Sanjana Narayanan
Assessing the Limitations of Large Language Models in Clinical Fact Decomposition
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Verifying factual claims is critical for using large language models (LLMs) in healthcare. Recent work has proposed fact decomposition, which uses LLMs to rewrite source text into concise sentences conveying a single piece of information, as an approach for fine-grained fact verification. Clinical documentation poses unique challenges for fact decomposition due to dense terminology and diverse note types. To explore these challenges, we present FactEHR, a dataset consisting of full document fact decompositions for 2,168 clinical notes spanning four types from three hospital systems. Our evaluation, including review by clinicians, highlights significant variability in the quality of fact decomposition for four commonly used LLMs, with some LLMs generating 2.6x more facts per sentence than others. The results underscore the need for better LLM capabilities to support factual verification in clinical text. To facilitate future research in this direction, we plan to release our code at \url{https://github.com/som-shahlab/factehr}.
(When) Are Contrastive Explanations of Reinforcement Learning Helpful?
Nov 14, 2022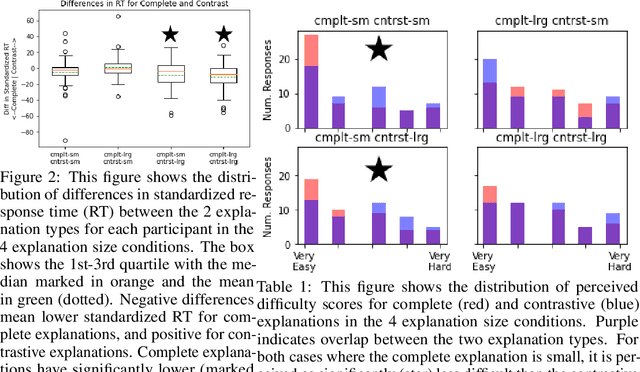
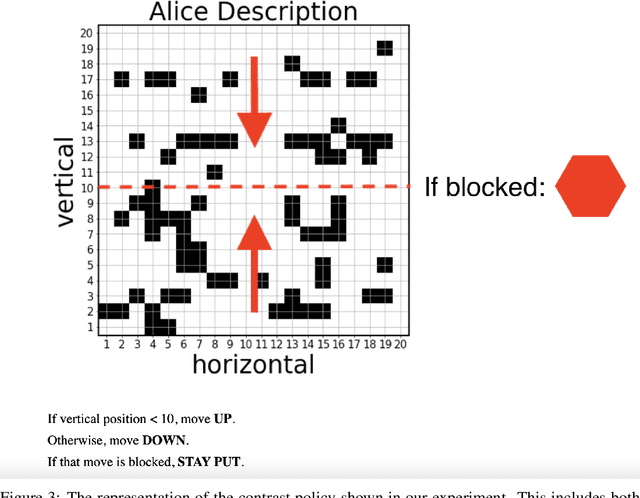

Abstract:Global explanations of a reinforcement learning (RL) agent's expected behavior can make it safer to deploy. However, such explanations are often difficult to understand because of the complicated nature of many RL policies. Effective human explanations are often contrastive, referencing a known contrast (policy) to reduce redundancy. At the same time, these explanations also require the additional effort of referencing that contrast when evaluating an explanation. We conduct a user study to understand whether and when contrastive explanations might be preferable to complete explanations that do not require referencing a contrast. We find that complete explanations are generally more effective when they are the same size or smaller than a contrastive explanation of the same policy, and no worse when they are larger. This suggests that contrastive explanations are not sufficient to solve the problem of effectively explaining reinforcement learning policies, and require additional careful study for use in this context.
On Learning Prediction-Focused Mixtures
Oct 27, 2021



Abstract:Probabilistic models help us encode latent structures that both model the data and are ideally also useful for specific downstream tasks. Among these, mixture models and their time-series counterparts, hidden Markov models, identify discrete components in the data. In this work, we focus on a constrained capacity setting, where we want to learn a model with relatively few components (e.g. for interpretability purposes). To maintain prediction performance, we introduce prediction-focused modeling for mixtures, which automatically selects the dimensions relevant to the prediction task. Our approach identifies relevant signal from the input, outperforms models that are not prediction-focused, and is easy to optimize; we also characterize when prediction-focused modeling can be expected to work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge