Sang-Hwy Lee
Automatic 3D Registration of Dental CBCT and Face Scan Data using 2D Projection images
May 17, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a fully automatic registration method of dental cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and face scan data. It can be used for a digital platform of 3D jaw-teeth-face models in a variety of applications, including 3D digital treatment planning and orthognathic surgery. Difficulties in accurately merging facial scans and CBCT images are due to the different image acquisition methods and limited area of correspondence between the two facial surfaces. In addition, it is difficult to use machine learning techniques because they use face-related 3D medical data with radiation exposure, which are difficult to obtain for training. The proposed method addresses these problems by reusing an existing machine-learning-based 2D landmark detection algorithm in an open-source library and developing a novel mathematical algorithm that identifies paired 3D landmarks from knowledge of the corresponding 2D landmarks. A main contribution of this study is that the proposed method does not require annotated training data of facial landmarks because it uses a pre-trained facial landmark detection algorithm that is known to be robust and generalized to various 2D face image models. Note that this reduces a 3D landmark detection problem to a 2D problem of identifying the corresponding landmarks on two 2D projection images generated from two different projection angles. Here, the 3D landmarks for registration were selected from the sub-surfaces with the least geometric change under the CBCT and face scan environments. For the final fine-tuning of the registration, the Iterative Closest Point method was applied, which utilizes geometrical information around the 3D landmarks. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieved an averaged surface distance error of 0.74 mm for three pairs of CBCT and face scan datasets.
Fully automatic integration of dental CBCT images and full-arch intraoral impressions with stitching error correction via individual tooth segmentation and identification
Dec 03, 2021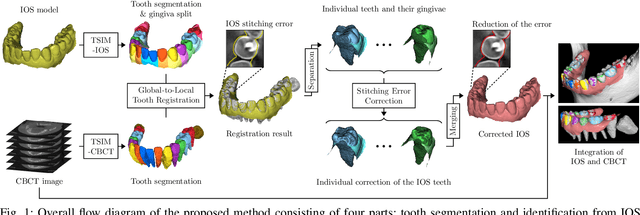
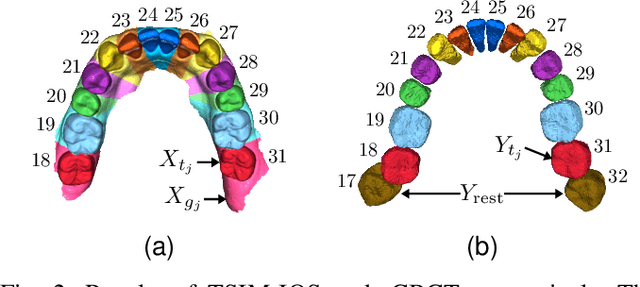
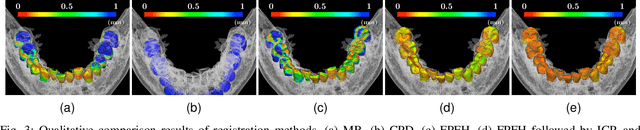
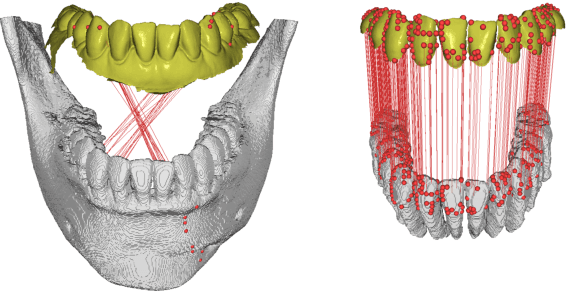
Abstract:We present a fully automated method of integrating intraoral scan (IOS) and dental cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) images into one image by complementing each image's weaknesses. Dental CBCT alone may not be able to delineate precise details of the tooth surface due to limited image resolution and various CBCT artifacts, including metal-induced artifacts. IOS is very accurate for the scanning of narrow areas, but it produces cumulative stitching errors during full-arch scanning. The proposed method is intended not only to compensate the low-quality of CBCT-derived tooth surfaces with IOS, but also to correct the cumulative stitching errors of IOS across the entire dental arch. Moreover, the integration provide both gingival structure of IOS and tooth roots of CBCT in one image. The proposed fully automated method consists of four parts; (i) individual tooth segmentation and identification module for IOS data (TSIM-IOS); (ii) individual tooth segmentation and identification module for CBCT data (TSIM-CBCT); (iii) global-to-local tooth registration between IOS and CBCT; and (iv) stitching error correction of full-arch IOS. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieved landmark and surface distance errors of 0.11mm and 0.30mm, respectively.
Automated 3D cephalometric landmark identification using computerized tomography
Dec 16, 2020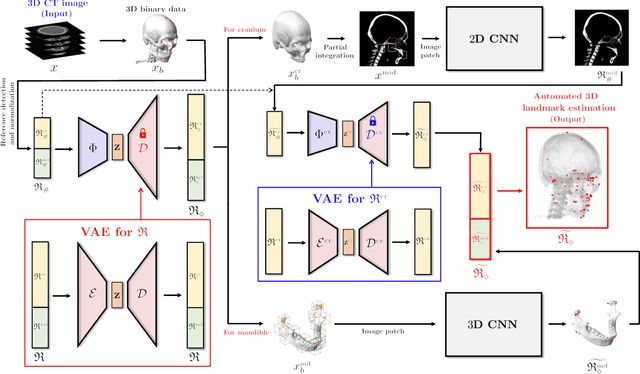
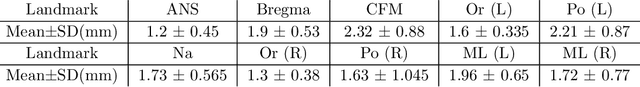
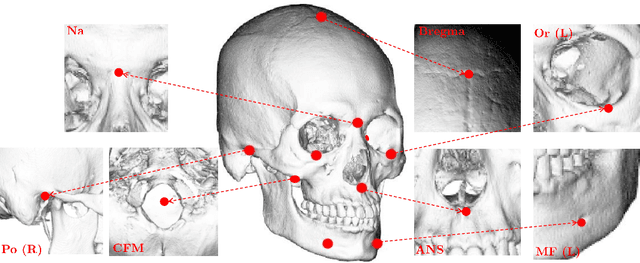
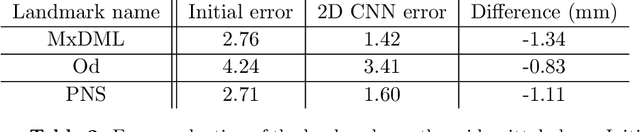
Abstract:Identification of 3D cephalometric landmarks that serve as proxy to the shape of human skull is the fundamental step in cephalometric analysis. Since manual landmarking from 3D computed tomography (CT) images is a cumbersome task even for the trained experts, automatic 3D landmark detection system is in a great need. Recently, automatic landmarking of 2D cephalograms using deep learning (DL) has achieved great success, but 3D landmarking for more than 80 landmarks has not yet reached a satisfactory level, because of the factors hindering machine learning such as the high dimensionality of the input data and limited amount of training data due to ethical restrictions on the use of medical data. This paper presents a semi-supervised DL method for 3D landmarking that takes advantage of anonymized landmark dataset with paired CT data being removed. The proposed method first detects a small number of easy-to-find reference landmarks, then uses them to provide a rough estimation of the entire landmarks by utilizing the low dimensional representation learned by variational autoencoder (VAE). Anonymized landmark dataset is used for training the VAE. Finally, coarse-to-fine detection is applied to the small bounding box provided by rough estimation, using separate strategies suitable for mandible and cranium. For mandibular landmarks, patch-based 3D CNN is applied to the segmented image of the mandible (separated from the maxilla), in order to capture 3D morphological features of mandible associated with the landmarks. We detect 6 landmarks around the condyle all at once, instead of one by one, because they are closely related to each other. For cranial landmarks, we again use VAE-based latent representation for more accurate annotation. In our experiment, the proposed method achieved an averaged 3D point-to-point error of 2.91 mm for 90 landmarks only with 15 paired training data.
Automatic Three-Dimensional Cephalometric Annotation System Using Three-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks
Nov 19, 2018



Abstract:Background: Three-dimensional (3D) cephalometric analysis using computerized tomography data has been rapidly adopted for dysmorphosis and anthropometry. Several different approaches to automatic 3D annotation have been proposed to overcome the limitations of traditional cephalometry. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of our newly-developed system using a deep learning algorithm for automatic 3D cephalometric annotation. Methods: To overcome current technical limitations, some measures were developed to directly annotate 3D human skull data. Our deep learning-based model system mainly consisted of a 3D convolutional neural network and image data resampling. Results: The discrepancies between the referenced and predicted coordinate values in three axes and in 3D distance were calculated to evaluate system accuracy. Our new model system yielded prediction errors of 3.26, 3.18, and 4.81 mm (for three axes) and 7.61 mm (for 3D). Moreover, there was no difference among the landmarks of the three groups, including the midsagittal plane, horizontal plane, and mandible (p>0.05). Conclusion: A new 3D convolutional neural network-based automatic annotation system for 3D cephalometry was developed. The strategies used to implement the system were detailed and measurement results were evaluated for accuracy. Further development of this system is planned for full clinical application of automatic 3D cephalometric annotation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge