Rujie Liu
RTAT: A Robust Two-stage Association Tracker for Multi-Object Tracking
Aug 14, 2024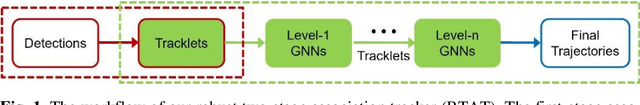
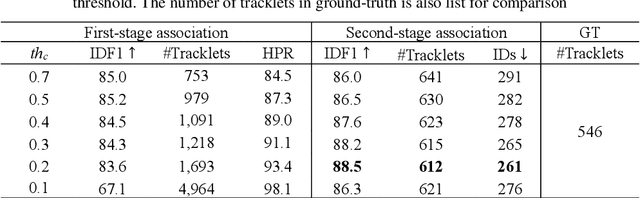
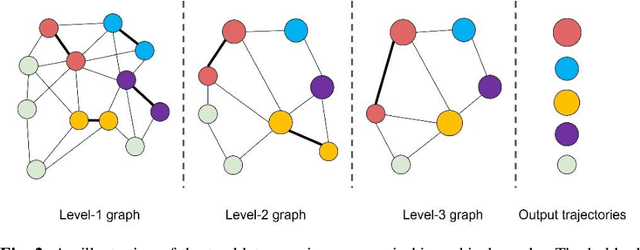
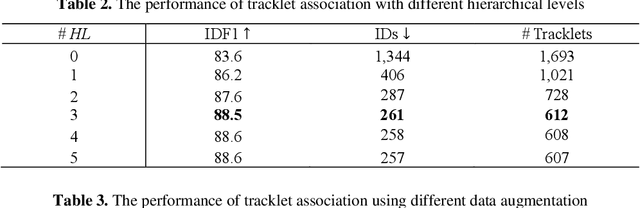
Abstract:Data association is an essential part in the tracking-by-detection based Multi-Object Tracking (MOT). Most trackers focus on how to design a better data association strategy to improve the tracking performance. The rule-based handcrafted association methods are simple and highly efficient but lack generalization capability to deal with complex scenes. While the learnt association methods can learn high-order contextual information to deal with various complex scenes, but they have the limitations of higher complexity and cost. To address these limitations, we propose a Robust Two-stage Association Tracker, named RTAT. The first-stage association is performed between tracklets and detections to generate tracklets with high purity, and the second-stage association is performed between tracklets to form complete trajectories. For the first-stage association, we use a simple data association strategy to generate tracklets with high purity by setting a low threshold for the matching cost in the assignment process. We conduct the tracklet association in the second-stage based on the framework of message-passing GNN. Our method models the tracklet association as a series of edge classification problem in hierarchical graphs, which can recursively merge short tracklets into longer ones. Our tracker RTAT ranks first on the test set of MOT17 and MOT20 benchmarks in most of the main MOT metrics: HOTA, IDF1, and AssA. We achieve 67.2 HOTA, 84.7 IDF1, and 69.7 AssA on MOT17, and 66.2 HOTA, 82.5 IDF1, and 68.1 AssA on MOT20.
Generative Modelling with High-Order Langevin Dynamics
Apr 19, 2024Abstract:Diffusion generative modelling (DGM) based on stochastic differential equations (SDEs) with score matching has achieved unprecedented results in data generation. In this paper, we propose a novel fast high-quality generative modelling method based on high-order Langevin dynamics (HOLD) with score matching. This motive is proved by third-order Langevin dynamics. By augmenting the previous SDEs, e.g. variance exploding or variance preserving SDEs for single-data variable processes, HOLD can simultaneously model position, velocity, and acceleration, thereby improving the quality and speed of the data generation at the same time. HOLD is composed of one Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process and two Hamiltonians, which reduce the mixing time by two orders of magnitude. Empirical experiments for unconditional image generation on the public data set CIFAR-10 and CelebA-HQ show that the effect is significant in both Frechet inception distance (FID) and negative log-likelihood, and achieves the state-of-the-art FID of 1.85 on CIFAR-10.
LoRRaL: Facial Action Unit Detection Based on Local Region Relation Learning
Sep 23, 2020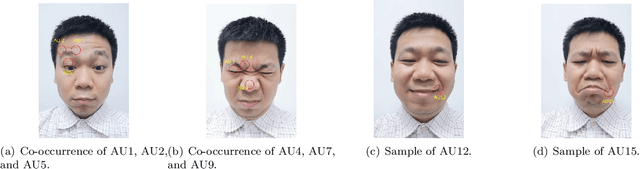
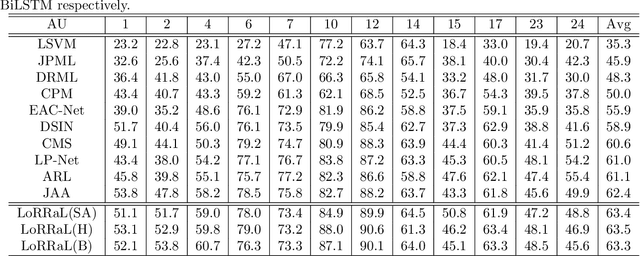
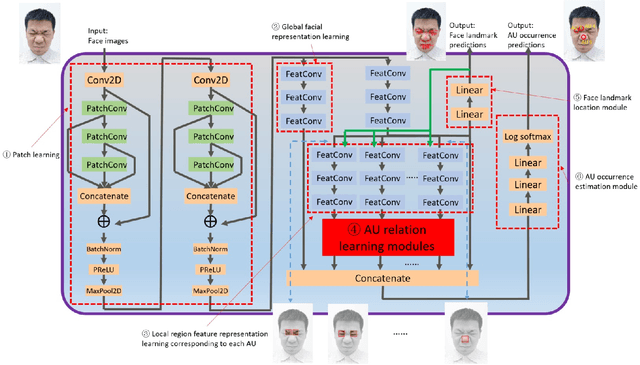
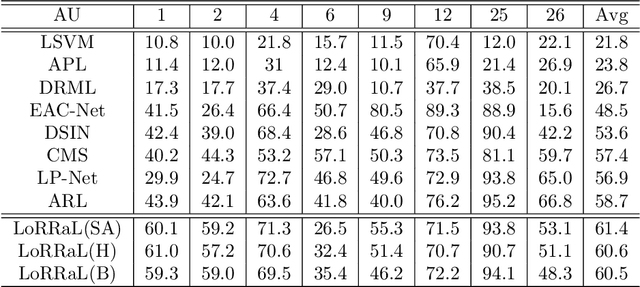
Abstract:End-to-end convolution representation learning has been proved to be very effective in facial action unit (AU) detection. Considering the co-occurrence and mutual exclusion between facial AUs, in this paper, we propose convolution neural networks with Local Region Relation Learning (LoRRaL), which can combine latent relationships among AUs for an end-to-end approach to facial AU occurrence detection. LoRRaL consists of 1) use bi-directional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) to dynamically and sequentially encode local AU feature maps, 2) use self-attention mechanism to dynamically compute correspondences from local facial regions and to re-aggregate AU feature maps considering AU co-occurrences and mutual exclusions, 3) use a continuous-state modern Hopfield network to encode and map local facial features to more discriminative AU feature maps, that all these networks take the facial image as input and map it to AU occurrences. Our experiments on the challenging BP4D and DISFA Benchmarks without any external data or pre-trained models results in F1-scores of 63.5% and 61.4% respectively, which shows our proposed networks can lead to performance improvement on the AU detection task.
Learning to Find Correlated Features by Maximizing Information Flow in Convolutional Neural Networks
Jun 30, 2019



Abstract:Training convolutional neural networks for image classification tasks usually causes information loss. Although most of the time the information lost is redundant with respect to the target task, there are still cases where discriminative information is also discarded. For example, if the samples that belong to the same category have multiple correlated features, the model may only learn a subset of the features and ignore the rest. This may not be a problem unless the classification in the test set highly depends on the ignored features. We argue that the discard of the correlated discriminative information is partially caused by the fact that the minimization of the classification loss doesn't ensure to learn the overall discriminative information but only the most discriminative information. To address this problem, we propose an information flow maximization (IFM) loss as a regularization term to find the discriminative correlated features. With less information loss the classifier can make predictions based on more informative features. We validate our method on the shiftedMNIST dataset and show the effectiveness of IFM loss in learning representative and discriminative features.
Learning to generate filters for convolutional neural networks
Dec 05, 2018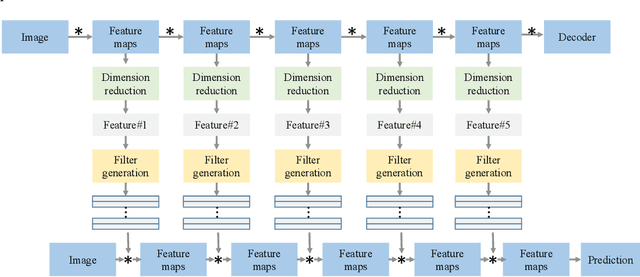



Abstract:Conventionally, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) process different images with the same set of filters. However, the variations in images pose a challenge to this fashion. In this paper, we propose to generate sample-specific filters for convolutional layers in the forward pass. Since the filters are generated on-the-fly, the model becomes more flexible and can better fit the training data compared to traditional CNNs. In order to obtain sample-specific features, we extract the intermediate feature maps from an autoencoder. As filters are usually high dimensional, we propose to learn a set of coefficients instead of a set of filters. These coefficients are used to linearly combine the base filters from a filter repository to generate the final filters for a CNN. The proposed method is evaluated on MNIST, MTFL and CIFAR10 datasets. Experiment results demonstrate that the classification accuracy of the baseline model can be improved by using the proposed filter generation method.
Tackling Early Sparse Gradients in Softmax Activation Using Leaky Squared Euclidean Distance
Nov 27, 2018



Abstract:Softmax activation is commonly used to output the probability distribution over categories based on certain distance metric. In scenarios like one-shot learning, the distance metric is often chosen to be squared Euclidean distance between the query sample and the category prototype. This practice works well in most time. However, we find that choosing squared Euclidean distance may cause distance explosion leading gradients to be extremely sparse in the early stage of back propagation. We term this phenomena as the early sparse gradients problem. Though it doesn't deteriorate the convergence of the model, it may set up a barrier to further model improvement. To tackle this problem, we propose to use leaky squared Euclidean distance to impose a restriction on distances. In this way, we can avoid distance explosion and increase the magnitude of gradients. Extensive experiments are conducted on Omniglot and miniImageNet datasets. We show that using leaky squared Euclidean distance can improve one-shot classification accuracy on both datasets.
Generating Attention from Classifier Activations for Fine-grained Recognition
Nov 27, 2018



Abstract:Recent advances in fine-grained recognition utilize attention maps to localize objects of interest. Although there are many ways to generate attention maps, most of them rely on sophisticated loss functions or complex training processes. In this work, we propose a simple and straightforward attention generation model based on the output activations of classifiers. The advantage of our model is that it can be easily trained with image level labels and softmax loss functions. More specifically, multiple linear local classifiers are firstly adopted to perform fine-grained classification at each location of high level CNN feature maps. The attention map is generated by aggregating and max-pooling the output activations. Then the attention map serves as a surrogate target object mask to train those local classifiers, similar to training models for semantic segmentation. Our model achieves state-of-the-art results on three heavily benchmarked datasets, i.e. 87.9% on CUB-200-2011 dataset, 94.1% on Stanford Cars dataset and 92.1% on FGVC-Aircraft dataset, demonstrating its effectiveness on fine-grained recognition tasks.
Multi-view (Joint) Probability Linear Discrimination Analysis for Multi-view Feature Verification
Jul 07, 2017



Abstract:Multi-view feature has been proved to be very effective in many multimedia applications. However, the current back-end classifiers cannot make full use of such features. In this paper, we propose a method to model the multi-faceted information in the multi-view features explicitly and jointly. In our approach, the feature was modeled as a result derived by a generative multi-view (joint\footnotemark[1]) Probability Linear Discriminant Analysis (PLDA) model, which contains multiple kinds of latent variables. The usual PLDA model only considers one single label. However, in practical use, when using multi-task learned network as feature extractor, the extracted feature are always attached to several labels. This type of feature is called multi-view feature. With multi-view (joint) PLDA, we are able to explicitly build a model that can combine multiple heterogeneous information from the multi-view features. In verification step, we calculated the likelihood to describe whether the two features having consistent labels or not. This likelihood are used in the following decision-making. Experiments have been conducted on large scale verification task. On the public RSR2015 data corpus, the results showed that our approach can achieve 0.02\% EER and 0.09\% EER for impostor wrong and impostor correct cases respectively.
Learning Residual Images for Face Attribute Manipulation
Apr 12, 2017



Abstract:Face attributes are interesting due to their detailed description of human faces. Unlike prior researches working on attribute prediction, we address an inverse and more challenging problem called face attribute manipulation which aims at modifying a face image according to a given attribute value. Instead of manipulating the whole image, we propose to learn the corresponding residual image defined as the difference between images before and after the manipulation. In this way, the manipulation can be operated efficiently with modest pixel modification. The framework of our approach is based on the Generative Adversarial Network. It consists of two image transformation networks and a discriminative network. The transformation networks are responsible for the attribute manipulation and its dual operation and the discriminative network is used to distinguish the generated images from real images. We also apply dual learning to allow transformation networks to learn from each other. Experiments show that residual images can be effectively learned and used for attribute manipulations. The generated images remain most of the details in attribute-irrelevant areas.
Online and stochastic Douglas-Rachford splitting method for large scale machine learning
Dec 21, 2016
Abstract:Online and stochastic learning has emerged as powerful tool in large scale optimization. In this work, we generalize the Douglas-Rachford splitting (DRs) method for minimizing composite functions to online and stochastic settings (to our best knowledge this is the first time DRs been generalized to sequential version). We first establish an $O(1/\sqrt{T})$ regret bound for batch DRs method. Then we proved that the online DRs splitting method enjoy an $O(1)$ regret bound and stochastic DRs splitting has a convergence rate of $O(1/\sqrt{T})$. The proof is simple and intuitive, and the results and technique can be served as a initiate for the research on the large scale machine learning employ the DRs method. Numerical experiments of the proposed method demonstrate the effectiveness of the online and stochastic update rule, and further confirm our regret and convergence analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge