Saahil Ognawala
Jina CLIP: Your CLIP Model Is Also Your Text Retriever
May 30, 2024



Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) is widely used to train models to align images and texts in a common embedding space by mapping them to fixed-sized vectors. These models are key to multimodal information retrieval and related tasks. However, CLIP models generally underperform in text-only tasks compared to specialized text models. This creates inefficiencies for information retrieval systems that keep separate embeddings and models for text-only and multimodal tasks. We propose a novel, multi-task contrastive training method to address this issue, which we use to train the jina-clip-v1 model to achieve the state-of-the-art performance on both text-image and text-text retrieval tasks.
Multi-Task Contrastive Learning for 8192-Token Bilingual Text Embeddings
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a novel suite of state-of-the-art bilingual text embedding models that are designed to support English and another target language. These models are capable of processing lengthy text inputs with up to 8192 tokens, making them highly versatile for a range of natural language processing tasks such as text retrieval, clustering, and semantic textual similarity (STS) calculations. By focusing on bilingual models and introducing a unique multi-task learning objective, we have significantly improved the model performance on STS tasks, which outperforms the capabilities of existing multilingual models in both target language understanding and cross-lingual evaluation tasks. Moreover, our bilingual models are more efficient, requiring fewer parameters and less memory due to their smaller vocabulary needs. Furthermore, we have expanded the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB) to include benchmarks for German and Spanish embedding models. This integration aims to stimulate further research and advancement in text embedding technologies for these languages.
ML-based tactile sensor calibration: A universal approach
Jun 21, 2016



Abstract:We study the responses of two tactile sensors, the fingertip sensor from the iCub and the BioTac under different external stimuli. The question of interest is to which degree both sensors i) allow the estimation of force exerted on the sensor and ii) enable the recognition of differing degrees of curvature. Making use of a force controlled linear motor affecting the tactile sensors we acquire several high-quality data sets allowing the study of both sensors under exactly the same conditions. We also examined the structure of the representation of tactile stimuli in the recorded tactile sensor data using t-SNE embeddings. The experiments show that both the iCub and the BioTac excel in different settings.
Regularizing Recurrent Networks - On Injected Noise and Norm-based Methods
Oct 21, 2014


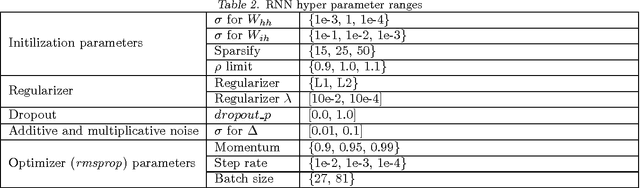
Abstract:Advancements in parallel processing have lead to a surge in multilayer perceptrons' (MLP) applications and deep learning in the past decades. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) give additional representational power to feedforward MLPs by providing a way to treat sequential data. However, RNNs are hard to train using conventional error backpropagation methods because of the difficulty in relating inputs over many time-steps. Regularization approaches from MLP sphere, like dropout and noisy weight training, have been insufficiently applied and tested on simple RNNs. Moreover, solutions have been proposed to improve convergence in RNNs but not enough to improve the long term dependency remembering capabilities thereof. In this study, we aim to empirically evaluate the remembering and generalization ability of RNNs on polyphonic musical datasets. The models are trained with injected noise, random dropout, norm-based regularizers and their respective performances compared to well-initialized plain RNNs and advanced regularization methods like fast-dropout. We conclude with evidence that training with noise does not improve performance as conjectured by a few works in RNN optimization before ours.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge