Sara Colantonio
Parameter-free entropy-regularized multi-view clustering with hierarchical feature selection
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Multi-view clustering faces critical challenges in automatically discovering patterns across heterogeneous data while managing high-dimensional features and eliminating irrelevant information. Traditional approaches suffer from manual parameter tuning and lack principled cross-view integration mechanisms. This work introduces two complementary algorithms: AMVFCM-U and AAMVFCM-U, providing a unified parameter-free framework. Our approach replaces fuzzification parameters with entropy regularization terms that enforce adaptive cross-view consensus. The core innovation employs signal-to-noise ratio based regularization ($\delta_j^h = \frac{\bar{x}_j^h}{(\sigma_j^h)^2}$) for principled feature weighting with convergence guarantees, coupled with dual-level entropy terms that automatically balance view and feature contributions. AAMVFCM-U extends this with hierarchical dimensionality reduction operating at feature and view levels through adaptive thresholding ($\theta^{h^{(t)}} = \frac{d_h^{(t)}}{n}$). Evaluation across five diverse benchmarks demonstrates superiority over 15 state-of-the-art methods. AAMVFCM-U achieves up to 97% computational efficiency gains, reduces dimensionality to 0.45% of original size, and automatically identifies critical view combinations for optimal pattern discovery.
Connectivity-Inspired Network for Context-Aware Recognition
Sep 06, 2024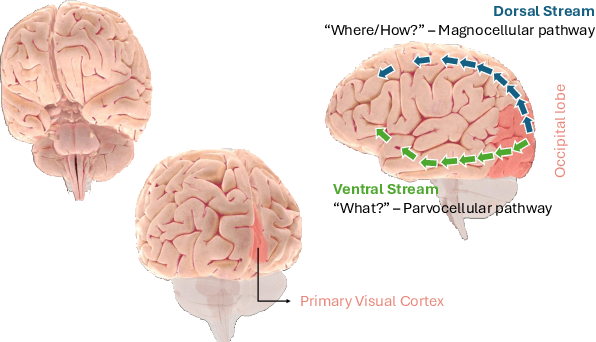
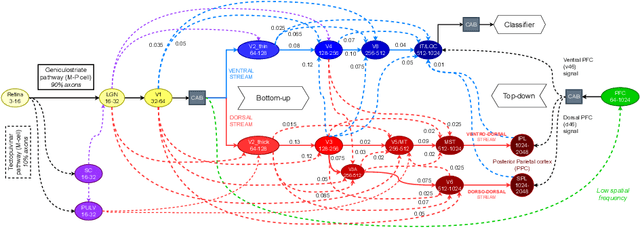
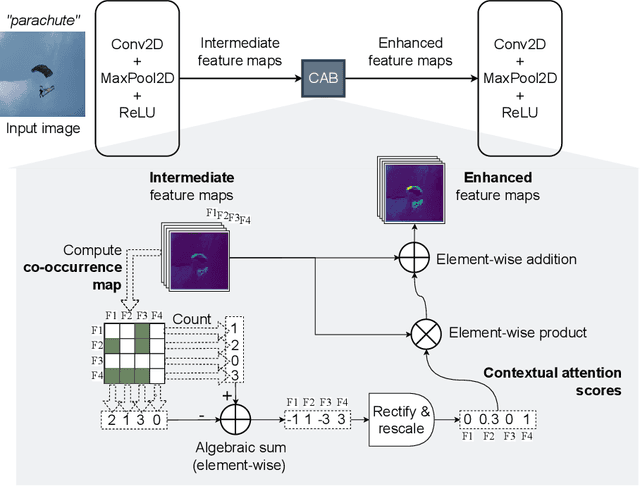
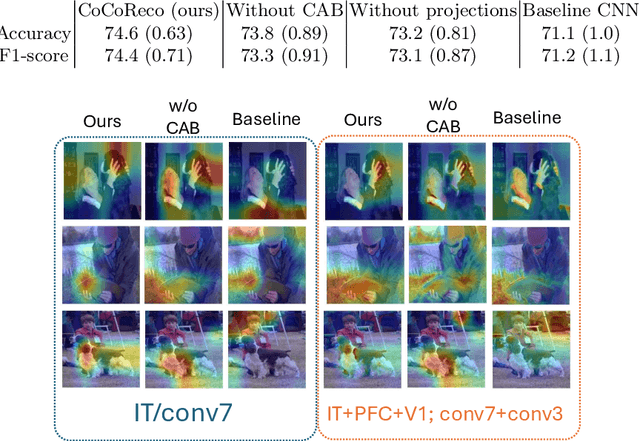
Abstract:The aim of this paper is threefold. We inform the AI practitioner about the human visual system with an extensive literature review; we propose a novel biologically motivated neural network for image classification; and, finally, we present a new plug-and-play module to model context awareness. We focus on the effect of incorporating circuit motifs found in biological brains to address visual recognition. Our convolutional architecture is inspired by the connectivity of human cortical and subcortical streams, and we implement bottom-up and top-down modulations that mimic the extensive afferent and efferent connections between visual and cognitive areas. Our Contextual Attention Block is simple and effective and can be integrated with any feed-forward neural network. It infers weights that multiply the feature maps according to their causal influence on the scene, modeling the co-occurrence of different objects in the image. We place our module at different bottlenecks to infuse a hierarchical context awareness into the model. We validated our proposals through image classification experiments on benchmark data and found a consistent improvement in performance and the robustness of the produced explanations via class activation. Our code is available at https://github.com/gianlucarloni/CoCoReco.
CROCODILE: Causality aids RObustness via COntrastive DIsentangled LEarning
Aug 09, 2024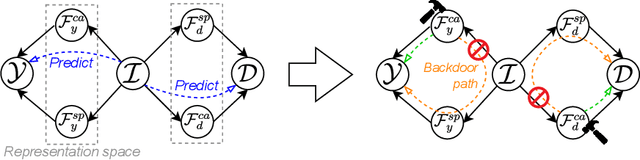
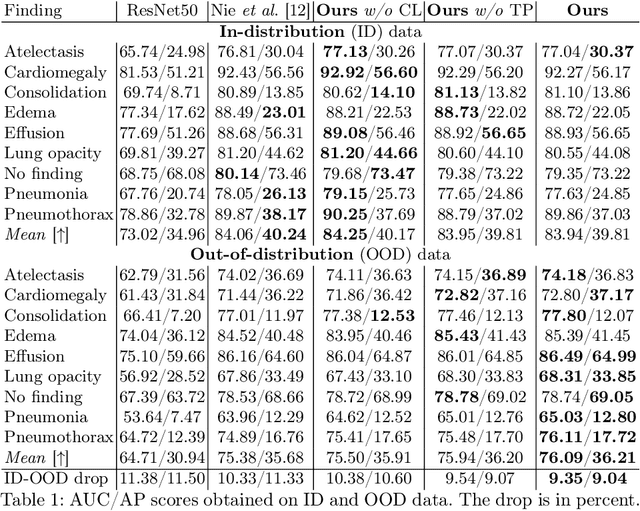
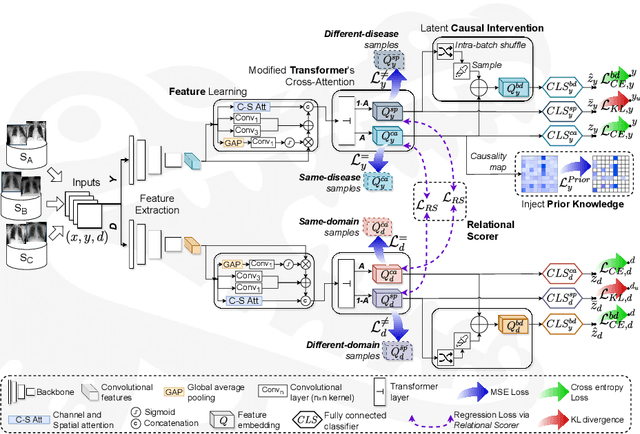
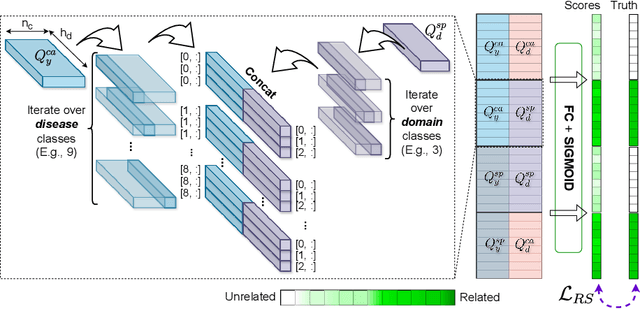
Abstract:Due to domain shift, deep learning image classifiers perform poorly when applied to a domain different from the training one. For instance, a classifier trained on chest X-ray (CXR) images from one hospital may not generalize to images from another hospital due to variations in scanner settings or patient characteristics. In this paper, we introduce our CROCODILE framework, showing how tools from causality can foster a model's robustness to domain shift via feature disentanglement, contrastive learning losses, and the injection of prior knowledge. This way, the model relies less on spurious correlations, learns the mechanism bringing from images to prediction better, and outperforms baselines on out-of-distribution (OOD) data. We apply our method to multi-label lung disease classification from CXRs, utilizing over 750000 images from four datasets. Our bias-mitigation method improves domain generalization and fairness, broadening the applicability and reliability of deep learning models for a safer medical image analysis. Find our code at: https://github.com/gianlucarloni/crocodile.
Boosting Few-Shot Learning with Disentangled Self-Supervised Learning and Meta-Learning for Medical Image Classification
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Background and objective: Employing deep learning models in critical domains such as medical imaging poses challenges associated with the limited availability of training data. We present a strategy for improving the performance and generalization capabilities of models trained in low-data regimes. Methods: The proposed method starts with a pre-training phase, where features learned in a self-supervised learning setting are disentangled to improve the robustness of the representations for downstream tasks. We then introduce a meta-fine-tuning step, leveraging related classes between meta-training and meta-testing phases but varying the granularity level. This approach aims to enhance the model's generalization capabilities by exposing it to more challenging classification tasks during meta-training and evaluating it on easier tasks but holding greater clinical relevance during meta-testing. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach through a series of experiments exploring several backbones, as well as diverse pre-training and fine-tuning schemes, on two distinct medical tasks, i.e., classification of prostate cancer aggressiveness from MRI data and classification of breast cancer malignity from microscopic images. Results: Our results indicate that the proposed approach consistently yields superior performance w.r.t. ablation experiments, maintaining competitiveness even when a distribution shift between training and evaluation data occurs. Conclusion: Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and wide applicability of the proposed approach. We hope that this work will add another solution to the arsenal of addressing learning issues in data-scarce imaging domains.
In-Bed Pose Estimation: A Review
Feb 01, 2024Abstract:Human pose estimation, the process of identifying joint positions in a person's body from images or videos, represents a widely utilized technology across diverse fields, including healthcare. One such healthcare application involves in-bed pose estimation, where the body pose of an individual lying under a blanket is analyzed. This task, for instance, can be used to monitor a person's sleep behavior and detect symptoms early for potential disease diagnosis in homes and hospitals. Several studies have utilized unimodal and multimodal methods to estimate in-bed human poses. The unimodal studies generally employ RGB images, whereas the multimodal studies use modalities including RGB, long-wavelength infrared, pressure map, and depth map. Multimodal studies have the advantage of using modalities in addition to RGB that might capture information useful to cope with occlusions. Moreover, some multimodal studies exclude RGB and, this way, better suit privacy preservation. To expedite advancements in this domain, we conduct a review of existing datasets and approaches. Our objectives are to show the limitations of the previous studies, current challenges, and provide insights for future works on the in-bed human pose estimation field.
A Systematic Review of Few-Shot Learning in Medical Imaging
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:The lack of annotated medical images limits the performance of deep learning models, which usually need large-scale labelled datasets. Few-shot learning techniques can reduce data scarcity issues and enhance medical image analysis, especially with meta-learning. This systematic review gives a comprehensive overview of few-shot learning in medical imaging. We searched the literature systematically and selected 80 relevant articles published from 2018 to 2023. We clustered the articles based on medical outcomes, such as tumour segmentation, disease classification, and image registration; anatomical structure investigated (i.e. heart, lung, etc.); and the meta-learning method used. For each cluster, we examined the papers' distributions and the results provided by the state-of-the-art. In addition, we identified a generic pipeline shared among all the studies. The review shows that few-shot learning can overcome data scarcity in most outcomes and that meta-learning is a popular choice to perform few-shot learning because it can adapt to new tasks with few labelled samples. In addition, following meta-learning, supervised learning and semi-supervised learning stand out as the predominant techniques employed to tackle few-shot learning challenges in medical imaging and also best performing. Lastly, we observed that the primary application areas predominantly encompass cardiac, pulmonary, and abdominal domains. This systematic review aims to inspire further research to improve medical image analysis and patient care.
Exploiting Causality Signals in Medical Images: A Pilot Study with Empirical Results
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:We present a new method for automatically classifying medical images that uses weak causal signals in the scene to model how the presence of a feature in one part of the image affects the appearance of another feature in a different part of the image. Our method consists of two components: a convolutional neural network backbone and a causality-factors extractor module. The latter computes weights for the feature maps to enhance each feature map according to its causal influence in the image's scene. We can modify the functioning of the causality module by using two external signals, thus obtaining different variants of our method. We evaluate our method on a public dataset of prostate MRI images for prostate cancer diagnosis, using quantitative experiments, qualitative assessment, and ablation studies. Our results show that our method improves classification performance and produces more robust predictions, focusing on relevant parts of the image. That is especially important in medical imaging, where accurate and reliable classifications are essential for effective diagnosis and treatment planning.
Causality-Driven One-Shot Learning for Prostate Cancer Grading from MRI
Sep 19, 2023
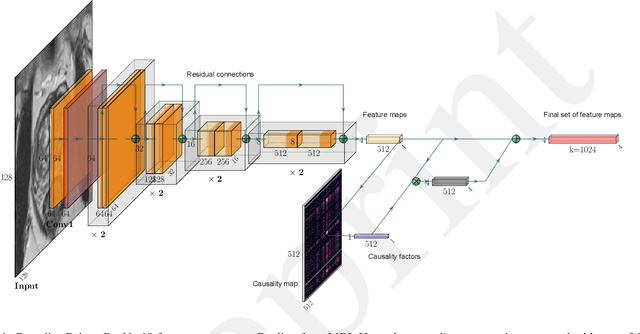


Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel method to automatically classify medical images that learns and leverages weak causal signals in the image. Our framework consists of a convolutional neural network backbone and a causality-extractor module that extracts cause-effect relationships between feature maps that can inform the model on the appearance of a feature in one place of the image, given the presence of another feature within some other place of the image. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approach in low-data scenarios, we train our causality-driven architecture in a One-shot learning scheme, where we propose a new meta-learning procedure entailing meta-training and meta-testing tasks that are designed using related classes but at different levels of granularity. We conduct binary and multi-class classification experiments on a publicly available dataset of prostate MRI images. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed causality-driven module, we perform an ablation study and conduct qualitative assessments using class activation maps to highlight regions strongly influencing the network's decision-making process. Our findings show that causal relationships among features play a crucial role in enhancing the model's ability to discern relevant information and yielding more reliable and interpretable predictions. This would make it a promising approach for medical image classification tasks.
The role of causality in explainable artificial intelligence
Sep 18, 2023



Abstract:Causality and eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) have developed as separate fields in computer science, even though the underlying concepts of causation and explanation share common ancient roots. This is further enforced by the lack of review works jointly covering these two fields. In this paper, we investigate the literature to try to understand how and to what extent causality and XAI are intertwined. More precisely, we seek to uncover what kinds of relationships exist between the two concepts and how one can benefit from them, for instance, in building trust in AI systems. As a result, three main perspectives are identified. In the first one, the lack of causality is seen as one of the major limitations of current AI and XAI approaches, and the "optimal" form of explanations is investigated. The second is a pragmatic perspective and considers XAI as a tool to foster scientific exploration for causal inquiry, via the identification of pursue-worthy experimental manipulations. Finally, the third perspective supports the idea that causality is propaedeutic to XAI in three possible manners: exploiting concepts borrowed from causality to support or improve XAI, utilizing counterfactuals for explainability, and considering accessing a causal model as explaining itself. To complement our analysis, we also provide relevant software solutions used to automate causal tasks. We believe our work provides a unified view of the two fields of causality and XAI by highlighting potential domain bridges and uncovering possible limitations.
Alzheimer Disease Detection from Raman Spectroscopy of the Cerebrospinal Fluid via Topological Machine Learning
Sep 07, 2023



Abstract:The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of 19 subjects who received a clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) as well as of 5 pathological controls have been collected and analysed by Raman spectroscopy (RS). We investigated whether the raw and preprocessed Raman spectra could be used to distinguish AD from controls. First, we applied standard Machine Learning (ML) methods obtaining unsatisfactory results. Then, we applied ML to a set of topological descriptors extracted from raw spectra, achieving a very good classification accuracy (>87%). Although our results are preliminary, they indicate that RS and topological analysis together may provide an effective combination to confirm or disprove a clinical diagnosis of AD. The next steps will include enlarging the dataset of CSF samples to validate the proposed method better and, possibly, to understand if topological data analysis could support the characterization of AD subtypes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge