Jinyong Park
Deepfake Detection for Facial Images with Facemasks
Feb 23, 2022
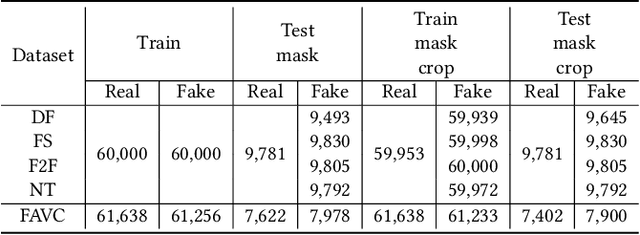
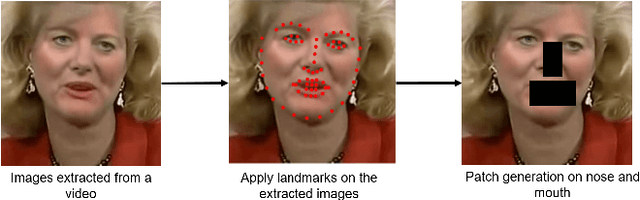
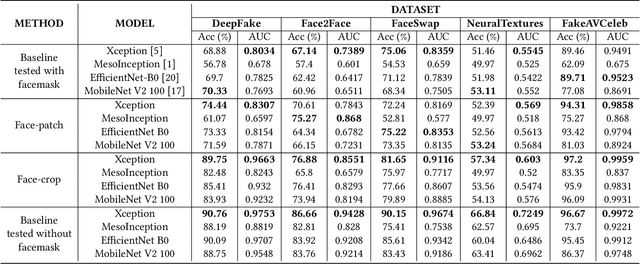
Abstract:Hyper-realistic face image generation and manipulation have givenrise to numerous unethical social issues, e.g., invasion of privacy,threat of security, and malicious political maneuvering, which re-sulted in the development of recent deepfake detection methodswith the rising demands of deepfake forensics. Proposed deepfakedetection methods to date have shown remarkable detection perfor-mance and robustness. However, none of the suggested deepfakedetection methods assessed the performance of deepfakes withthe facemask during the pandemic crisis after the outbreak of theCovid-19. In this paper, we thoroughly evaluate the performance ofstate-of-the-art deepfake detection models on the deepfakes withthe facemask. Also, we propose two approaches to enhance themasked deepfakes detection:face-patchandface-crop. The experi-mental evaluations on both methods are assessed through the base-line deepfake detection models on the various deepfake datasets.Our extensive experiments show that, among the two methods,face-cropperforms better than theface-patch, and could be a trainmethod for deepfake detection models to detect fake faces withfacemask in real world.
Fast Perception, Planning, and Execution for a Robotic Butler: Wheeled Humanoid M-Hubo
Jan 02, 2020
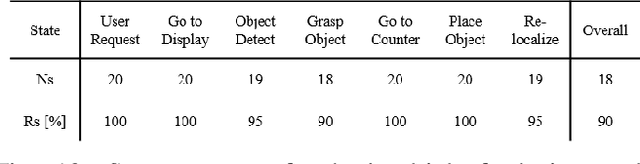
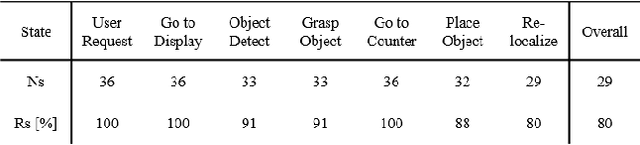
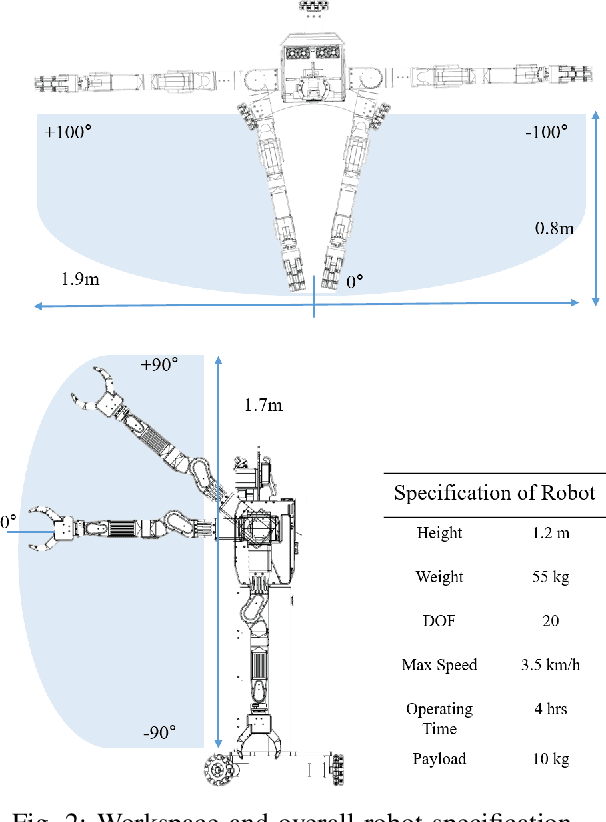
Abstract:As the aging population grows at a rapid rate, there is an ever growing need for service robot platforms that can provide daily assistance at practical speed with reliable performance. In order to assist with daily tasks such as fetching a beverage, a service robot must be able to perceive its environment and generate corresponding motion trajectories. This becomes a challenging and computationally complex problem when the environment is unknown and thus the path planner must sample numerous trajectories that often are sub-optimal, extending the execution time. To address this issue, we propose a unique strategy of integrating a 3D object detection pipeline with a kinematically optimal manipulation planner to significantly increase speed performance at runtime. In addition, we develop a new robotic butler system for a wheeled humanoid that is capable of fetching requested objects at 24% of the speed a human needs to fulfill the same task. The proposed system was evaluated and demonstrated in a real-world environment setup as well as in public exhibition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge