Angel Felipe Magnossão de Paula
The Effects of Demographic Instructions on LLM Personas
May 17, 2025Abstract:Social media platforms must filter sexist content in compliance with governmental regulations. Current machine learning approaches can reliably detect sexism based on standardized definitions, but often neglect the subjective nature of sexist language and fail to consider individual users' perspectives. To address this gap, we adopt a perspectivist approach, retaining diverse annotations rather than enforcing gold-standard labels or their aggregations, allowing models to account for personal or group-specific views of sexism. Using demographic data from Twitter, we employ large language models (LLMs) to personalize the identification of sexism.
AI-UPV at EXIST 2023 -- Sexism Characterization Using Large Language Models Under The Learning with Disagreements Regime
Jul 07, 2023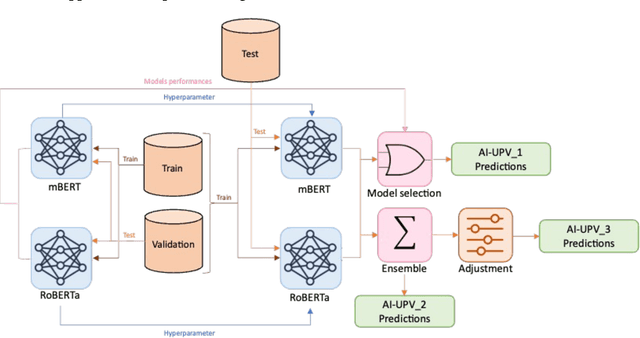
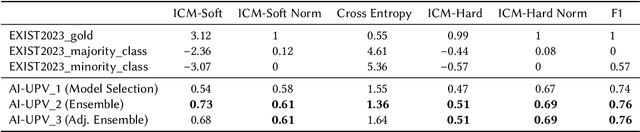
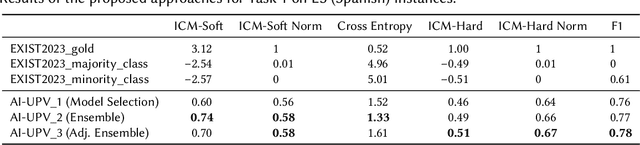
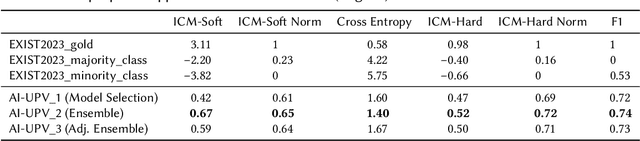
Abstract:With the increasing influence of social media platforms, it has become crucial to develop automated systems capable of detecting instances of sexism and other disrespectful and hateful behaviors to promote a more inclusive and respectful online environment. Nevertheless, these tasks are considerably challenging considering different hate categories and the author's intentions, especially under the learning with disagreements regime. This paper describes AI-UPV team's participation in the EXIST (sEXism Identification in Social neTworks) Lab at CLEF 2023. The proposed approach aims at addressing the task of sexism identification and characterization under the learning with disagreements paradigm by training directly from the data with disagreements, without using any aggregated label. Yet, performances considering both soft and hard evaluations are reported. The proposed system uses large language models (i.e., mBERT and XLM-RoBERTa) and ensemble strategies for sexism identification and classification in English and Spanish. In particular, our system is articulated in three different pipelines. The ensemble approach outperformed the individual large language models obtaining the best performances both adopting a soft and a hard label evaluation. This work describes the participation in all the three EXIST tasks, considering a soft evaluation, it obtained fourth place in Task 2 at EXIST and first place in Task 3, with the highest ICM-Soft of -2.32 and a normalized ICM-Soft of 0.79. The source code of our approaches is publicly available at https://github.com/AngelFelipeMP/Sexism-LLM-Learning-With-Disagreement.
Mitigating Negative Transfer with Task Awareness for Sexism, Hate Speech, and Toxic Language Detection
Jul 07, 2023Abstract:This paper proposes a novelty approach to mitigate the negative transfer problem. In the field of machine learning, the common strategy is to apply the Single-Task Learning approach in order to train a supervised model to solve a specific task. Training a robust model requires a lot of data and a significant amount of computational resources, making this solution unfeasible in cases where data are unavailable or expensive to gather. Therefore another solution, based on the sharing of information between tasks, has been developed: Multi-Task Learning (MTL). Despite the recent developments regarding MTL, the problem of negative transfer has still to be solved. Negative transfer is a phenomenon that occurs when noisy information is shared between tasks, resulting in a drop in performance. This paper proposes a new approach to mitigate the negative transfer problem based on the task awareness concept. The proposed approach results in diminishing the negative transfer together with an improvement of performance over classic MTL solution. Moreover, the proposed approach has been implemented in two unified architectures to detect Sexism, Hate Speech, and Toxic Language in text comments. The proposed architectures set a new state-of-the-art both in EXIST-2021 and HatEval-2019 benchmarks.
Transformers and Ensemble methods: A solution for Hate Speech Detection in Arabic languages
Mar 17, 2023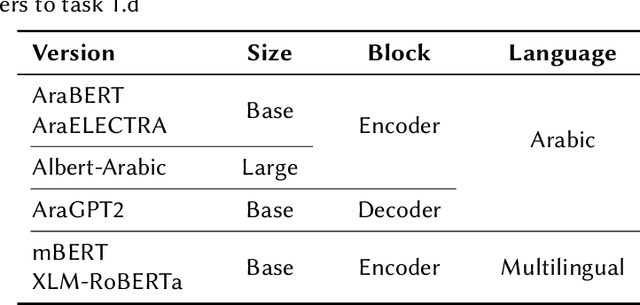
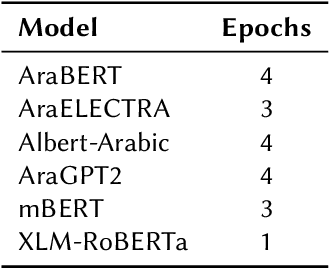
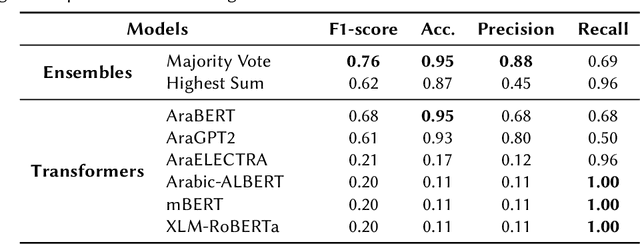
Abstract:This paper describes our participation in the shared task of hate speech detection, which is one of the subtasks of the CERIST NLP Challenge 2022. Our experiments evaluate the performance of six transformer models and their combination using 2 ensemble approaches. The best results on the training set, in a five-fold cross validation scenario, were obtained by using the ensemble approach based on the majority vote. The evaluation of this approach on the test set resulted in an F1-score of 0.60 and an Accuracy of 0.86.
UPV at TREC Health Misinformation Track 2021 Ranking with SBERT and Quality Estimators
Dec 11, 2021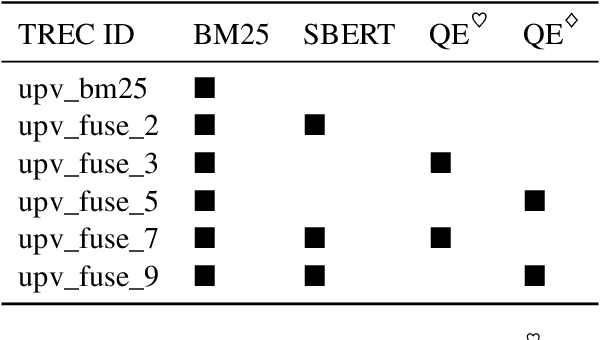


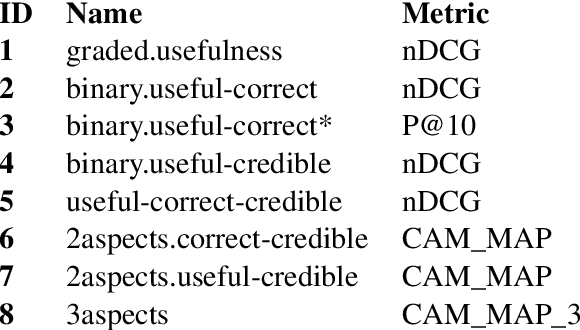
Abstract:Health misinformation on search engines is a significant problem that could negatively affect individuals or public health. To mitigate the problem, TREC organizes a health misinformation track. This paper presents our submissions to this track. We use a BM25 and a domain-specific semantic search engine for retrieving initial documents. Later, we examine a health news schema for quality assessment and apply it to re-rank documents. We merge the scores from the different components by using reciprocal rank fusion. Finally, we discuss the results and conclude with future works.
Sexism Prediction in Spanish and English Tweets Using Monolingual and Multilingual BERT and Ensemble Models
Nov 08, 2021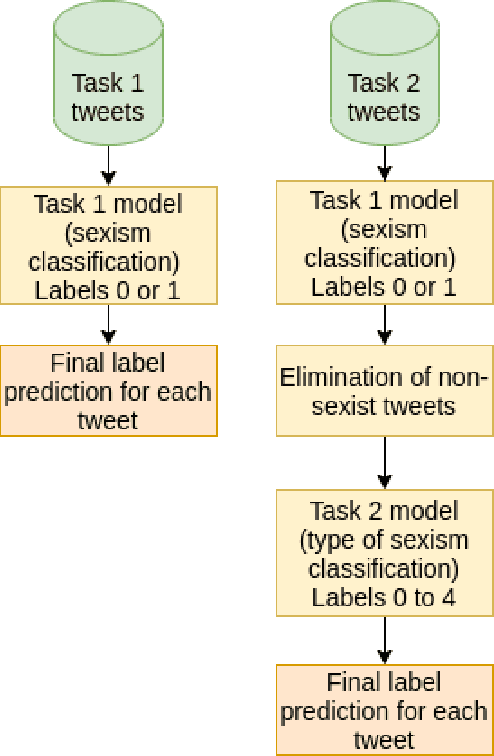
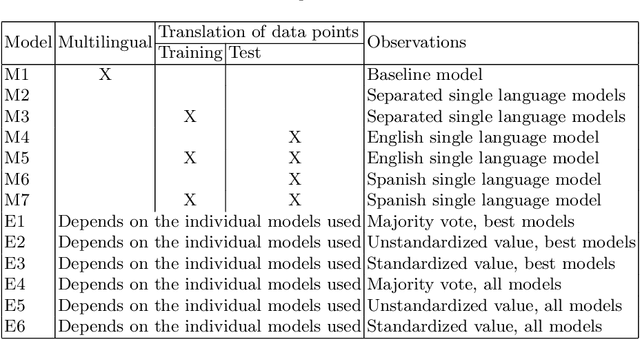
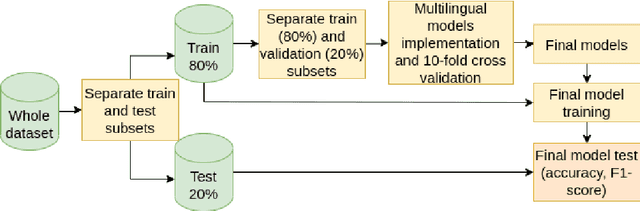
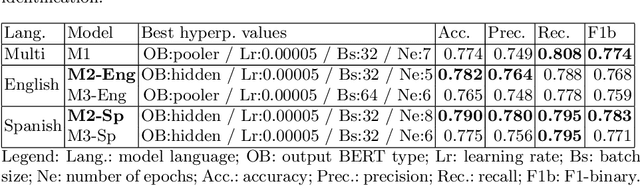
Abstract:The popularity of social media has created problems such as hate speech and sexism. The identification and classification of sexism in social media are very relevant tasks, as they would allow building a healthier social environment. Nevertheless, these tasks are considerably challenging. This work proposes a system to use multilingual and monolingual BERT and data points translation and ensemble strategies for sexism identification and classification in English and Spanish. It was conducted in the context of the sEXism Identification in Social neTworks shared 2021 (EXIST 2021) task, proposed by the Iberian Languages Evaluation Forum (IberLEF). The proposed system and its main components are described, and an in-depth hyperparameters analysis is conducted. The main results observed were: (i) the system obtained better results than the baseline model (multilingual BERT); (ii) ensemble models obtained better results than monolingual models; and (iii) an ensemble model considering all individual models and the best standardized values obtained the best accuracies and F1-scores for both tasks. This work obtained first place in both tasks at EXIST, with the highest accuracies (0.780 for task 1 and 0.658 for task 2) and F1-scores (F1-binary of 0.780 for task 1 and F1-macro of 0.579 for task 2).
AI-UPV at IberLEF-2021 DETOXIS task: Toxicity Detection in Immigration-Related Web News Comments Using Transformers and Statistical Models
Nov 08, 2021
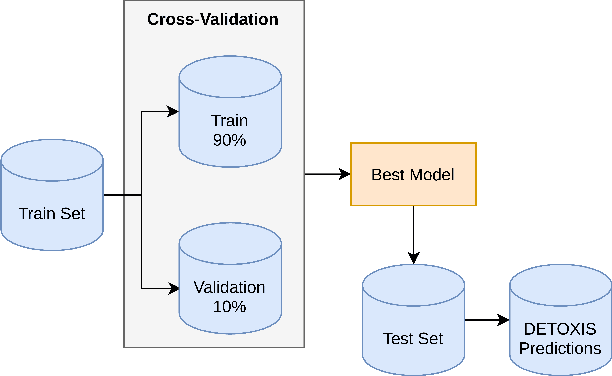
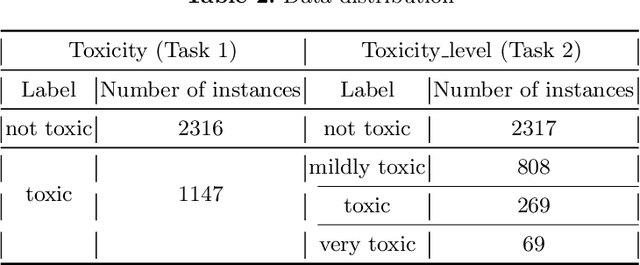

Abstract:This paper describes our participation in the DEtection of TOXicity in comments In Spanish (DETOXIS) shared task 2021 at the 3rd Workshop on Iberian Languages Evaluation Forum. The shared task is divided into two related classification tasks: (i) Task 1: toxicity detection and; (ii) Task 2: toxicity level detection. They focus on the xenophobic problem exacerbated by the spread of toxic comments posted in different online news articles related to immigration. One of the necessary efforts towards mitigating this problem is to detect toxicity in the comments. Our main objective was to implement an accurate model to detect xenophobia in comments about web news articles within the DETOXIS shared task 2021, based on the competition's official metrics: the F1-score for Task 1 and the Closeness Evaluation Metric (CEM) for Task 2. To solve the tasks, we worked with two types of machine learning models: (i) statistical models and (ii) Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding (BERT) models. We obtained our best results in both tasks using BETO, an BERT model trained on a big Spanish corpus. We obtained the 3rd place in Task 1 official ranking with the F1-score of 0.5996, and we achieved the 6th place in Task 2 official ranking with the CEM of 0.7142. Our results suggest: (i) BERT models obtain better results than statistical models for toxicity detection in text comments; (ii) Monolingual BERT models have an advantage over multilingual BERT models in toxicity detection in text comments in their pre-trained language.
Unified and Multilingual Author Profiling for Detecting Haters
Sep 19, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents a unified user profiling framework to identify hate speech spreaders by processing their tweets regardless of the language. The framework encodes the tweets with sentence transformers and applies an attention mechanism to select important tweets for learning user profiles. Furthermore, the attention layer helps to explain why a user is a hate speech spreader by producing attention weights at both token and post level. Our proposed model outperformed the state-of-the-art multilingual transformer models.
* 9 pages, 2 figures, see the original paper: http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2936/paper-157.pdf
UPV at CheckThat! 2021: Mitigating Cultural Differences for Identifying Multilingual Check-worthy Claims
Sep 19, 2021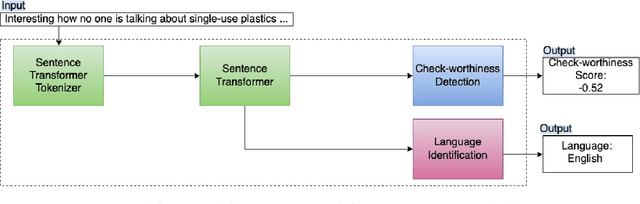
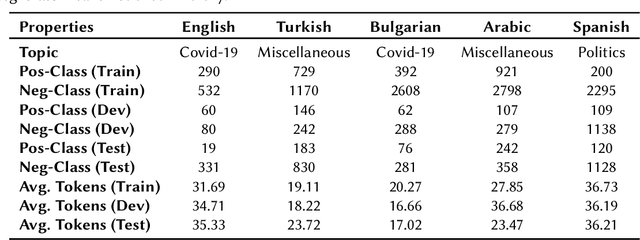
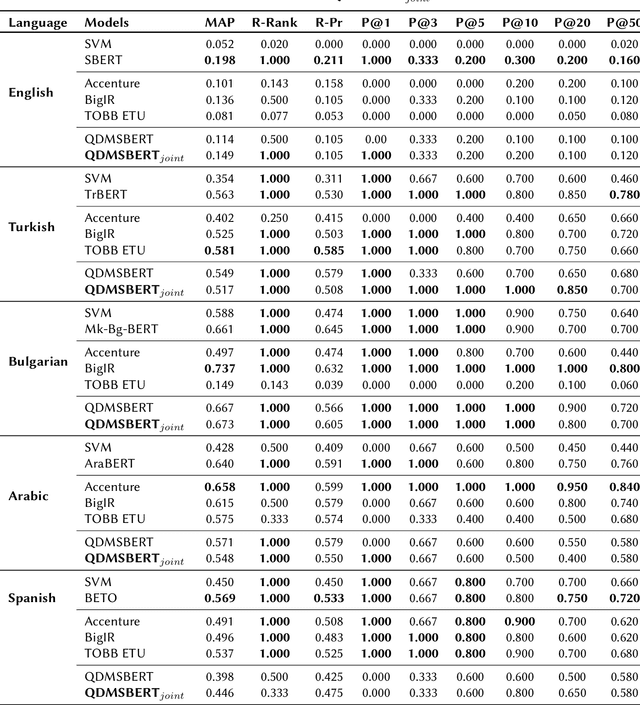
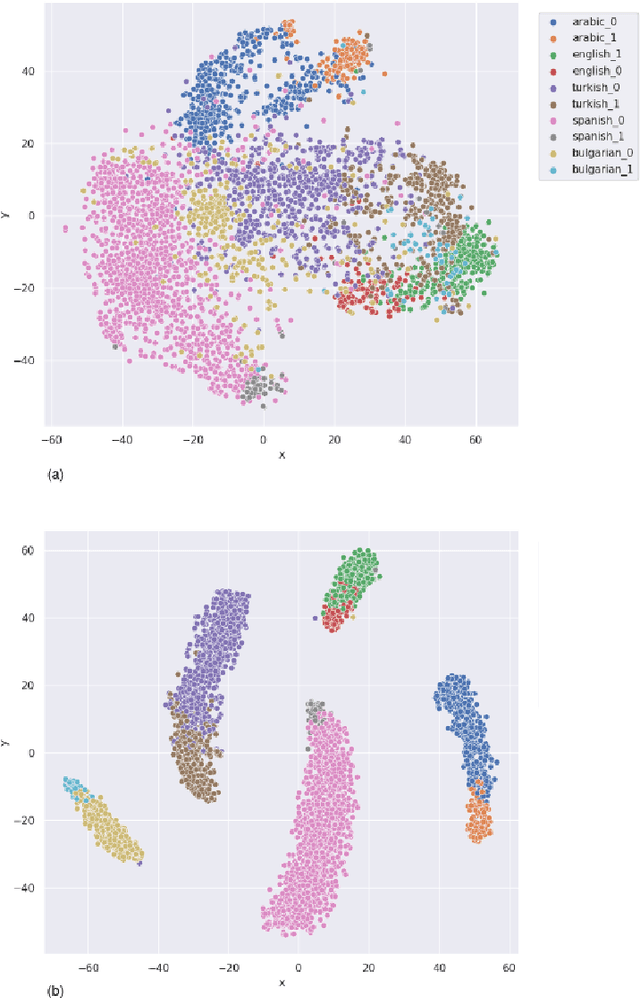
Abstract:Identifying check-worthy claims is often the first step of automated fact-checking systems. Tackling this task in a multilingual setting has been understudied. Encoding inputs with multilingual text representations could be one approach to solve the multilingual check-worthiness detection. However, this approach could suffer if cultural bias exists within the communities on determining what is check-worthy.In this paper, we propose a language identification task as an auxiliary task to mitigate unintended bias.With this purpose, we experiment joint training by using the datasets from CLEF-2021 CheckThat!, that contain tweets in English, Arabic, Bulgarian, Spanish and Turkish. Our results show that joint training of language identification and check-worthy claim detection tasks can provide performance gains for some of the selected languages.
* 11 pages, 2 figures. Link to the original paper: http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2936/paper-36.pdf
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge