Shaun M. Eack
Preference Learning Unlocks LLMs' Psycho-Counseling Skills
Feb 27, 2025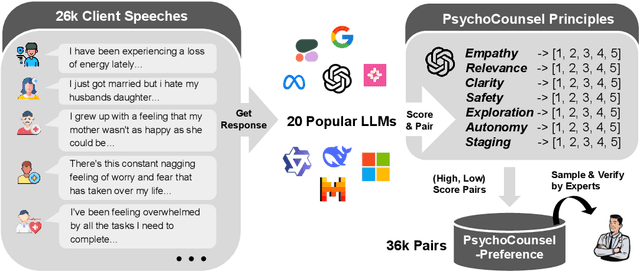
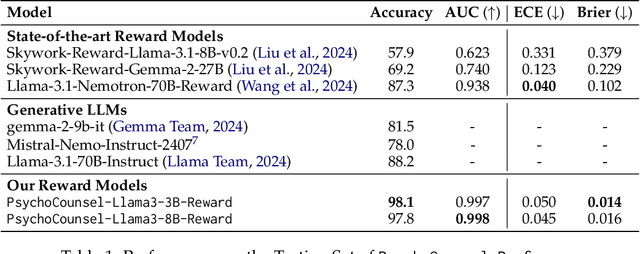
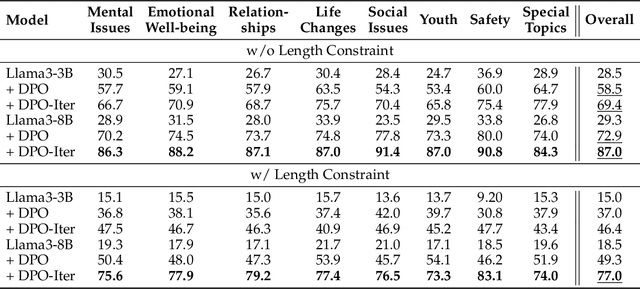
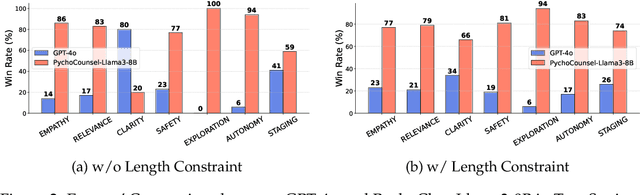
Abstract:Applying large language models (LLMs) to assist in psycho-counseling is an emerging and meaningful approach, driven by the significant gap between patient needs and the availability of mental health support. However, current LLMs struggle to consistently provide effective responses to client speeches, largely due to the lack of supervision from high-quality real psycho-counseling data, whose content is typically inaccessible due to client privacy concerns. Furthermore, the quality of therapists' responses in available sessions can vary significantly based on their professional training and experience. Assessing the quality of therapists' responses remains an open challenge. In this work, we address these challenges by first proposing a set of professional and comprehensive principles to evaluate therapists' responses to client speeches. Using these principles, we create a preference dataset, PsychoCounsel-Preference, which contains 36k high-quality preference comparison pairs. This dataset aligns with the preferences of professional psychotherapists, providing a robust foundation for evaluating and improving LLMs in psycho-counseling. Experiments on reward modeling and preference learning demonstrate that PsychoCounsel-Preference is an excellent resource for LLMs to acquire essential skills for responding to clients in a counseling session. Our best-aligned model, PsychoCounsel-Llama3-8B, achieves an impressive win rate of 87% against GPT-4o. We release PsychoCounsel-Preference, PsychoCounsel-Llama3-8B and the reward model PsychoCounsel Llama3-8B-Reward to facilitate the research of psycho-counseling with LLMs at: https://hf.co/Psychotherapy-LLM.
CBT-Bench: Evaluating Large Language Models on Assisting Cognitive Behavior Therapy
Oct 17, 2024
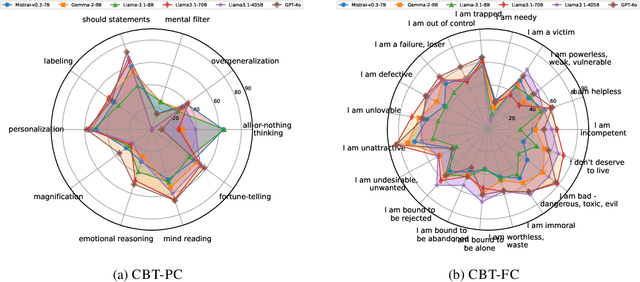

Abstract:There is a significant gap between patient needs and available mental health support today. In this paper, we aim to thoroughly examine the potential of using Large Language Models (LLMs) to assist professional psychotherapy. To this end, we propose a new benchmark, CBT-BENCH, for the systematic evaluation of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) assistance. We include three levels of tasks in CBT-BENCH: I: Basic CBT knowledge acquisition, with the task of multiple-choice questions; II: Cognitive model understanding, with the tasks of cognitive distortion classification, primary core belief classification, and fine-grained core belief classification; III: Therapeutic response generation, with the task of generating responses to patient speech in CBT therapy sessions. These tasks encompass key aspects of CBT that could potentially be enhanced through AI assistance, while also outlining a hierarchy of capability requirements, ranging from basic knowledge recitation to engaging in real therapeutic conversations. We evaluated representative LLMs on our benchmark. Experimental results indicate that while LLMs perform well in reciting CBT knowledge, they fall short in complex real-world scenarios requiring deep analysis of patients' cognitive structures and generating effective responses, suggesting potential future work.
PATIENT-Ψ: Using Large Language Models to Simulate Patients for Training Mental Health Professionals
May 30, 2024Abstract:Mental illness remains one of the most critical public health issues, with a significant gap between the available mental health support and patient needs. Many mental health professionals highlight a disconnect between their training and real-world patient interactions, leaving some trainees feeling unprepared and potentially affecting their early career success. In this paper, we propose PATIENT-{\Psi}, a novel patient simulation framework for cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) training. To build PATIENT-{\Psi}, we constructed diverse patient profiles and their corresponding cognitive models based on CBT principles, and then used large language models (LLMs) programmed with the patient cognitive models to act as a simulated therapy patient. We propose an interactive training scheme, PATIENT-{\Psi}-TRAINER, for mental health trainees to practice a key skill in CBT -- formulating the cognitive model of the patient -- through role-playing a therapy session with PATIENT-{\Psi}. To evaluate PATIENT-{\Psi}, we conducted a user study of 4 mental health trainees and 10 experts. The results demonstrate that practice using PATIENT-{\Psi}-TRAINER greatly enhances the perceived skill acquisition and confidence of the trainees beyond existing forms of training such as textbooks, videos, and role-play with non-patients. Based on the experts' perceptions, PATIENT-{\Psi} is perceived to be closer to real patient interactions than GPT-4, and PATIENT-{\Psi}-TRAINER holds strong promise to improve trainee competencies. Our pioneering patient simulation training framework, using LLMs, holds great potential to enhance and advance mental health training, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes. We will release all our data, code, and the training platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge