Sachin Pathiyan Cherumanal
The Effects of Demographic Instructions on LLM Personas
May 17, 2025Abstract:Social media platforms must filter sexist content in compliance with governmental regulations. Current machine learning approaches can reliably detect sexism based on standardized definitions, but often neglect the subjective nature of sexist language and fail to consider individual users' perspectives. To address this gap, we adopt a perspectivist approach, retaining diverse annotations rather than enforcing gold-standard labels or their aggregations, allowing models to account for personal or group-specific views of sexism. Using demographic data from Twitter, we employ large language models (LLMs) to personalize the identification of sexism.
Towards Investigating Biases in Spoken Conversational Search
Sep 02, 2024


Abstract:Voice-based systems like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri, along with the growing popularity of OpenAI's ChatGPT and Microsoft's Copilot, serve diverse populations, including visually impaired and low-literacy communities. This reflects a shift in user expectations from traditional search to more interactive question-answering models. However, presenting information effectively in voice-only channels remains challenging due to their linear nature. This limitation can impact the presentation of complex queries involving controversial topics with multiple perspectives. Failing to present diverse viewpoints may perpetuate or introduce biases and affect user attitudes. Balancing information load and addressing biases is crucial in designing a fair and effective voice-based system. To address this, we (i) review how biases and user attitude changes have been studied in screen-based web search, (ii) address challenges in studying these changes in voice-based settings like SCS, (iii) outline research questions, and (iv) propose an experimental setup with variables, data, and instruments to explore biases in a voice-based setting like Spoken Conversational Search.
Towards Detecting and Mitigating Cognitive Bias in Spoken Conversational Search
May 21, 2024Abstract:Instruments such as eye-tracking devices have contributed to understanding how users interact with screen-based search engines. However, user-system interactions in audio-only channels -- as is the case for Spoken Conversational Search (SCS) -- are harder to characterize, given the lack of instruments to effectively and precisely capture interactions. Furthermore, in this era of information overload, cognitive bias can significantly impact how we seek and consume information -- especially in the context of controversial topics or multiple viewpoints. This paper draws upon insights from multiple disciplines (including information seeking, psychology, cognitive science, and wearable sensors) to provoke novel conversations in the community. To this end, we discuss future opportunities and propose a framework including multimodal instruments and methods for experimental designs and settings. We demonstrate preliminary results as an example. We also outline the challenges and offer suggestions for adopting this multimodal approach, including ethical considerations, to assist future researchers and practitioners in exploring cognitive biases in SCS.
Walert: Putting Conversational Search Knowledge into Action by Building and Evaluating a Large Language Model-Powered Chatbot
Jan 14, 2024


Abstract:Creating and deploying customized applications is crucial for operational success and enriching user experiences in the rapidly evolving modern business world. A prominent facet of modern user experiences is the integration of chatbots or voice assistants. The rapid evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) has provided a powerful tool to build conversational applications. We present Walert, a customized LLM-based conversational agent able to answer frequently asked questions about computer science degrees and programs at RMIT University. Our demo aims to showcase how conversational information-seeking researchers can effectively communicate the benefits of using best practices to stakeholders interested in developing and deploying LLM-based chatbots. These practices are well-known in our community but often overlooked by practitioners who may not have access to this knowledge. The methodology and resources used in this demo serve as a bridge to facilitate knowledge transfer from experts, address industry professionals' practical needs, and foster a collaborative environment. The data and code of the demo are available at https://github.com/rmit-ir/walert.
Evaluating Fairness in Argument Retrieval
Aug 23, 2021
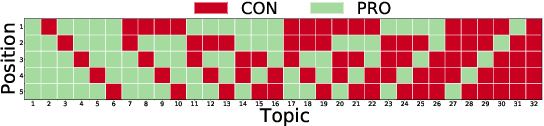
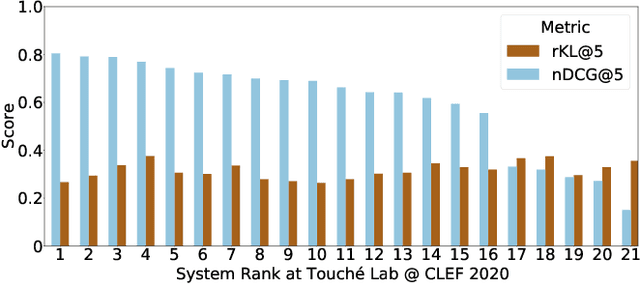
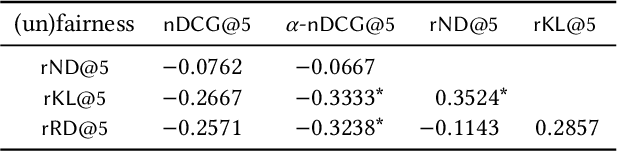
Abstract:Existing commercial search engines often struggle to represent different perspectives of a search query. Argument retrieval systems address this limitation of search engines and provide both positive (PRO) and negative (CON) perspectives about a user's information need on a controversial topic (e.g., climate change). The effectiveness of such argument retrieval systems is typically evaluated based on topical relevance and argument quality, without taking into account the often differing number of documents shown for the argument stances (PRO or CON). Therefore, systems may retrieve relevant passages, but with a biased exposure of arguments. In this work, we analyze a range of non-stochastic fairness-aware ranking and diversity metrics to evaluate the extent to which argument stances are fairly exposed in argument retrieval systems. Using the official runs of the argument retrieval task Touch\'e at CLEF 2020, as well as synthetic data to control the amount and order of argument stances in the rankings, we show that systems with the best effectiveness in terms of topical relevance are not necessarily the most fair or the most diverse in terms of argument stance. The relationships we found between (un)fairness and diversity metrics shed light on how to evaluate group fairness -- in addition to topical relevance -- in argument retrieval settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge