Ruizhi Li
WearVox: An Egocentric Multichannel Voice Assistant Benchmark for Wearables
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Wearable devices such as AI glasses are transforming voice assistants into always-available, hands-free collaborators that integrate seamlessly with daily life, but they also introduce challenges like egocentric audio affected by motion and noise, rapid micro-interactions, and the need to distinguish device-directed speech from background conversations. Existing benchmarks largely overlook these complexities, focusing instead on clean or generic conversational audio. To bridge this gap, we present WearVox, the first benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate voice assistants in realistic wearable scenarios. WearVox comprises 3,842 multi-channel, egocentric audio recordings collected via AI glasses across five diverse tasks including Search-Grounded QA, Closed-Book QA, Side-Talk Rejection, Tool Calling, and Speech Translation, spanning a wide range of indoor and outdoor environments and acoustic conditions. Each recording is accompanied by rich metadata, enabling nuanced analysis of model performance under real-world constraints. We benchmark leading proprietary and open-source speech Large Language Models (SLLMs) and find that most real-time SLLMs achieve accuracies on WearVox ranging from 29% to 59%, with substantial performance degradation on noisy outdoor audio, underscoring the difficulty and realism of the benchmark. Additionally, we conduct a case study with two new SLLMs that perform inference with single-channel and multi-channel audio, demonstrating that multi-channel audio inputs significantly enhance model robustness to environmental noise and improve discrimination between device-directed and background speech. Our results highlight the critical importance of spatial audio cues for context-aware voice assistants and establish WearVox as a comprehensive testbed for advancing wearable voice AI research.
Two-Stage Augmentation and Adaptive CTC Fusion for Improved Robustness of Multi-Stream End-to-End ASR
Feb 05, 2021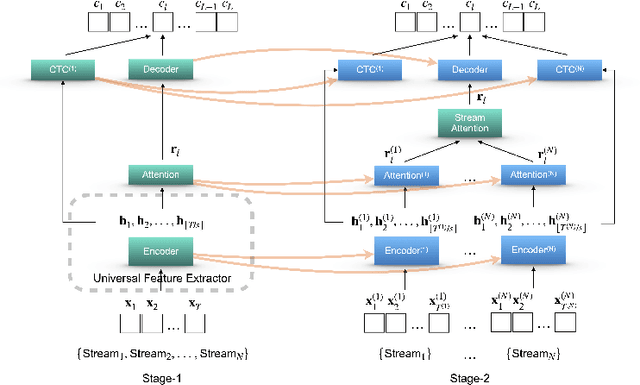

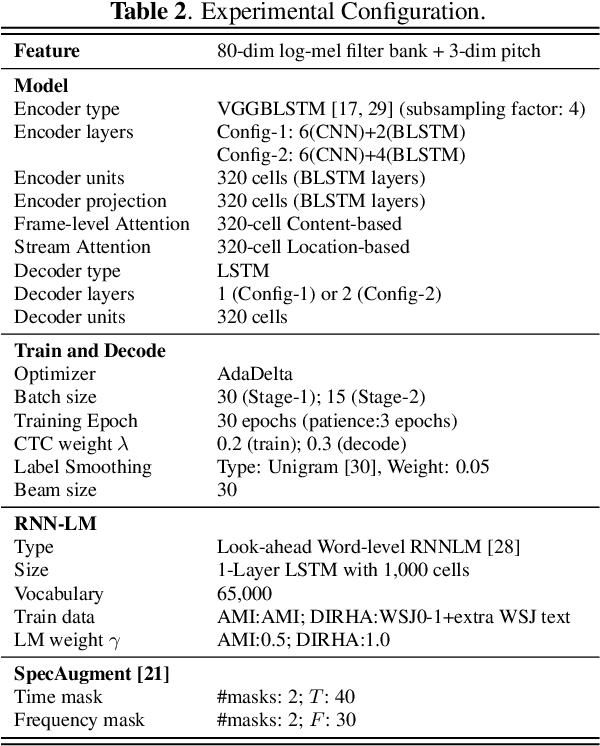
Abstract:Performance degradation of an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system is commonly observed when the test acoustic condition is different from training. Hence, it is essential to make ASR systems robust against various environmental distortions, such as background noises and reverberations. In a multi-stream paradigm, improving robustness takes account of handling a variety of unseen single-stream conditions and inter-stream dynamics. Previously, a practical two-stage training strategy was proposed within multi-stream end-to-end ASR, where Stage-2 formulates the multi-stream model with features from Stage-1 Universal Feature Extractor (UFE). In this paper, as an extension, we introduce a two-stage augmentation scheme focusing on mismatch scenarios: Stage-1 Augmentation aims to address single-stream input varieties with data augmentation techniques; Stage-2 Time Masking applies temporal masks on UFE features of randomly selected streams to simulate diverse stream combinations. During inference, we also present adaptive Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) fusion with the help of hierarchical attention mechanisms. Experiments have been conducted on two datasets, DIRHA and AMI, as a multi-stream scenario. Compared with the previous training strategy, substantial improvements are reported with relative word error rate reductions of 29.7-59.3% across several unseen stream combinations.
A practical two-stage training strategy for multi-stream end-to-end speech recognition
Oct 23, 2019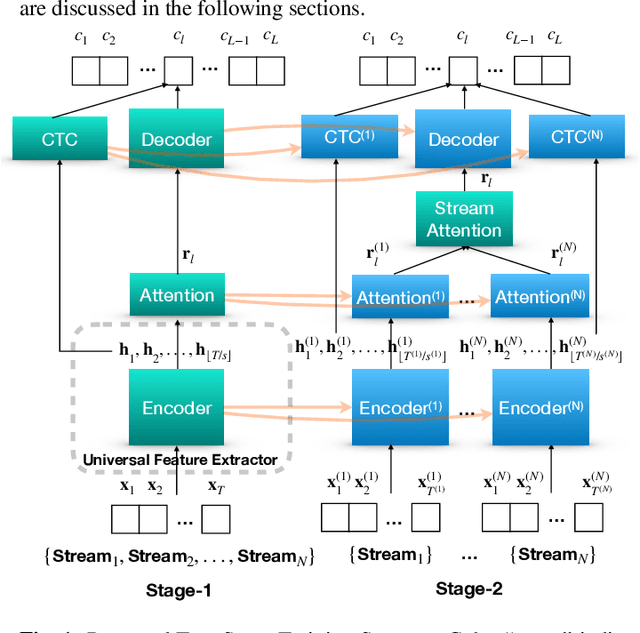
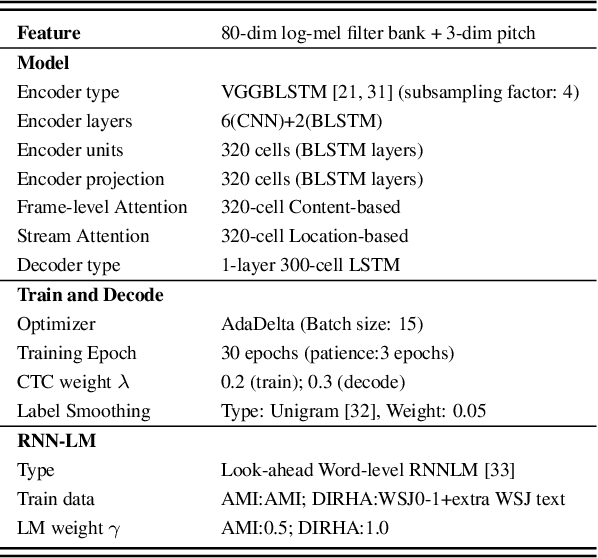
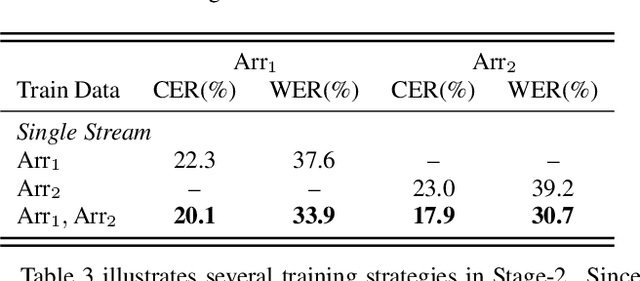
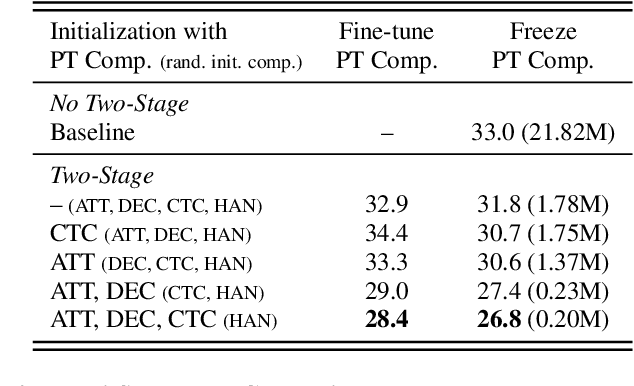
Abstract:The multi-stream paradigm of audio processing, in which several sources are simultaneously considered, has been an active research area for information fusion. Our previous study offered a promising direction within end-to-end automatic speech recognition, where parallel encoders aim to capture diverse information followed by a stream-level fusion based on attention mechanisms to combine the different views. However, with an increasing number of streams resulting in an increasing number of encoders, the previous approach could require substantial memory and massive amounts of parallel data for joint training. In this work, we propose a practical two-stage training scheme. Stage-1 is to train a Universal Feature Extractor (UFE), where encoder outputs are produced from a single-stream model trained with all data. Stage-2 formulates a multi-stream scheme intending to solely train the attention fusion module using the UFE features and pretrained components from Stage-1. Experiments have been conducted on two datasets, DIRHA and AMI, as a multi-stream scenario. Compared with our previous method, this strategy achieves relative word error rate reductions of 8.2--32.4%, while consistently outperforming several conventional combination methods.
Multi-Stream End-to-End Speech Recognition
Jun 17, 2019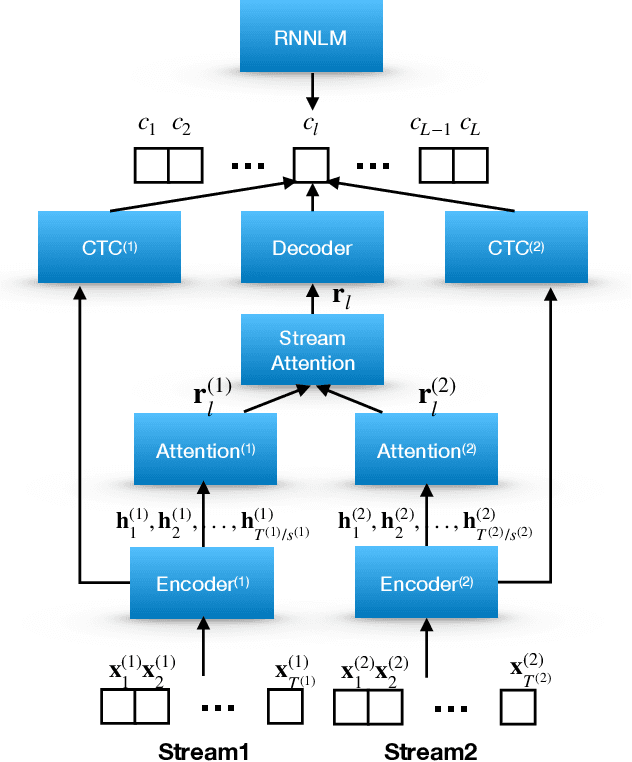
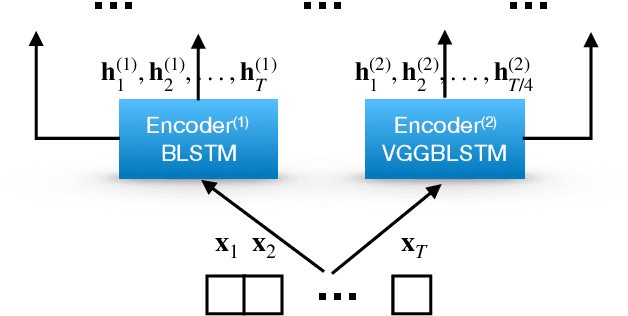
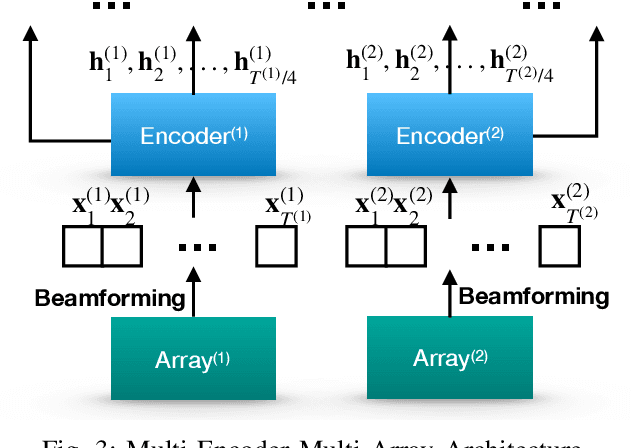
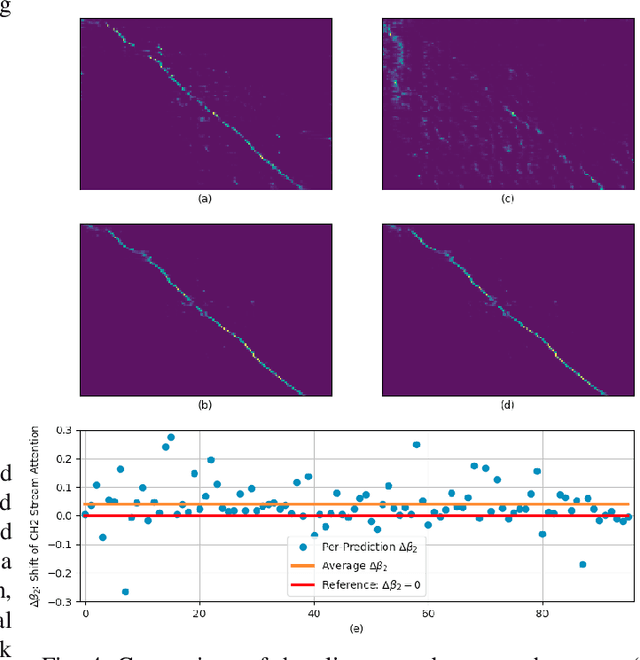
Abstract:Attention-based methods and Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) network have been promising research directions for end-to-end (E2E) Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). The joint CTC/Attention model has achieved great success by utilizing both architectures during multi-task training and joint decoding. In this work, we present a multi-stream framework based on joint CTC/Attention E2E ASR with parallel streams represented by separate encoders aiming to capture diverse information. On top of the regular attention networks, the Hierarchical Attention Network (HAN) is introduced to steer the decoder toward the most informative encoders. A separate CTC network is assigned to each stream to force monotonic alignments. Two representative framework have been proposed and discussed, which are Multi-Encoder Multi-Resolution (MEM-Res) framework and Multi-Encoder Multi-Array (MEM-Array) framework, respectively. In MEM-Res framework, two heterogeneous encoders with different architectures, temporal resolutions and separate CTC networks work in parallel to extract complimentary information from same acoustics. Experiments are conducted on Wall Street Journal (WSJ) and CHiME-4, resulting in relative Word Error Rate (WER) reduction of 18.0-32.1% and the best WER of 3.6% in the WSJ eval92 test set. The MEM-Array framework aims at improving the far-field ASR robustness using multiple microphone arrays which are activated by separate encoders. Compared with the best single-array results, the proposed framework has achieved relative WER reduction of 3.7% and 9.7% in AMI and DIRHA multi-array corpora, respectively, which also outperforms conventional fusion strategies.
Performance Monitoring for End-to-End Speech Recognition
Apr 09, 2019
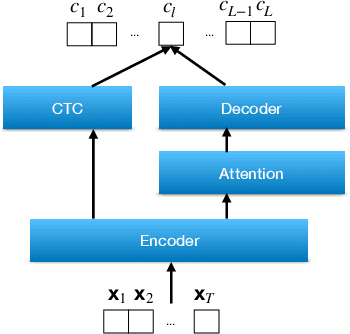

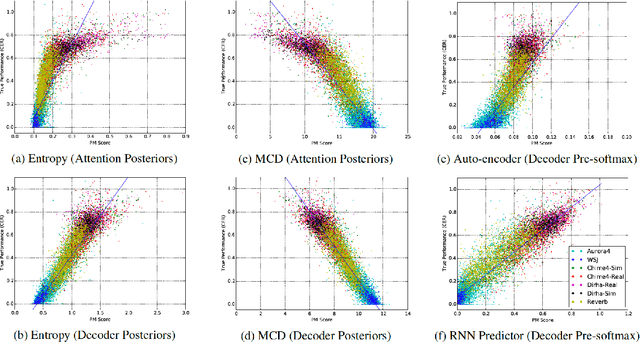
Abstract:Measuring performance of an automatic speech recognition (ASR) system without ground-truth could be beneficial in many scenarios, especially with data from unseen domains, where performance can be highly inconsistent. In conventional ASR systems, several performance monitoring (PM) techniques have been well-developed to monitor performance by looking at tri-phone posteriors or pre-softmax activations from neural network acoustic modeling. However, strategies for monitoring more recently developed end-to-end ASR systems have not yet been explored, and so that is the focus of this paper. We adapt previous PM measures (Entropy, M-measure and Auto-encoder) and apply our proposed RNN predictor in the end-to-end setting. These measures utilize the decoder output layer and attention probability vectors, and their predictive power is measured with simple linear models. Our findings suggest that decoder-level features are more feasible and informative than attention-level probabilities for PM measures, and that M-measure on the decoder posteriors achieves the best overall predictive performance with an average prediction error 8.8%. Entropy measures and RNN-based prediction also show competitive predictability, especially for unseen conditions.
Exploring Methods for the Automatic Detection of Errors in Manual Transcription
Apr 08, 2019


Abstract:Quality of data plays an important role in most deep learning tasks. In the speech community, transcription of speech recording is indispensable. Since the transcription is usually generated artificially, automatically finding errors in manual transcriptions not only saves time and labors but benefits the performance of tasks that need the training process. Inspired by the success of hybrid automatic speech recognition using both language model and acoustic model, two approaches of automatic error detection in the transcriptions have been explored in this work. Previous study using a biased language model approach, relying on a strong transcription-dependent language model, has been reviewed. In this work, we propose a novel acoustic model based approach, focusing on the phonetic sequence of speech. Both methods have been evaluated on a completely real dataset, which was originally transcribed with errors and strictly corrected manually afterwards.
Stream attention-based multi-array end-to-end speech recognition
Nov 12, 2018



Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) using multiple microphone arrays has achieved great success in the far-field robustness. Taking advantage of all the information that each array shares and contributes is crucial in this task. Motivated by the advances of joint Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC)/attention mechanism in the End-to-End (E2E) ASR, a stream attention-based multi-array framework is proposed in this work. Microphone arrays, acting as information streams, are activated by separate encoders and decoded under the instruction of both CTC and attention networks. In terms of attention, a hierarchical structure is adopted. On top of the regular attention networks, stream attention is introduced to steer the decoder toward the most informative encoders. Experiments have been conducted on AMI and DIRHA multi-array corpora using the encoder-decoder architecture. Compared with the best single-array results, the proposed framework has achieved relative Word Error Rates (WERs) reduction of 3.7% and 9.7% in the two datasets, respectively, which is better than conventional strategies as well.
Multi-encoder multi-resolution framework for end-to-end speech recognition
Nov 12, 2018



Abstract:Attention-based methods and Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) network have been promising research directions for end-to-end Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). The joint CTC/Attention model has achieved great success by utilizing both architectures during multi-task training and joint decoding. In this work, we present a novel Multi-Encoder Multi-Resolution (MEMR) framework based on the joint CTC/Attention model. Two heterogeneous encoders with different architectures, temporal resolutions and separate CTC networks work in parallel to extract complimentary acoustic information. A hierarchical attention mechanism is then used to combine the encoder-level information. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model, experiments are conducted on Wall Street Journal (WSJ) and CHiME-4, resulting in relative Word Error Rate (WER) reduction of 18.0-32.1%. Moreover, the proposed MEMR model achieves 3.6% WER in the WSJ eval92 test set, which is the best WER reported for an end-to-end system on this benchmark.
Large-scale Artificial Neural Network: MapReduce-based Deep Learning
Oct 09, 2015



Abstract:Faced with continuously increasing scale of data, original back-propagation neural network based machine learning algorithm presents two non-trivial challenges: huge amount of data makes it difficult to maintain both efficiency and accuracy; redundant data aggravates the system workload. This project is mainly focused on the solution to the issues above, combining deep learning algorithm with cloud computing platform to deal with large-scale data. A MapReduce-based handwriting character recognizer will be designed in this project to verify the efficiency improvement this mechanism will achieve on training and practical large-scale data. Careful discussion and experiment will be developed to illustrate how deep learning algorithm works to train handwritten digits data, how MapReduce is implemented on deep learning neural network, and why this combination accelerates computation. Besides performance, the scalability and robustness will be mentioned in this report as well. Our system comes with two demonstration software that visually illustrates our handwritten digit recognition/encoding application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge