S L Happy
How Unique Is a Face: An Investigative Study
Feb 09, 2021



Abstract:Face recognition has been widely accepted as a means of identification in applications ranging from border control to security in the banking sector. Surprisingly, while widely accepted, we still lack the understanding of uniqueness or distinctiveness of faces as biometric modality. In this work, we study the impact of factors such as image resolution, feature representation, database size, age and gender on uniqueness denoted by the Kullback-Leibler divergence between genuine and impostor distributions. Towards understanding the impact, we present experimental results on the datasets AT&T, LFW, IMDb-Face, as well as ND-TWINS, with the feature extraction algorithms VGGFace, VGG16, ResNet50, InceptionV3, MobileNet and DenseNet121, that reveal the quantitative impact of the named factors. While these are early results, our findings indicate the need for a better understanding of the concept of biometric uniqueness and its implication on face recognition.
SemI2I: Semantically Consistent Image-to-Image Translation for Domain Adaptation of Remote Sensing Data
Feb 21, 2020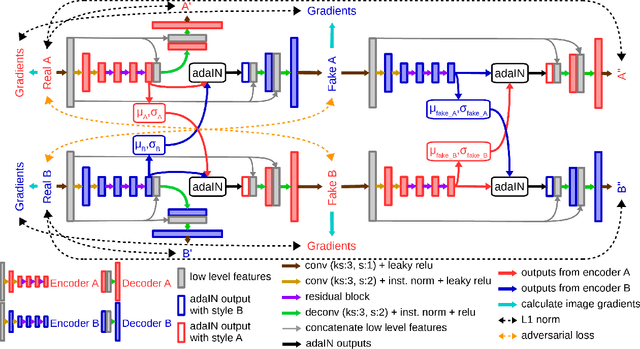
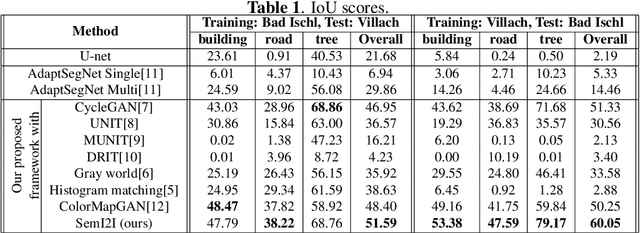

Abstract:Although convolutional neural networks have been proven to be an effective tool to generate high quality maps from remote sensing images, their performance significantly deteriorates when there exists a large domain shift between training and test data. To address this issue, we propose a new data augmentation approach that transfers the style of test data to training data using generative adversarial networks. Our semantic segmentation framework consists in first training a U-net from the real training data and then fine-tuning it on the test stylized fake training data generated by the proposed approach. Our experimental results prove that our framework outperforms the existing domain adaptation methods.
ColorMapGAN: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation Using Color Mapping Generative Adversarial Networks
Jul 30, 2019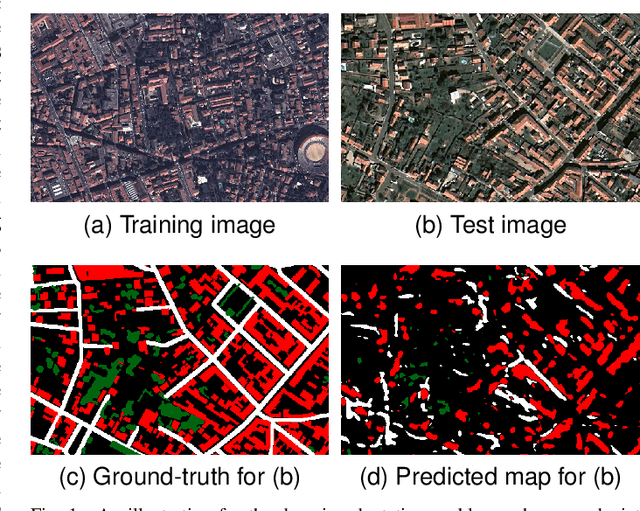
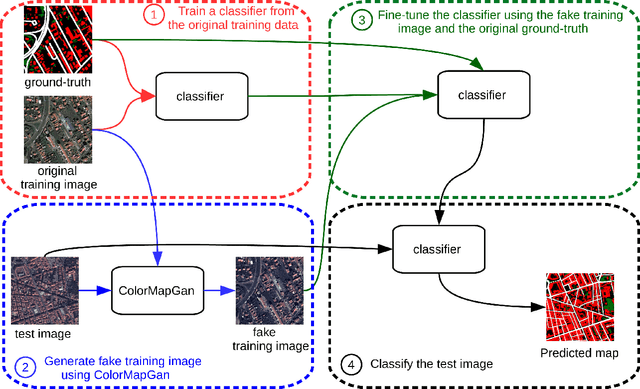
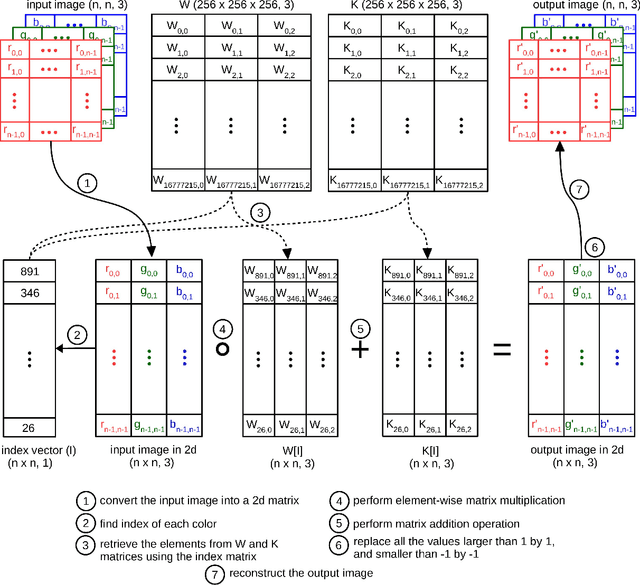
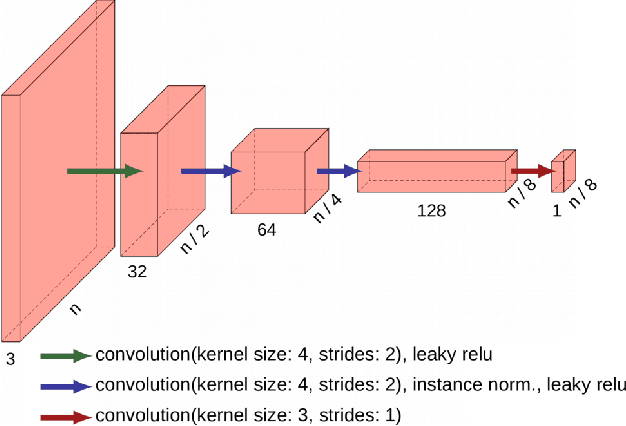
Abstract:Due to the various reasons such as atmospheric effects and differences in acquisition, it is often the case that there exists a large difference between spectral bands of satellite images collected from different geographic locations. The large shift between spectral distributions of training and test data causes the current state of the art supervised learning approaches to output poor maps. We present a novel end to end semantic segmentation framework that is robust to such shift. The key component of the proposed framework is Color Mapping Generative Adversarial Networks (ColorMapGAN), which can generate fake training images that are semantically exactly the same as training images, but whose spectral distribution is similar to the distribution of the test images. We then use the fake images and the ground-truth for the training images to fine-tune the already trained classifier. Contrary to the existing Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), the generator in ColorMapGAN does not have any convolutional or pooling layers. It learns to transform the colors of the training data to the colors of the test data by performing only one element-wise matrix multiplication and one matrix addition operations. Thanks to the architecturally simple but powerful design of ColorMapGAN, the proposed framework outperforms the existing approaches with a large margin in terms of both accuracy and computational complexity.
Spatial-Spectral Regularized Local Scaling Cut for Dimensionality Reduction in Hyperspectral Image Classification
Dec 07, 2018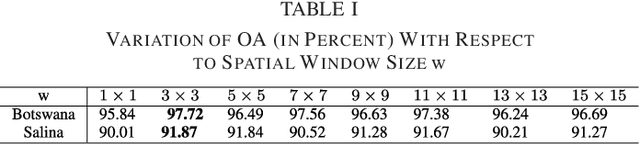
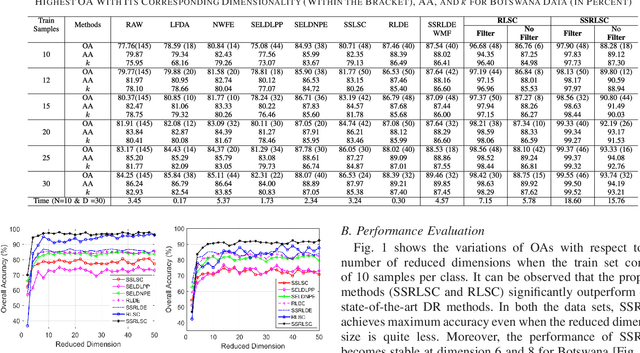
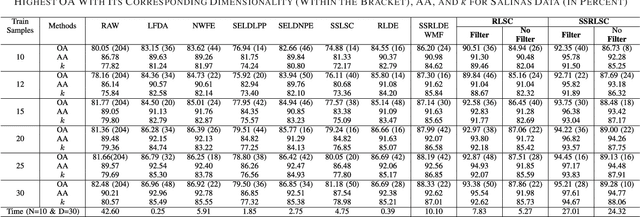
Abstract:Dimensionality reduction (DR) methods have attracted extensive attention to provide discriminative information and reduce the computational burden of the hyperspectral image (HSI) classification. However, the DR methods face many challenges due to limited training samples with high dimensional spectra. To address this issue, a graph-based spatial and spectral regularized local scaling cut (SSRLSC) for DR of HSI data is proposed. The underlying idea of the proposed method is to utilize the information from both the spectral and spatial domains to achieve better classification accuracy than its spectral domain counterpart. In SSRLSC, a guided filter is initially used to smoothen and homogenize the pixels of the HSI data in order to preserve the pixel consistency. This is followed by generation of between-class and within-class dissimilarity matrices in both spectral and spatial domains by regularized local scaling cut (RLSC) and neighboring pixel local scaling cut (NPLSC) respectively. Finally, we obtain the projection matrix by optimizing the updated spatial-spectral between-class and total-class dissimilarity. The effectiveness of the proposed DR algorithm is illustrated with two popular real-world HSI datasets.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:1811.08223
A Trace Lasso Regularized L1-norm Graph Cut for Highly Correlated Noisy Hyperspectral Image
Jul 22, 2018


Abstract:This work proposes an adaptive trace lasso regularized L1-norm based graph cut method for dimensionality reduction of Hyperspectral images, called as `Trace Lasso-L1 Graph Cut' (TL-L1GC). The underlying idea of this method is to generate the optimal projection matrix by considering both the sparsity as well as the correlation of the data samples. The conventional L2-norm used in the objective function is sensitive to noise and outliers. Therefore, in this work L1-norm is utilized as a robust alternative to L2-norm. Besides, for further improvement of the results, we use a penalty function of trace lasso with the L1GC method. It adaptively balances the L2-norm and L1-norm simultaneously by considering the data correlation along with the sparsity. We obtain the optimal projection matrix by maximizing the ratio of between-class dispersion to within-class dispersion using L1-norm with trace lasso as the penalty. Furthermore, an iterative procedure for this TL-L1GC method is proposed to solve the optimization function. The effectiveness of this proposed method is evaluated on two benchmark HSI datasets.
A Supervised Geometry-Aware Mapping Approach for Classification of Hyperspectral Images
Jul 07, 2018



Abstract:The lack of proper class discrimination among the Hyperspectral (HS) data points poses a potential challenge in HS classification. To address this issue, this paper proposes an optimal geometry-aware transformation for enhancing the classification accuracy. The underlying idea of this method is to obtain a linear projection matrix by solving a nonlinear objective function based on the intrinsic geometrical structure of the data. The objective function is constructed to quantify the discrimination between the points from dissimilar classes on the projected data space. Then the obtained projection matrix is used to linearly map the data to more discriminative space. The effectiveness of the proposed transformation is illustrated with three benchmark real-world HS data sets. The experiments reveal that the classification and dimensionality reduction methods on the projected discriminative space outperform their counterpart in the original space.
Graph Scaling Cut with L1-Norm for Classification of Hyperspectral Images
Sep 09, 2017


Abstract:In this paper, we propose an L1 normalized graph based dimensionality reduction method for Hyperspectral images, called as L1-Scaling Cut (L1-SC). The underlying idea of this method is to generate the optimal projection matrix by retaining the original distribution of the data. Though L2-norm is generally preferred for computation, it is sensitive to noise and outliers. However, L1-norm is robust to them. Therefore, we obtain the optimal projection matrix by maximizing the ratio of between-class dispersion to within-class dispersion using L1-norm. Furthermore, an iterative algorithm is described to solve the optimization problem. The experimental results of the HSI classification confirm the effectiveness of the proposed L1-SC method on both noisy and noiseless data.
An Effective Feature Selection Method Based on Pair-Wise Feature Proximity for High Dimensional Low Sample Size Data
Aug 08, 2017



Abstract:Feature selection has been studied widely in the literature. However, the efficacy of the selection criteria for low sample size applications is neglected in most cases. Most of the existing feature selection criteria are based on the sample similarity. However, the distance measures become insignificant for high dimensional low sample size (HDLSS) data. Moreover, the variance of a feature with a few samples is pointless unless it represents the data distribution efficiently. Instead of looking at the samples in groups, we evaluate their efficiency based on pairwise fashion. In our investigation, we noticed that considering a pair of samples at a time and selecting the features that bring them closer or put them far away is a better choice for feature selection. Experimental results on benchmark data sets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method with low sample size, which outperforms many other state-of-the-art feature selection methods.
An Unsupervised Approach for Overlapping Cervical Cell Cytoplasm Segmentation
Feb 17, 2017
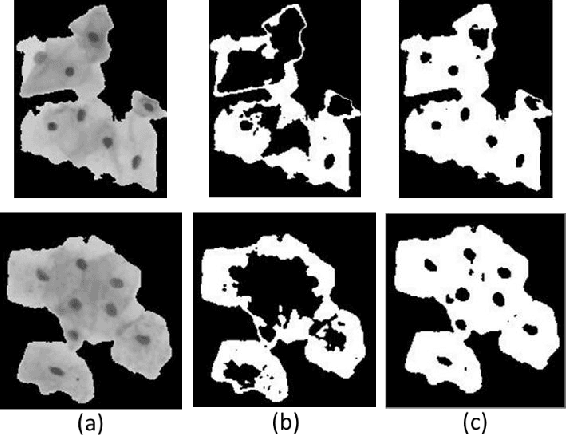
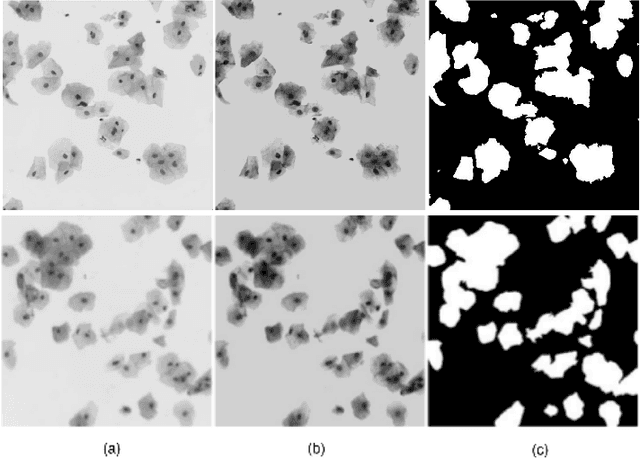


Abstract:The poor contrast and the overlapping of cervical cell cytoplasm are the major issues in the accurate segmentation of cervical cell cytoplasm. This paper presents an automated unsupervised cytoplasm segmentation approach which can effectively find the cytoplasm boundaries in overlapping cells. The proposed approach first segments the cell clumps from the cervical smear image and detects the nuclei in each cell clump. A modified Otsu method with prior class probability is proposed for accurate segmentation of nuclei from the cell clumps. Using distance regularized level set evolution, the contour around each nucleus is evolved until it reaches the cytoplasm boundaries. Promising results were obtained by experimenting on ISBI 2015 challenge dataset.
* 4 pages, 4 figures, Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), 2016 IEEE EMBS Conference on. IEEE, 2016
The Indian Spontaneous Expression Database for Emotion Recognition
Jun 16, 2016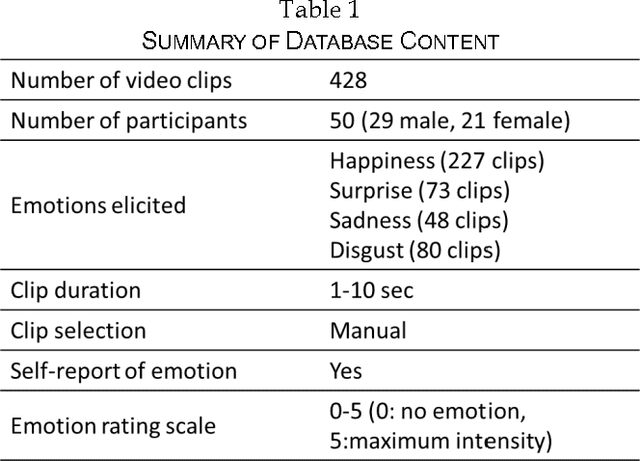
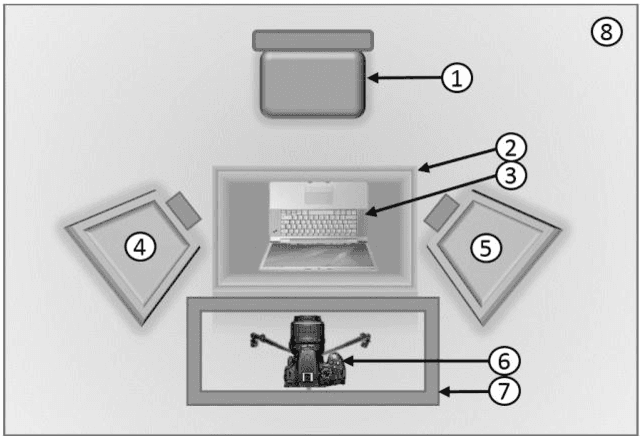
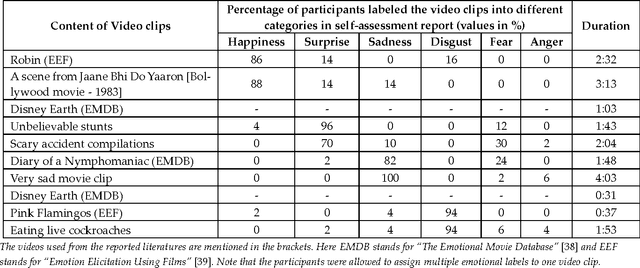
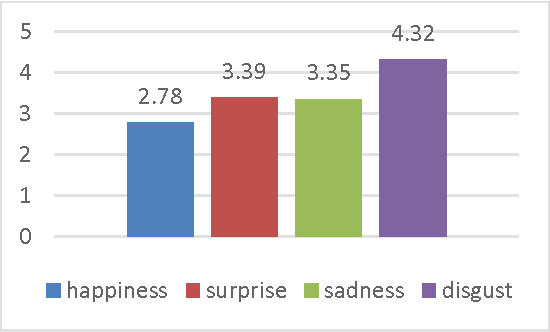
Abstract:Automatic recognition of spontaneous facial expressions is a major challenge in the field of affective computing. Head rotation, face pose, illumination variation, occlusion etc. are the attributes that increase the complexity of recognition of spontaneous expressions in practical applications. Effective recognition of expressions depends significantly on the quality of the database used. Most well-known facial expression databases consist of posed expressions. However, currently there is a huge demand for spontaneous expression databases for the pragmatic implementation of the facial expression recognition algorithms. In this paper, we propose and establish a new facial expression database containing spontaneous expressions of both male and female participants of Indian origin. The database consists of 428 segmented video clips of the spontaneous facial expressions of 50 participants. In our experiment, emotions were induced among the participants by using emotional videos and simultaneously their self-ratings were collected for each experienced emotion. Facial expression clips were annotated carefully by four trained decoders, which were further validated by the nature of stimuli used and self-report of emotions. An extensive analysis was carried out on the database using several machine learning algorithms and the results are provided for future reference. Such a spontaneous database will help in the development and validation of algorithms for recognition of spontaneous expressions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge