WaterClear-GS, the first pure 3DGS-based framework that explicitly integrates underwater optical properties of local attenuation and scattering into Gaussian primitives, eliminating the need for an auxiliary medium network. Our method employs a dual-branch optimization strategy to ensure underwater photometric consistency while naturally recovering water-free appearances. This strategy is enhanced by depth-guided geometry regularization and perception-driven image loss, together with exposure constraints, spatially-adaptive regularization, and physically guided spectral regularization, which collectively enforce local 3D coherence and maintain natural visual perception. Experiments on standard benchmarks and our newly collected dataset demonstrate that WaterClear-GS achieves outstanding performance on both novel view synthesis (NVS) and underwater image restoration (UIR) tasks, while maintaining real-time rendering. The code will be available at https://buaaxrzhang.github.io/WaterClear-GS/.
Chat-Edit-3D: Interactive 3D Scene Editing via Text Prompts
Jul 10, 2024



Abstract:Recent work on image content manipulation based on vision-language pre-training models has been effectively extended to text-driven 3D scene editing. However, existing schemes for 3D scene editing still exhibit certain shortcomings, hindering their further interactive design. Such schemes typically adhere to fixed input patterns, limiting users' flexibility in text input. Moreover, their editing capabilities are constrained by a single or a few 2D visual models and require intricate pipeline design to integrate these models into 3D reconstruction processes. To address the aforementioned issues, we propose a dialogue-based 3D scene editing approach, termed CE3D, which is centered around a large language model that allows for arbitrary textual input from users and interprets their intentions, subsequently facilitating the autonomous invocation of the corresponding visual expert models. Furthermore, we design a scheme utilizing Hash-Atlas to represent 3D scene views, which transfers the editing of 3D scenes onto 2D atlas images. This design achieves complete decoupling between the 2D editing and 3D reconstruction processes, enabling CE3D to flexibly integrate a wide range of existing 2D or 3D visual models without necessitating intricate fusion designs. Experimental results demonstrate that CE3D effectively integrates multiple visual models to achieve diverse editing visual effects, possessing strong scene comprehension and multi-round dialog capabilities. The code is available at https://sk-fun.fun/CE3D.
Text-driven Editing of 3D Scenes without Retraining
Sep 10, 2023



Abstract:Numerous diffusion models have recently been applied to image synthesis and editing. However, editing 3D scenes is still in its early stages. It poses various challenges, such as the requirement to design specific methods for different editing types, retraining new models for various 3D scenes, and the absence of convenient human interaction during editing. To tackle these issues, we introduce a text-driven editing method, termed DN2N, which allows for the direct acquisition of a NeRF model with universal editing capabilities, eliminating the requirement for retraining. Our method employs off-the-shelf text-based editing models of 2D images to modify the 3D scene images, followed by a filtering process to discard poorly edited images that disrupt 3D consistency. We then consider the remaining inconsistency as a problem of removing noise perturbation, which can be solved by generating training data with similar perturbation characteristics for training. We further propose cross-view regularization terms to help the generalized NeRF model mitigate these perturbations. Our text-driven method allows users to edit a 3D scene with their desired description, which is more friendly, intuitive, and practical than prior works. Empirical results show that our method achieves multiple editing types, including but not limited to appearance editing, weather transition, material changing, and style transfer. Most importantly, our method generalizes well with editing abilities shared among a set of model parameters without requiring a customized editing model for some specific scenes, thus inferring novel views with editing effects directly from user input. The project website is available at http://sk-fun.fun/DN2N
PVD-AL: Progressive Volume Distillation with Active Learning for Efficient Conversion Between Different NeRF Architectures
Apr 08, 2023Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have been widely adopted as practical and versatile representations for 3D scenes, facilitating various downstream tasks. However, different architectures, including plain Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), Tensors, low-rank Tensors, Hashtables, and their compositions, have their trade-offs. For instance, Hashtables-based representations allow for faster rendering but lack clear geometric meaning, making spatial-relation-aware editing challenging. To address this limitation and maximize the potential of each architecture, we propose Progressive Volume Distillation with Active Learning (PVD-AL), a systematic distillation method that enables any-to-any conversions between different architectures. PVD-AL decomposes each structure into two parts and progressively performs distillation from shallower to deeper volume representation, leveraging effective information retrieved from the rendering process. Additionally, a Three-Levels of active learning technique provides continuous feedback during the distillation process, resulting in high-performance results. Empirical evidence is presented to validate our method on multiple benchmark datasets. For example, PVD-AL can distill an MLP-based model from a Hashtables-based model at a 10~20X faster speed and 0.8dB~2dB higher PSNR than training the NeRF model from scratch. Moreover, PVD-AL permits the fusion of diverse features among distinct structures, enabling models with multiple editing properties and providing a more efficient model to meet real-time requirements. Project website:http://sk-fun.fun/PVD-AL.
One is All: Bridging the Gap Between Neural Radiance Fields Architectures with Progressive Volume Distillation
Nov 30, 2022Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) methods have proved effective as compact, high-quality and versatile representations for 3D scenes, and enable downstream tasks such as editing, retrieval, navigation, etc. Various neural architectures are vying for the core structure of NeRF, including the plain Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), sparse tensors, low-rank tensors, hashtables and their compositions. Each of these representations has its particular set of trade-offs. For example, the hashtable-based representations admit faster training and rendering but their lack of clear geometric meaning hampers downstream tasks like spatial-relation-aware editing. In this paper, we propose Progressive Volume Distillation (PVD), a systematic distillation method that allows any-to-any conversions between different architectures, including MLP, sparse or low-rank tensors, hashtables and their compositions. PVD consequently empowers downstream applications to optimally adapt the neural representations for the task at hand in a post hoc fashion. The conversions are fast, as distillation is progressively performed on different levels of volume representations, from shallower to deeper. We also employ special treatment of density to deal with its specific numerical instability problem. Empirical evidence is presented to validate our method on the NeRF-Synthetic, LLFF and TanksAndTemples datasets. For example, with PVD, an MLP-based NeRF model can be distilled from a hashtable-based Instant-NGP model at a 10X~20X faster speed than being trained the original NeRF from scratch, while achieving a superior level of synthesis quality. Code is available at https://github.com/megvii-research/AAAI2023-PVD.
Arch-Net: Model Distillation for Architecture Agnostic Model Deployment
Nov 01, 2021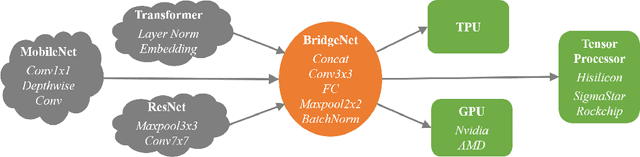
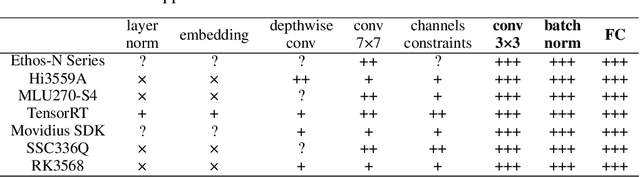
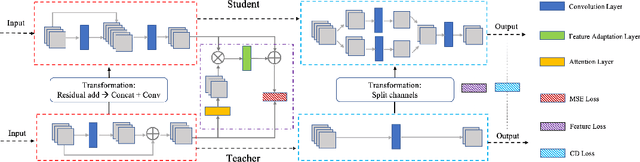
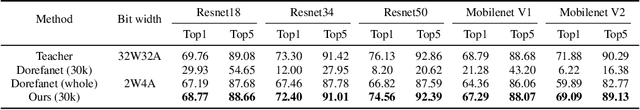
Abstract:Vast requirement of computation power of Deep Neural Networks is a major hurdle to their real world applications. Many recent Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) chips feature dedicated hardware support for Neural Network Acceleration. However, as ASICs take multiple years to develop, they are inevitably out-paced by the latest development in Neural Architecture Research. For example, Transformer Networks do not have native support on many popular chips, and hence are difficult to deploy. In this paper, we propose Arch-Net, a family of Neural Networks made up of only operators efficiently supported across most architectures of ASICs. When a Arch-Net is produced, less common network constructs, like Layer Normalization and Embedding Layers, are eliminated in a progressive manner through label-free Blockwise Model Distillation, while performing sub-eight bit quantization at the same time to maximize performance. Empirical results on machine translation and image classification tasks confirm that we can transform latest developed Neural Architectures into fast running and as-accurate Arch-Net, ready for deployment on multiple mass-produced ASIC chips. The code will be available at https://github.com/megvii-research/Arch-Net.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge