Saad Hassan
Towards an AI-Driven Video-Based American Sign Language Dictionary: Exploring Design and Usage Experience with Learners
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:Searching for unfamiliar American Sign Language (ASL) signs is challenging for learners because, unlike spoken languages, they cannot type a text-based query to look up an unfamiliar sign. Advances in isolated sign recognition have enabled the creation of video-based dictionaries, allowing users to submit a video and receive a list of the closest matching signs. Previous HCI research using Wizard-of-Oz prototypes has explored interface designs for ASL dictionaries. Building on these studies, we incorporate their design recommendations and leverage state-of-the-art sign-recognition technology to develop an automated video-based dictionary. We also present findings from an observational study with twelve novice ASL learners who used this dictionary during video-comprehension and question-answering tasks. Our results address human-AI interaction challenges not covered in previous WoZ research, including recording and resubmitting signs, unpredictable outputs, system latency, and privacy concerns. These insights offer guidance for designing and deploying video-based ASL dictionary systems.
TabulaTime: A Novel Multimodal Deep Learning Framework for Advancing Acute Coronary Syndrome Prediction through Environmental and Clinical Data Integration
Feb 24, 2025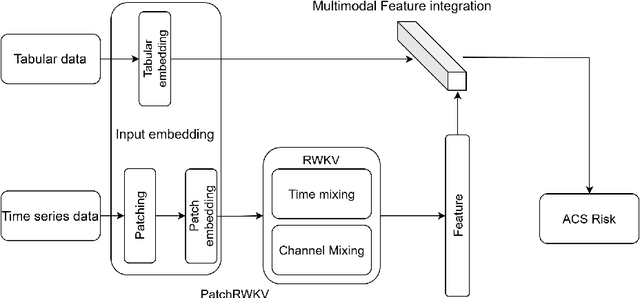

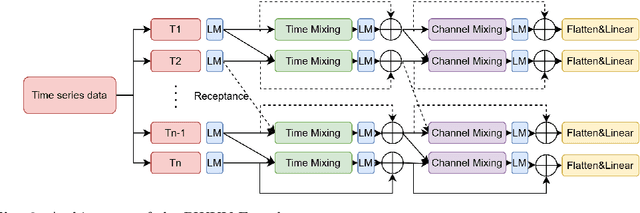

Abstract:Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS), including ST-segment elevation myocardial infarctions (STEMI) and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarctions (NSTEMI), remain a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Traditional cardiovascular risk scores rely primarily on clinical data, often overlooking environmental influences like air pollution that significantly impact heart health. Moreover, integrating complex time-series environmental data with clinical records is challenging. We introduce TabulaTime, a multimodal deep learning framework that enhances ACS risk prediction by combining clinical risk factors with air pollution data. TabulaTime features three key innovations: First, it integrates time-series air pollution data with clinical tabular data to improve prediction accuracy. Second, its PatchRWKV module automatically extracts complex temporal patterns, overcoming limitations of traditional feature engineering while maintaining linear computational complexity. Third, attention mechanisms enhance interpretability by revealing interactions between clinical and environmental factors. Experimental results show that TabulaTime improves prediction accuracy by over 20% compared to conventional models such as CatBoost, Random Forest, and LightGBM, with air pollution data alone contributing over a 10% improvement. Feature importance analysis identifies critical predictors including previous angina, systolic blood pressure, PM10, and NO2. Overall, TabulaTime bridges clinical and environmental insights, supporting personalized prevention strategies and informing public health policies to mitigate ACS risk.
FSboard: Over 3 million characters of ASL fingerspelling collected via smartphones
Jul 22, 2024Abstract:Progress in machine understanding of sign languages has been slow and hampered by limited data. In this paper, we present FSboard, an American Sign Language fingerspelling dataset situated in a mobile text entry use case, collected from 147 paid and consenting Deaf signers using Pixel 4A selfie cameras in a variety of environments. Fingerspelling recognition is an incomplete solution that is only one small part of sign language translation, but it could provide some immediate benefit to Deaf/Hard of Hearing signers as more broadly capable technology develops. At >3 million characters in length and >250 hours in duration, FSboard is the largest fingerspelling recognition dataset to date by a factor of >10x. As a simple baseline, we finetune 30 Hz MediaPipe Holistic landmark inputs into ByT5-Small and achieve 11.1% Character Error Rate (CER) on a test set with unique phrases and signers. This quality degrades gracefully when decreasing frame rate and excluding face/body landmarks: plausible optimizations to help models run on device in real time.
ASL-Homework-RGBD Dataset: An annotated dataset of 45 fluent and non-fluent signers performing American Sign Language homeworks
Jul 08, 2022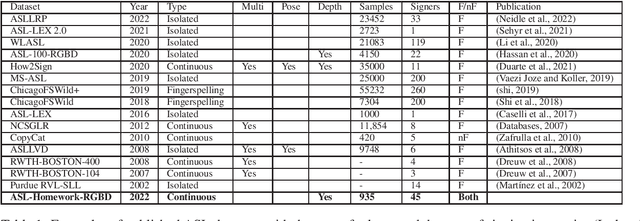
Abstract:We are releasing a dataset containing videos of both fluent and non-fluent signers using American Sign Language (ASL), which were collected using a Kinect v2 sensor. This dataset was collected as a part of a project to develop and evaluate computer vision algorithms to support new technologies for automatic detection of ASL fluency attributes. A total of 45 fluent and non-fluent participants were asked to perform signing homework assignments that are similar to the assignments used in introductory or intermediate level ASL courses. The data is annotated to identify several aspects of signing including grammatical features and non-manual markers. Sign language recognition is currently very data-driven and this dataset can support the design of recognition technologies, especially technologies that can benefit ASL learners. This dataset might also be interesting to ASL education researchers who want to contrast fluent and non-fluent signing.
Using BERT Embeddings to Model Word Importance in Conversational Transcripts for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Users
Jun 24, 2022



Abstract:Deaf and hard of hearing individuals regularly rely on captioning while watching live TV. Live TV captioning is evaluated by regulatory agencies using various caption evaluation metrics. However, caption evaluation metrics are often not informed by preferences of DHH users or how meaningful the captions are. There is a need to construct caption evaluation metrics that take the relative importance of words in a transcript into account. We conducted correlation analysis between two types of word embeddings and human-annotated labeled word-importance scores in existing corpus. We found that normalized contextualized word embeddings generated using BERT correlated better with manually annotated importance scores than word2vec-based word embeddings. We make available a pairing of word embeddings and their human-annotated importance scores. We also provide proof-of-concept utility by training word importance models, achieving an F1-score of 0.57 in the 6-class word importance classification task.
Unpacking the Interdependent Systems of Discrimination: Ableist Bias in NLP Systems through an Intersectional Lens
Oct 01, 2021



Abstract:Much of the world's population experiences some form of disability during their lifetime. Caution must be exercised while designing natural language processing (NLP) systems to prevent systems from inadvertently perpetuating ableist bias against people with disabilities, i.e., prejudice that favors those with typical abilities. We report on various analyses based on word predictions of a large-scale BERT language model. Statistically significant results demonstrate that people with disabilities can be disadvantaged. Findings also explore overlapping forms of discrimination related to interconnected gender and race identities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge