Shaoyi Liu
Road to 6G Digital Twin Networks: Multi-Task Adaptive Ray-Tracing as a Key Enabler
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:As a virtual, synchronized replica of physical network, the digital twin network (DTN) is envisioned to sense, predict, optimize and manage the intricate wireless technologies and architectures brought by 6G. Given that the properties of wireless channel fundamentally determine the system performances from the physical layer to network layer, it is a critical prerequisite that the invisible wireless channel in physical world be accurately and efficiently twinned. To support 6G DTN, this paper first proposes a multi-task adaptive ray-tracing platform for 6G (MART-6G) to generate the channel with 6G features, specially designed for DTN online real-time and offline high-accurate tasks. Specifically, the MART-6G platform comprises three core modules, i.e., environment twin module to enhance the sensing ability of dynamic environment; RT engine module to incorporate the main algorithms of propagations, accelerations, calibrations, 6G-specific new features; and channel twin module to generate channel multipath, parameters, statistical distributions, and corresponding three-dimensional (3D) environment information. Moreover, MART-6G is tailored for DTN tasks through the adaptive selection of proper sensing methods, antenna and material libraries, propagation models and calibration strategy, etc. To validate MART-6G performance, we present two real-world case studies to demonstrate the accuracy, efficiency and generality in both offline coverage prediction and online real-time channel prediction. Finally, some open issues and challenges are outlined to further support future diverse DTN tasks.
Wireless Environmental Information Theory: A New Paradigm towards 6G Online and Proactive Environment Intelligence Communication
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:The channel is one of the five critical components of a communication system, and its ergodic capacity is based on all realizations of statistic channel model. This statistical paradigm has successfully guided the design of mobile communication systems from 1G to 5G. However, this approach relies on offline channel measurements in specific environments, and the system passively adapts to new environments, resulting in deviation from the optimal performance. With the pursuit of higher capacity and data rate of 6G, especially facing the ubiquitous environments, there is an urgent need for a new paradigm to combat the randomness of channel, i.e., more proactive and online manner. Motivated by this, we propose an environment intelligence communication (EIC) based on wireless environmental information theory (WEIT) for 6G. The proposed EIC architecture is composed of three steps: Firstly, wireless environmental information (WEI) is acquired using sensing techniques. Then, leveraging WEI and channel data, AI techniques are employed to predict channel fading, thereby mitigating channel uncertainty. Thirdly, the communication system autonomously determines the optimal air-interface transmission strategy based on real-time channel predictions, enabling intelligent interaction with the physical environment. To make this attractive paradigm shift from theory to practice, we answer three key problems to establish WEIT for the first time. How should WEI be defined? Can it be quantified? Does it hold the same properties as statistical communication information? Furthermore, EIC aided by WEI (EIC-WEI) is validated across multiple air-interface tasks, including CSI prediction, beam prediction, and radio resource management. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed EIC-WEI significantly outperforms the statistical paradigm in decreasing overhead and performance optimization.
A Wideband MIMO Channel Model for Aerial Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Assisted Wireless Communications
Sep 05, 2023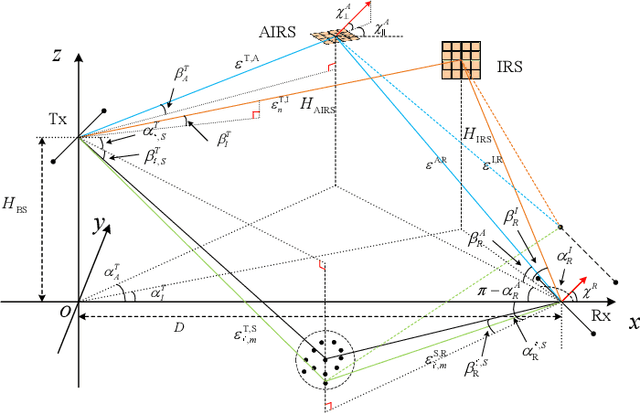
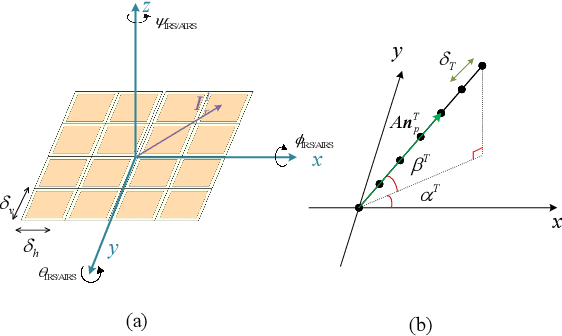
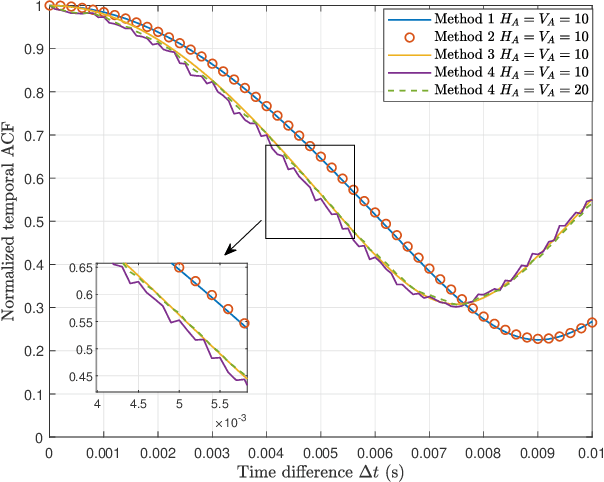
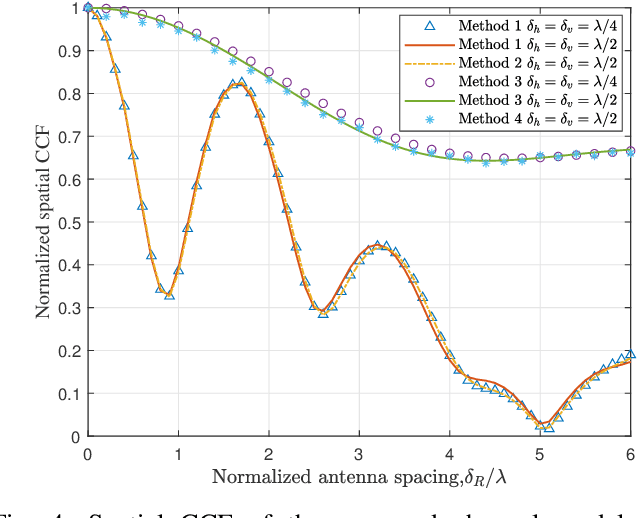
Abstract:Compared to traditional intelligent reflecting surfaces(IRS), aerial IRS (AIRS) has unique advantages, such as more flexible deployment and wider service coverage. However, modeling AIRS in the channel presents new challenges due to their mobility. In this paper, a three-dimensional (3D) wideband channel model for AIRS and IRS joint-assisted multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication system is proposed, where considering the rotational degrees of freedom in three directions and the motion angles of AIRS in space. Based on the proposed model, the channel impulse response (CIR), correlation function, and channel capacity are derived, and several feasible joint phase shifts schemes for AIRS and IRS units are proposed. Simulation results show that the proposed model can capture the channel characteristics accurately, and the proposed phase shifts methods can effectively improve the channel statistical characteristics and increase the system capacity. Additionally, we observe that in certain scenarios, the paths involving the IRS and the line-of-sight (LoS) paths exhibit similar characteristics. These findings provide valuable insights for the future development of intelligent communication systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge