Ryosuke Korekata
Affordance RAG: Hierarchical Multimodal Retrieval with Affordance-Aware Embodied Memory for Mobile Manipulation
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:In this study, we address the problem of open-vocabulary mobile manipulation, where a robot is required to carry a wide range of objects to receptacles based on free-form natural language instructions. This task is challenging, as it involves understanding visual semantics and the affordance of manipulation actions. To tackle these challenges, we propose Affordance RAG, a zero-shot hierarchical multimodal retrieval framework that constructs Affordance-Aware Embodied Memory from pre-explored images. The model retrieves candidate targets based on regional and visual semantics and reranks them with affordance scores, allowing the robot to identify manipulation options that are likely to be executable in real-world environments. Our method outperformed existing approaches in retrieval performance for mobile manipulation instruction in large-scale indoor environments. Furthermore, in real-world experiments where the robot performed mobile manipulation in indoor environments based on free-form instructions, the proposed method achieved a task success rate of 85%, outperforming existing methods in both retrieval performance and overall task success.
Mobile Manipulation Instruction Generation from Multiple Images with Automatic Metric Enhancement
Jan 28, 2025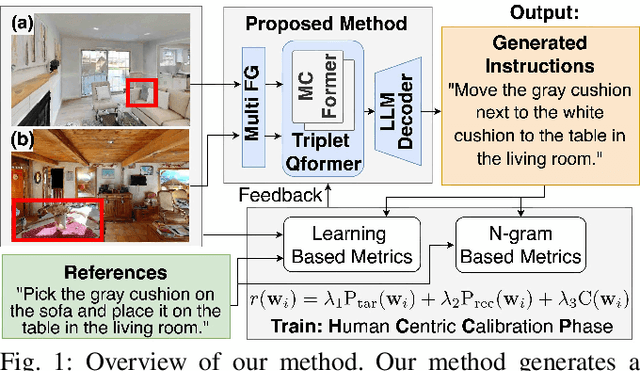
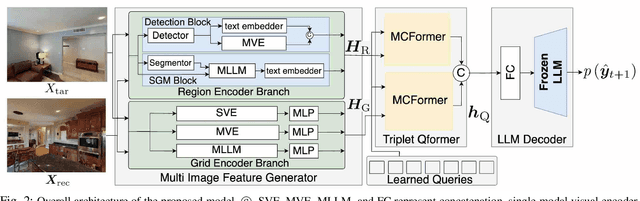
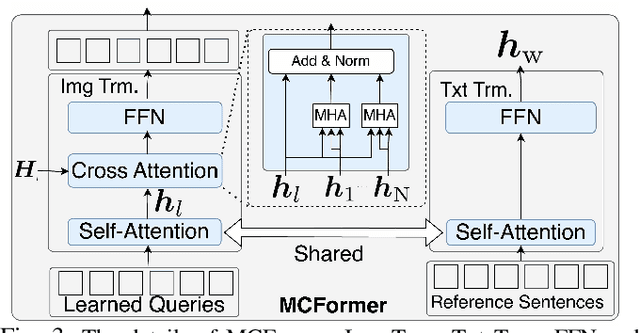

Abstract:We consider the problem of generating free-form mobile manipulation instructions based on a target object image and receptacle image. Conventional image captioning models are not able to generate appropriate instructions because their architectures are typically optimized for single-image. In this study, we propose a model that handles both the target object and receptacle to generate free-form instruction sentences for mobile manipulation tasks. Moreover, we introduce a novel training method that effectively incorporates the scores from both learning-based and n-gram based automatic evaluation metrics as rewards. This method enables the model to learn the co-occurrence relationships between words and appropriate paraphrases. Results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms baseline methods including representative multimodal large language models on standard automatic evaluation metrics. Moreover, physical experiments reveal that using our method to augment data on language instructions improves the performance of an existing multimodal language understanding model for mobile manipulation.
Open-Vocabulary Mobile Manipulation Based on Double Relaxed Contrastive Learning with Dense Labeling
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:Growing labor shortages are increasing the demand for domestic service robots (DSRs) to assist in various settings. In this study, we develop a DSR that transports everyday objects to specified pieces of furniture based on open-vocabulary instructions. Our approach focuses on retrieving images of target objects and receptacles from pre-collected images of indoor environments. For example, given an instruction "Please get the right red towel hanging on the metal towel rack and put it in the white washing machine on the left," the DSR is expected to carry the red towel to the washing machine based on the retrieved images. This is challenging because the correct images should be retrieved from thousands of collected images, which may include many images of similar towels and appliances. To address this, we propose RelaX-Former, which learns diverse and robust representations from among positive, unlabeled positive, and negative samples. We evaluated RelaX-Former on a dataset containing real-world indoor images and human annotated instructions including complex referring expressions. The experimental results demonstrate that RelaX-Former outperformed existing baseline models across standard image retrieval metrics. Moreover, we performed physical experiments using a DSR to evaluate the performance of our approach in a zero-shot transfer setting. The experiments involved the DSR to carry objects to specific receptacles based on open-vocabulary instructions, achieving an overall success rate of 75%.
DM2RM: Dual-Mode Multimodal Ranking for Target Objects and Receptacles Based on Open-Vocabulary Instructions
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:In this study, we aim to develop a domestic service robot (DSR) that, guided by open-vocabulary instructions, can carry everyday objects to the specified pieces of furniture. Few existing methods handle mobile manipulation tasks with open-vocabulary instructions in the image retrieval setting, and most do not identify both the target objects and the receptacles. We propose the Dual-Mode Multimodal Ranking model (DM2RM), which enables images of both the target objects and receptacles to be retrieved using a single model based on multimodal foundation models. We introduce a switching mechanism that leverages a mode token and phrase identification via a large language model to switch the embedding space based on the prediction target. To evaluate the DM2RM, we construct a novel dataset including real-world images collected from hundreds of building-scale environments and crowd-sourced instructions with referring expressions. The evaluation results show that the proposed DM2RM outperforms previous approaches in terms of standard metrics in image retrieval settings. Furthermore, we demonstrate the application of the DM2RM on a standardized real-world DSR platform including fetch-and-carry actions, where it achieves a task success rate of 82% despite the zero-shot transfer setting. Demonstration videos, code, and more materials are available at https://kkrr10.github.io/dm2rm/.
Learning-To-Rank Approach for Identifying Everyday Objects Using a Physical-World Search Engine
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:Domestic service robots offer a solution to the increasing demand for daily care and support. A human-in-the-loop approach that combines automation and operator intervention is considered to be a realistic approach to their use in society. Therefore, we focus on the task of retrieving target objects from open-vocabulary user instructions in a human-in-the-loop setting, which we define as the learning-to-rank physical objects (LTRPO) task. For example, given the instruction "Please go to the dining room which has a round table. Pick up the bottle on it," the model is required to output a ranked list of target objects that the operator/user can select. In this paper, we propose MultiRankIt, which is a novel approach for the LTRPO task. MultiRankIt introduces the Crossmodal Noun Phrase Encoder to model the relationship between phrases that contain referring expressions and the target bounding box, and the Crossmodal Region Feature Encoder to model the relationship between the target object and multiple images of its surrounding contextual environment. Additionally, we built a new dataset for the LTRPO task that consists of instructions with complex referring expressions accompanied by real indoor environmental images that feature various target objects. We validated our model on the dataset and it outperformed the baseline method in terms of the mean reciprocal rank and recall@k. Furthermore, we conducted physical experiments in a setting where a domestic service robot retrieved everyday objects in a standardized domestic environment, based on users' instruction in a human--in--the--loop setting. The experimental results demonstrate that the success rate for object retrieval achieved 80%. Our code is available at https://github.com/keio-smilab23/MultiRankIt.
DialMAT: Dialogue-Enabled Transformer with Moment-Based Adversarial Training
Nov 12, 2023Abstract:This paper focuses on the DialFRED task, which is the task of embodied instruction following in a setting where an agent can actively ask questions about the task. To address this task, we propose DialMAT. DialMAT introduces Moment-based Adversarial Training, which incorporates adversarial perturbations into the latent space of language, image, and action. Additionally, it introduces a crossmodal parallel feature extraction mechanism that applies foundation models to both language and image. We evaluated our model using a dataset constructed from the DialFRED dataset and demonstrated superior performance compared to the baseline method in terms of success rate and path weighted success rate. The model secured the top position in the DialFRED Challenge, which took place at the CVPR 2023 Embodied AI workshop.
Switching Head-Tail Funnel UNITER for Dual Referring Expression Comprehension with Fetch-and-Carry Tasks
Jul 14, 2023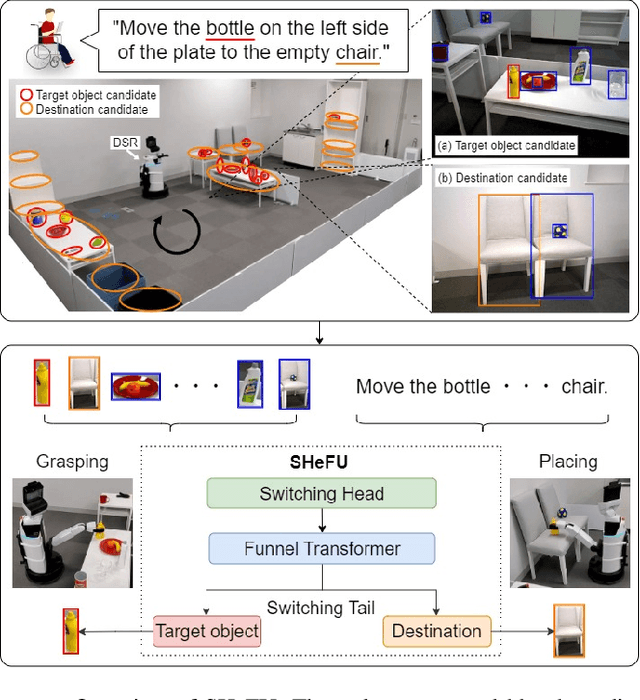
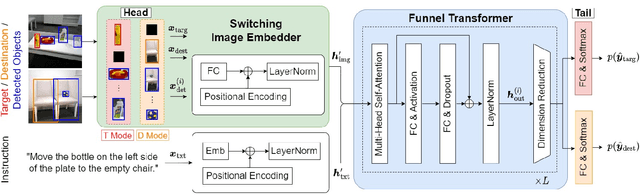
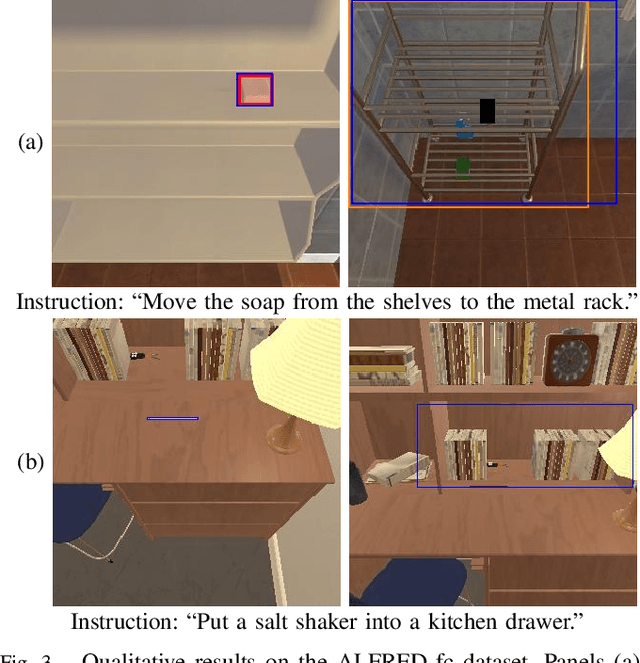

Abstract:This paper describes a domestic service robot (DSR) that fetches everyday objects and carries them to specified destinations according to free-form natural language instructions. Given an instruction such as "Move the bottle on the left side of the plate to the empty chair," the DSR is expected to identify the bottle and the chair from multiple candidates in the environment and carry the target object to the destination. Most of the existing multimodal language understanding methods are impractical in terms of computational complexity because they require inferences for all combinations of target object candidates and destination candidates. We propose Switching Head-Tail Funnel UNITER, which solves the task by predicting the target object and the destination individually using a single model. Our method is validated on a newly-built dataset consisting of object manipulation instructions and semi photo-realistic images captured in a standard Embodied AI simulator. The results show that our method outperforms the baseline method in terms of language comprehension accuracy. Furthermore, we conduct physical experiments in which a DSR delivers standardized everyday objects in a standardized domestic environment as requested by instructions with referring expressions. The experimental results show that the object grasping and placing actions are achieved with success rates of more than 90%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge