Sangjun Lee
Fisheye-Calib-Adapter: An Easy Tool for Fisheye Camera Model Conversion
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:The increasing necessity for fisheye cameras in fields such as robotics and autonomous driving has led to the proposal of various fisheye camera models. While the evolution of camera models has facilitated the development of diverse systems in the field, the lack of adaptation between different fisheye camera models means that recalibration is always necessary, which is cumbersome. This paper introduces a conversion tool for various previously proposed fisheye camera models. It is user-friendly, simple, yet extremely fast and accurate, offering conversion capabilities for a broader range of models compared to existing tools. We have verified that models converted using our system perform correctly in applications such as SLAM. By utilizing our system, researchers can obtain output parameters directly from input parameters without the need for an image set and any recalibration processes, thus serving as a bridge across different fisheye camera models in various research fields. We provide our system as an open source tool available at: https://github.com/eowjd0512/fisheye-calib-adapter
SelecMix: Debiased Learning by Contradicting-pair Sampling
Nov 04, 2022Abstract:Neural networks trained with ERM (empirical risk minimization) sometimes learn unintended decision rules, in particular when their training data is biased, i.e., when training labels are strongly correlated with undesirable features. To prevent a network from learning such features, recent methods augment training data such that examples displaying spurious correlations (i.e., bias-aligned examples) become a minority, whereas the other, bias-conflicting examples become prevalent. However, these approaches are sometimes difficult to train and scale to real-world data because they rely on generative models or disentangled representations. We propose an alternative based on mixup, a popular augmentation that creates convex combinations of training examples. Our method, coined SelecMix, applies mixup to contradicting pairs of examples, defined as showing either (i) the same label but dissimilar biased features, or (ii) different labels but similar biased features. Identifying such pairs requires comparing examples with respect to unknown biased features. For this, we utilize an auxiliary contrastive model with the popular heuristic that biased features are learned preferentially during training. Experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the method, in particular when label noise complicates the identification of bias-conflicting examples.
Deepfake Detection for Facial Images with Facemasks
Feb 23, 2022
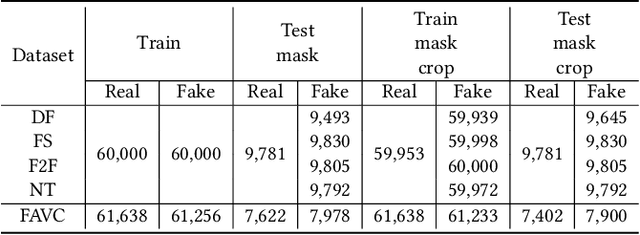
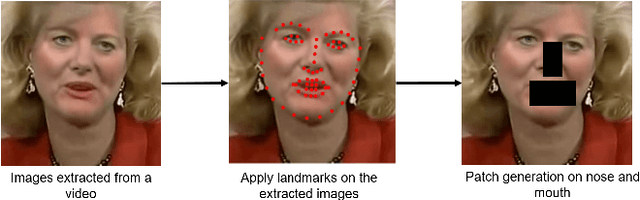
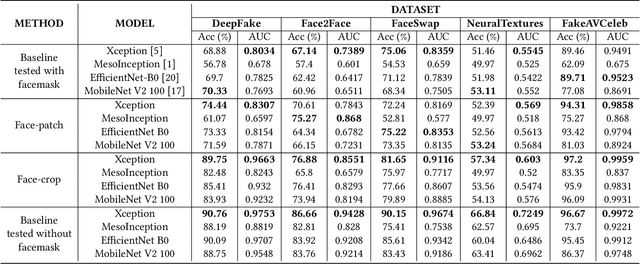
Abstract:Hyper-realistic face image generation and manipulation have givenrise to numerous unethical social issues, e.g., invasion of privacy,threat of security, and malicious political maneuvering, which re-sulted in the development of recent deepfake detection methodswith the rising demands of deepfake forensics. Proposed deepfakedetection methods to date have shown remarkable detection perfor-mance and robustness. However, none of the suggested deepfakedetection methods assessed the performance of deepfakes withthe facemask during the pandemic crisis after the outbreak of theCovid-19. In this paper, we thoroughly evaluate the performance ofstate-of-the-art deepfake detection models on the deepfakes withthe facemask. Also, we propose two approaches to enhance themasked deepfakes detection:face-patchandface-crop. The experi-mental evaluations on both methods are assessed through the base-line deepfake detection models on the various deepfake datasets.Our extensive experiments show that, among the two methods,face-cropperforms better than theface-patch, and could be a trainmethod for deepfake detection models to detect fake faces withfacemask in real world.
Distributed Control of Multi-Robot Systems in the Presence of Deception and Denial of Service Attacks
Jan 29, 2021



Abstract:This research proposes a distributed switching control to secure multi-robot systems in the presence of cyberattacks. Two major types of cyberattack are considered: deception attack and denial of service (DoS) attack, which compromise the integrity and availability of resources, respectively. First, a residual-based attack detection scheme is introduced to identify the type of attacks. Then, a switching control is designed to neutralize the effect of the identified attacks, satisfying the performance guarantees required for state consensus among robots. For the type of a deception attack, coordination-free consensus protocols are designed to tune the weights of each robot in a way that uncompromised robots gain more weight than compromised robots. For the type of a DoS attack, leader-follower protocols that reconfigure the communication topology are utilized to transform the compromised robots into sub-robots following the leaders. The performance of the proposed approach is evaluated on the Robotarium multi-robot testbed. A full demonstration with extensive cases is available at https://youtu.be/eSj0XS2pdxI.
A Directional Antenna based Leader-Follower Relay System for End-to-End Robot Communications
Nov 07, 2017



Abstract:In this paper, we present a directional antenna-based leader-follower robotic relay system capable of building end-to-end communication in complicated and dynamically changing environments. The proposed system consists of multiple networked robots - one is a mobile end node and the others are leaders or followers acting as radio relays. Every follower uses directional antennas to relay a communication radio and to estimate the location of the leader robot as a sensory device. For bearing estimation, we employ a weight centroid algorithm (WCA) and present a theoretical analysis of the use of WCA for this work. Using a robotic convoy method, we develop online, distributed control strategies that satisfy the scalability requirements of robotic network systems and enable cooperating robots to work independently. The performance of the proposed system is evaluated by conducting extensive real-world experiments that successfully build actual communication between two end nodes.
Attack-Aware Multi-Sensor Integration Algorithm for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation Systems
Sep 07, 2017



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a fault detection and isolation based attack-aware multi-sensor integration algorithm for the detection of cyberattacks in autonomous vehicle navigation systems. The proposed algorithm uses an extended Kalman filter to construct robust residuals in the presence of noise, and then uses a parametric statistical tool to identify cyberattacks. The parametric statistical tool is based on the residuals constructed by the measurement history rather than one measurement at a time in the properties of discrete-time signals and dynamic systems. This approach allows the proposed multi-sensor integration algorithm to provide quick detection and low false alarm rates for applications in dynamic systems. An example of INS/GNSS integration of autonomous navigation systems is presented to validate the proposed algorithm by using a software-in-the-loop simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge