Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay
A Survey of using Large Language Models for Generating Infrastructure as Code
Mar 30, 2024Abstract:Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a revolutionary approach which has gained significant prominence in the Industry. IaC manages and provisions IT infrastructure using machine-readable code by enabling automation, consistency across the environments, reproducibility, version control, error reduction and enhancement in scalability. However, IaC orchestration is often a painstaking effort which requires specialised skills as well as a lot of manual effort. Automation of IaC is a necessity in the present conditions of the Industry and in this survey, we study the feasibility of applying Large Language Models (LLM) to address this problem. LLMs are large neural network-based models which have demonstrated significant language processing abilities and shown to be capable of following a range of instructions within a broad scope. Recently, they have also been adapted for code understanding and generation tasks successfully, which makes them a promising choice for the automatic generation of IaC configurations. In this survey, we delve into the details of IaC, usage of IaC in different platforms, their challenges, LLMs in terms of code-generation aspects and the importance of LLMs in IaC along with our own experiments. Finally, we conclude by presenting the challenges in this area and highlighting the scope for future research.
A Comparative Study of Text Embedding Models for Semantic Text Similarity in Bug Reports
Aug 17, 2023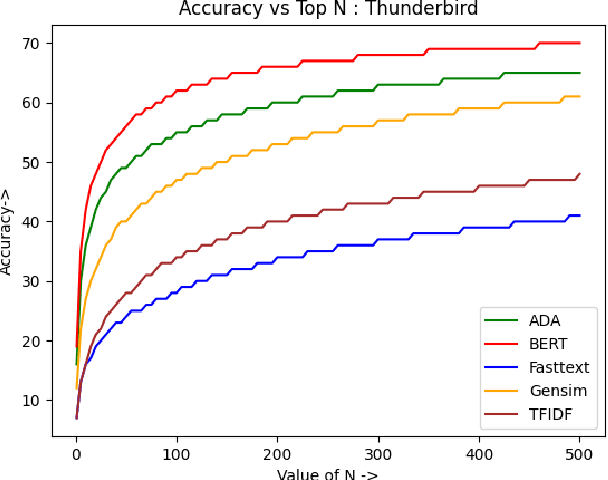
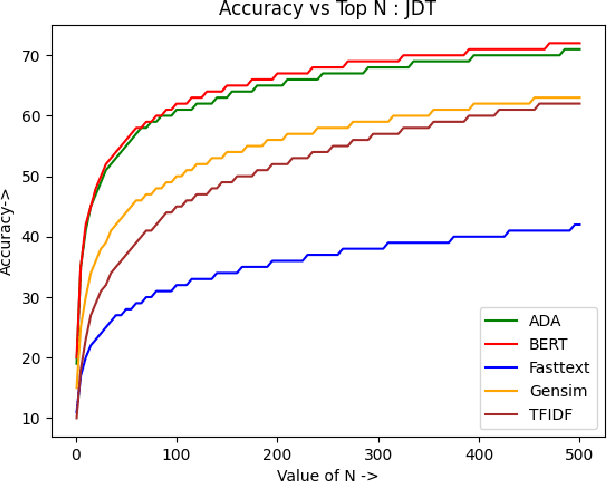
Abstract:Bug reports are an essential aspect of software development, and it is crucial to identify and resolve them quickly to ensure the consistent functioning of software systems. Retrieving similar bug reports from an existing database can help reduce the time and effort required to resolve bugs. In this paper, we compared the effectiveness of semantic textual similarity methods for retrieving similar bug reports based on a similarity score. We explored several embedding models such as TF-IDF (Baseline), FastText, Gensim, BERT, and ADA. We used the Software Defects Data containing bug reports for various software projects to evaluate the performance of these models. Our experimental results showed that BERT generally outperformed the rest of the models regarding recall, followed by ADA, Gensim, FastText, and TFIDF. Our study provides insights into the effectiveness of different embedding methods for retrieving similar bug reports and highlights the impact of selecting the appropriate one for this task. Our code is available on GitHub.
Multiclass Classification of Cervical Cancer Tissues by Hidden Markov Model
Dec 04, 2016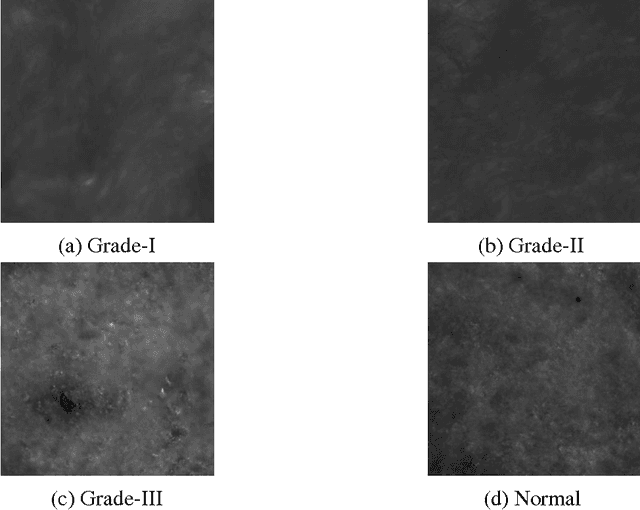

Abstract:In this paper, we report a hidden Markov model based multiclass classification of cervical cancer tissues. This model has been validated directly over time series generated by the medium refractive index fluctuations extracted from differential interference contrast images of healthy and different stages of cancer tissues. The method shows promising results for multiclass classification with higher accuracy.
Application of S-Transform on Hyper kurtosis based Modified Duo Histogram Equalized DIC images for Pre-cancer Detection
Apr 30, 2015Abstract:Our proposed hyper kurtosis based histogram equalized DIC images enhances the contrast by preserving the brightness. The evolution and development of precancerous activity among tissues are studied through S-transform (ST). The significant variations of amplitude spectra can be observed due to increased medium roughness from normal tissue were observed in time-frequency domain. The randomness and inhomogeneity of the tissue structures among human normal and different grades of DIC tissues is recognized by ST based timefrequency analysis. This study offers a simpler and better way to recognize the substantial changes among different stages of DIC tissues, which are reflected by spatial information containing within the inhomogeneity structures of different types of tissue.
A comparative study between proposed Hyper Kurtosis based Modified Duo-Histogram Equalization (HKMDHE) and Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) for Contrast Enhancement Purpose of Low Contrast Human Brain CT scan images
Apr 07, 2015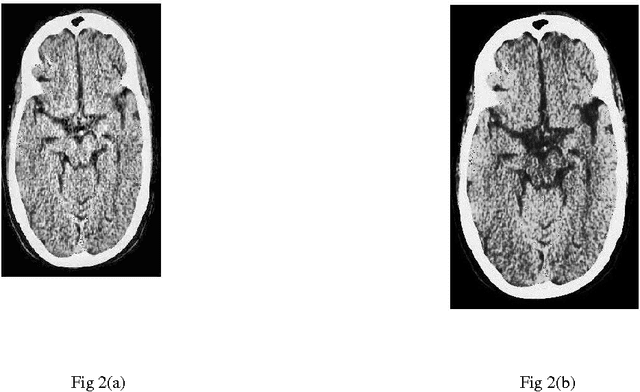
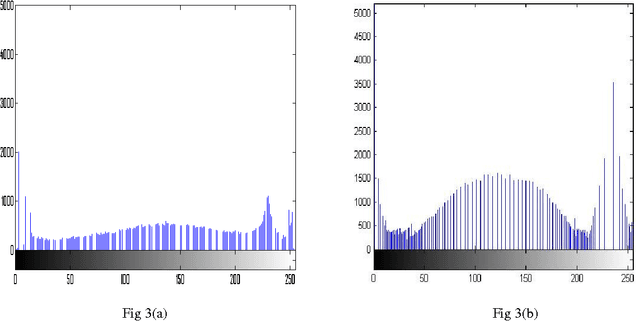

Abstract:In this paper, a comparative study between proposed hyper kurtosis based modified duo-histogram equalization (HKMDHE) algorithm and contrast limited adaptive histogram enhancement (CLAHE) has been presented for the implementation of contrast enhancement and brightness preservation of low contrast human brain CT scan images. In HKMDHE algorithm, contrast enhancement is done on the hyper-kurtosis based application. The results are very promising of proposed HKMDHE technique with improved PSNR values and lesser AMMBE values than CLAHE technique.
Wavelet based approach for tissue fractal parameter measurement: Pre cancer detection
Mar 21, 2015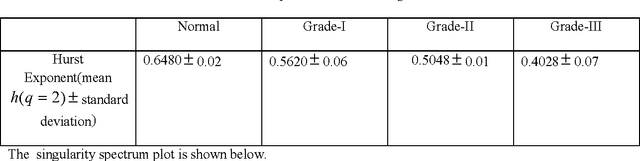
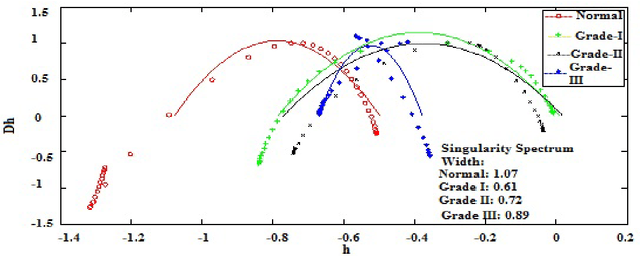
Abstract:In this paper, we have carried out the detail studies of pre-cancer by wavelet coherency and multifractal based detrended fluctuation analysis (MFDFA) on differential interference contrast (DIC) images of stromal region among different grades of pre-cancer tissues. Discrete wavelet transform (DWT) through Daubechies basis has been performed for identifying fluctuations over polynomial trends for clear characterization and differentiation of tissues. Wavelet coherence plots are performed for identifying the level of correlation in time scale plane between normal and various grades of DIC samples. Applying MFDFA on refractive index variations of cervical tissues, we have observed that the values of Hurst exponent (correlation) decreases from healthy (normal) to pre-cancer tissues. The width of singularity spectrum has a sudden degradation at grade-I in comparison of healthy (normal) tissue but later on it increases as cancer progresses from grade-II to grade-III.
Diagnosing Heterogeneous Dynamics for CT Scan Images of Human Brain in Wavelet and MFDFA domain
Mar 12, 2015Abstract:CT scan images of human brain of a particular patient in different cross sections are taken, on which wavelet transform and multi-fractal analysis are applied. The vertical and horizontal unfolding of images are done before analyzing these images. A systematic investigation of de-noised CT scan images of human brain in different cross-sections are carried out through wavelet normalized energy and wavelet semi-log plots, which clearly points out the mismatch between results of vertical and horizontal unfolding. The mismatch of results confirms the heterogeneity in spatial domain. Using the multi-fractal de-trended fluctuation analysis (MFDFA), the mismatch between the values of Hurst exponent and width of singularity spectrum by vertical and horizontal unfolding confirms the same.
Wavelet and Fast Fourier Transform based analysis of Solar Image
Dec 10, 2013Abstract:Both of Wavelet and Fast Fourier Transform are strong signal processing tools in the field of Data Analysis. In this paper fast fourier transform (FFT) and Wavelet Transform are employed to observe some important features of Solar image (December, 2004). We have tried to find out the periodicity and coherence of different sections of the solar image. We plotted the distribution of energy in solar surface by analyzing the solar image with scalograms and 3D-coefficient plots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge