Sarah E. Finch
Jason
Finding A Voice: Evaluating African American Dialect Generation for Chatbot Technology
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:As chatbots become increasingly integrated into everyday tasks, designing systems that accommodate diverse user populations is crucial for fostering trust, engagement, and inclusivity. This study investigates the ability of contemporary Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate African American Vernacular English (AAVE) and evaluates the impact of AAVE usage on user experiences in chatbot applications. We analyze the performance of three LLM families (Llama, GPT, and Claude) in producing AAVE-like utterances at varying dialect intensities and assess user preferences across multiple domains, including healthcare and education. Despite LLMs' proficiency in generating AAVE-like language, findings indicate that AAVE-speaking users prefer Standard American English (SAE) chatbots, with higher levels of AAVE correlating with lower ratings for a variety of characteristics, including chatbot trustworthiness and role appropriateness. These results highlight the complexities of creating inclusive AI systems and underscore the need for further exploration of diversity to enhance human-computer interactions.
Leveraging Explicit Reasoning for Inference Integration in Commonsense-Augmented Dialogue Models
Jun 13, 2024Abstract:Open-domain dialogue systems need to grasp social commonsense to understand and respond effectively to human users. Commonsense-augmented dialogue models have been proposed that aim to infer commonsense knowledge from dialogue contexts in order to improve response quality. However, existing approaches to commonsense-augmented dialogue rely on implicit reasoning to integrate commonsense inferences during response generation. In this study, we explore the impact of explicit reasoning against implicit reasoning over commonsense for dialogue response generation. Our findings demonstrate that separating commonsense reasoning into explicit steps for generating, selecting, and integrating commonsense into responses leads to better dialogue interactions, improving naturalness, engagement, specificity, and overall quality. Subsequent analyses of these findings unveil insights into the effectiveness of various types of commonsense in generating responses and the particular response traits enhanced through explicit reasoning for commonsense integration. Our work advances research in open-domain dialogue by achieving a new state-of-the-art in commonsense-augmented response generation.
ConvoSense: Overcoming Monotonous Commonsense Inferences for Conversational AI
Jan 27, 2024Abstract:Mastering commonsense understanding and reasoning is a pivotal skill essential for conducting engaging conversations. While there have been several attempts to create datasets that facilitate commonsense inferences in dialogue contexts, existing datasets tend to lack in-depth details, restate information already present in the conversation, and often fail to capture the multifaceted nature of commonsense reasoning. In response to these limitations, we compile a new synthetic dataset for commonsense reasoning in dialogue contexts using GPT, ConvoSense, that boasts greater contextual novelty, offers a higher volume of inferences per example, and substantially enriches the detail conveyed by the inferences. Our dataset contains over 500,000 inferences across 12,000 dialogues with 10 popular inference types, which empowers the training of generative commonsense models for dialogue that are superior in producing plausible inferences with high novelty when compared to models trained on the previous datasets. To the best of our knowledge, ConvoSense is the first of its kind to provide such a multitude of novel inferences at such a large scale.
Exploring the Impact of Human Evaluator Group on Chat-Oriented Dialogue Evaluation
Sep 14, 2023
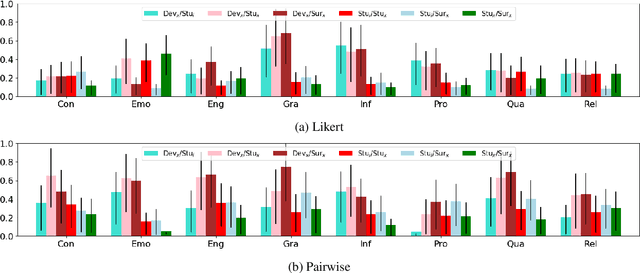


Abstract:Human evaluation has been widely accepted as the standard for evaluating chat-oriented dialogue systems. However, there is a significant variation in previous work regarding who gets recruited as evaluators. Evaluator groups such as domain experts, university students, and professional annotators have been used to assess and compare dialogue systems, although it is unclear to what extent the choice of an evaluator group can affect results. This paper analyzes the evaluator group impact on dialogue system evaluation by testing 4 state-of-the-art dialogue systems using 4 distinct evaluator groups. Our analysis reveals a robustness towards evaluator groups for Likert evaluations that is not seen for Pairwise, with only minor differences observed when changing evaluator groups. Furthermore, two notable limitations to this robustness are observed, which reveal discrepancies between evaluators with different levels of chatbot expertise and indicate that evaluator objectivity is beneficial for certain dialogue metrics.
Leveraging Large Language Models for Automated Dialogue Analysis
Sep 12, 2023Abstract:Developing high-performing dialogue systems benefits from the automatic identification of undesirable behaviors in system responses. However, detecting such behaviors remains challenging, as it draws on a breadth of general knowledge and understanding of conversational practices. Although recent research has focused on building specialized classifiers for detecting specific dialogue behaviors, the behavior coverage is still incomplete and there is a lack of testing on real-world human-bot interactions. This paper investigates the ability of a state-of-the-art large language model (LLM), ChatGPT-3.5, to perform dialogue behavior detection for nine categories in real human-bot dialogues. We aim to assess whether ChatGPT can match specialized models and approximate human performance, thereby reducing the cost of behavior detection tasks. Our findings reveal that neither specialized models nor ChatGPT have yet achieved satisfactory results for this task, falling short of human performance. Nevertheless, ChatGPT shows promising potential and often outperforms specialized detection models. We conclude with an in-depth examination of the prevalent shortcomings of ChatGPT, offering guidance for future research to enhance LLM capabilities.
Don't Forget Your ABC's: Evaluating the State-of-the-Art in Chat-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Dec 18, 2022



Abstract:There has been great recent advancement in human-computer chat. However, proper evaluation currently requires human judgements that produce notoriously high-variance metrics due to their inherent subjectivity. Furthermore, there is little standardization in the methods and labels used for evaluation, with an overall lack of work to compare and assess the validity of various evaluation approaches. As a consequence, existing evaluation results likely leave an incomplete picture of the strengths and weaknesses of open-domain chatbots. We aim towards a dimensional evaluation of human-computer chat that can reliably measure several distinct aspects of chat quality. To this end, we present our novel human evaluation method that quantifies the rate of several quality-related chatbot behaviors. Our results demonstrate our method to be more suitable for dimensional chat evaluation than alternative likert-style or comparative methods. We then use our validated method and existing methods to evaluate four open-domain chat models from the recent literature.
What Went Wrong? Explaining Overall Dialogue Quality through Utterance-Level Impacts
Oct 31, 2021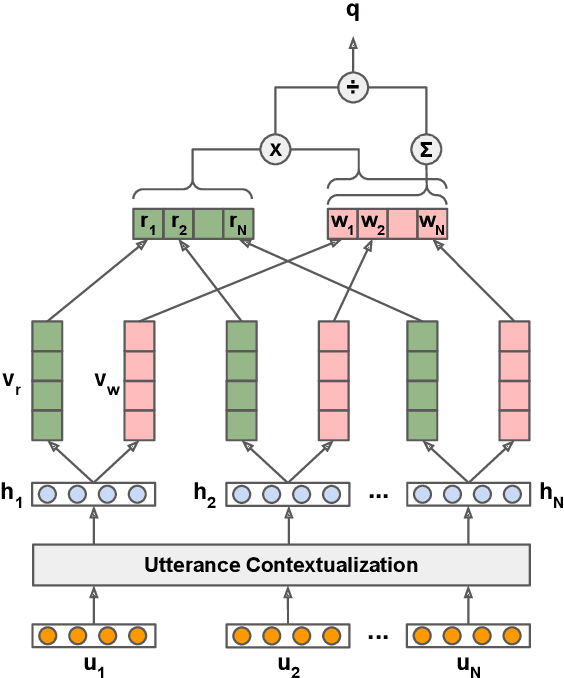
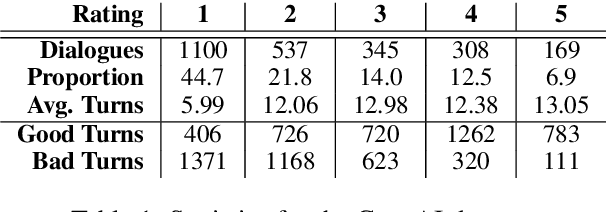
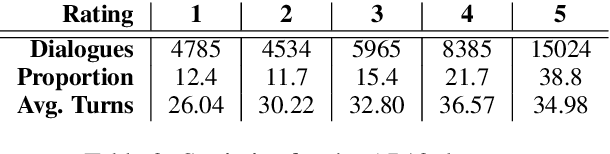
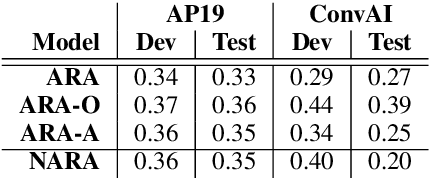
Abstract:Improving user experience of a dialogue system often requires intensive developer effort to read conversation logs, run statistical analyses, and intuit the relative importance of system shortcomings. This paper presents a novel approach to automated analysis of conversation logs that learns the relationship between user-system interactions and overall dialogue quality. Unlike prior work on utterance-level quality prediction, our approach learns the impact of each interaction from the overall user rating without utterance-level annotation, allowing resultant model conclusions to be derived on the basis of empirical evidence and at low cost. Our model identifies interactions that have a strong correlation with the overall dialogue quality in a chatbot setting. Experiments show that the automated analysis from our model agrees with expert judgments, making this work the first to show that such weakly-supervised learning of utterance-level quality prediction is highly achievable.
An Approach to Inference-Driven Dialogue Management within a Social Chatbot
Oct 31, 2021
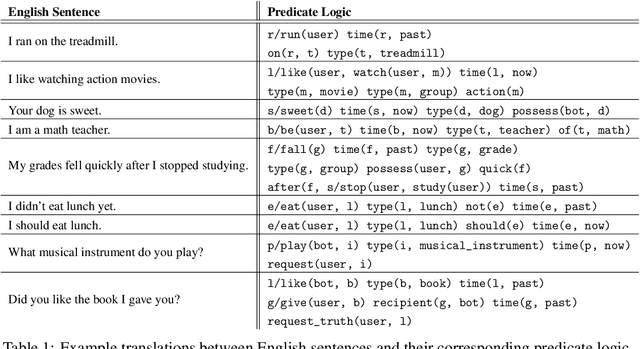

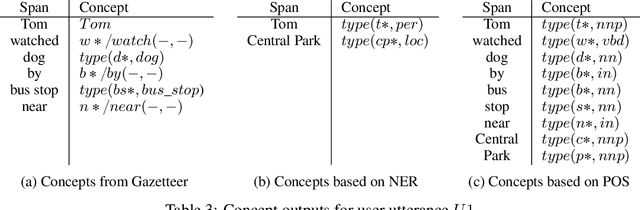
Abstract:We present a chatbot implementing a novel dialogue management approach based on logical inference. Instead of framing conversation a sequence of response generation tasks, we model conversation as a collaborative inference process in which speakers share information to synthesize new knowledge in real time. Our chatbot pipeline accomplishes this modelling in three broad stages. The first stage translates user utterances into a symbolic predicate representation. The second stage then uses this structured representation in conjunction with a larger knowledge base to synthesize new predicates using efficient graph matching. In the third and final stage, our bot selects a small subset of predicates and translates them into an English response. This approach lends itself to understanding latent semantics of user inputs, flexible initiative taking, and responses that are novel and coherent with the dialogue context.
Emora: An Inquisitive Social Chatbot Who Cares For You
Sep 10, 2020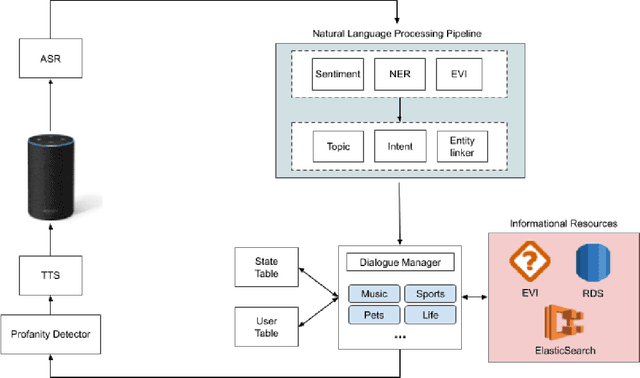
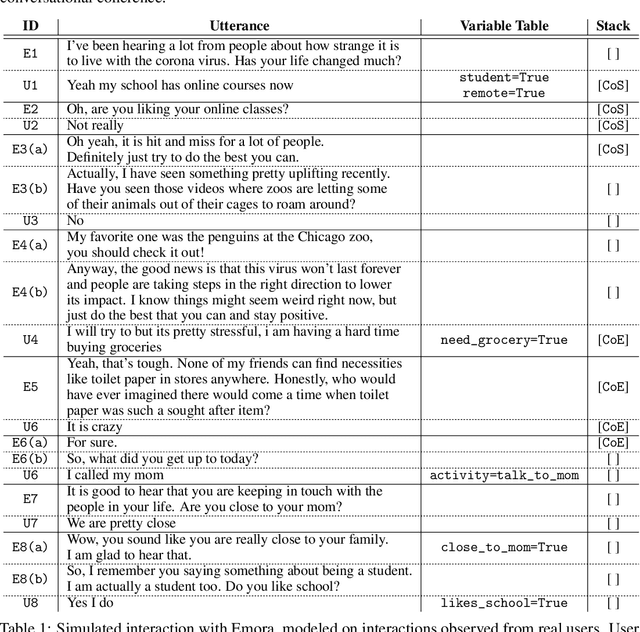
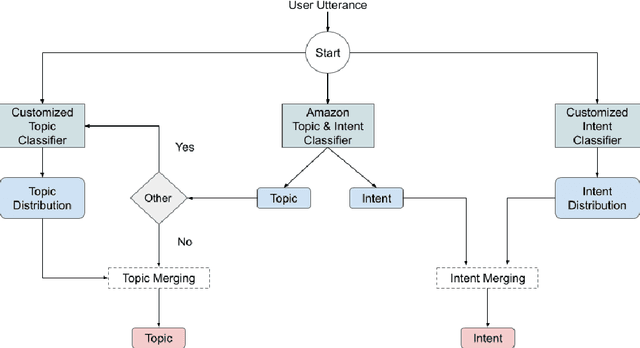
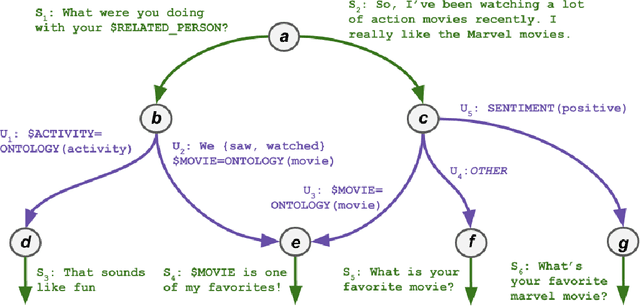
Abstract:Inspired by studies on the overwhelming presence of experience-sharing in human-human conversations, Emora, the social chatbot developed by Emory University, aims to bring such experience-focused interaction to the current field of conversational AI. The traditional approach of information-sharing topic handlers is balanced with a focus on opinion-oriented exchanges that Emora delivers, and new conversational abilities are developed that support dialogues that consist of a collaborative understanding and learning process of the partner's life experiences. We present a curated dialogue system that leverages highly expressive natural language templates, powerful intent classification, and ontology resources to provide an engaging and interesting conversational experience to every user.
Towards Unified Dialogue System Evaluation: A Comprehensive Analysis of Current Evaluation Protocols
Jun 10, 2020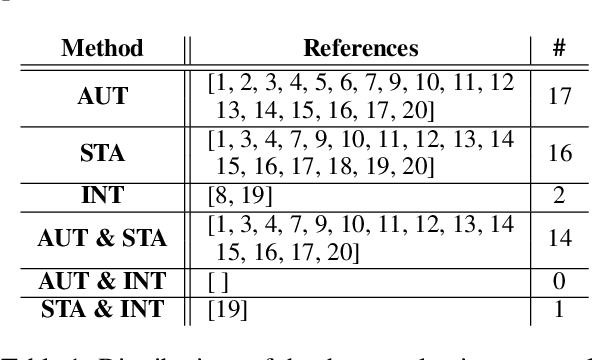
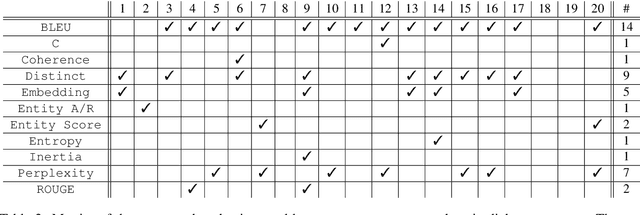
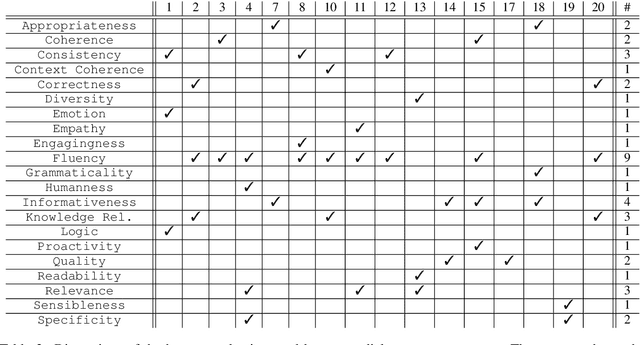
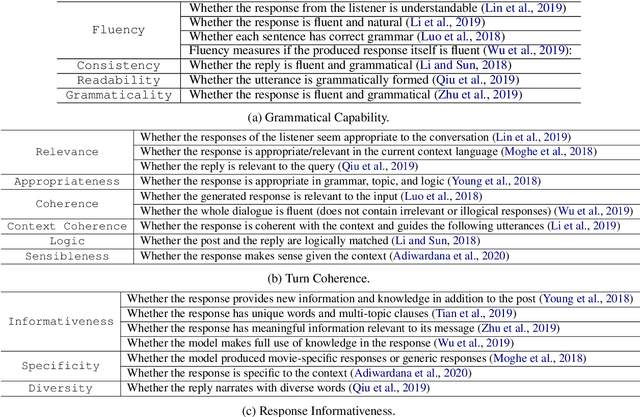
Abstract:As conversational AI-based dialogue management has increasingly become a trending topic, the need for a standardized and reliable evaluation procedure grows even more pressing. The current state of affairs suggests various evaluation protocols to assess chat-oriented dialogue management systems, rendering it difficult to conduct fair comparative studies across different approaches and gain an insightful understanding of their values. To foster this research, a more robust evaluation protocol must be set in place. This paper presents a comprehensive synthesis of both automated and human evaluation methods on dialogue systems, identifying their shortcomings while accumulating evidence towards the most effective evaluation dimensions. A total of 20 papers from the last two years are surveyed to analyze three types of evaluation protocols: automated, static, and interactive. Finally, the evaluation dimensions used in these papers are compared against our expert evaluation on the system-user dialogue data collected from the Alexa Prize 2020.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge