Ruixuan Tu
FaithBench: A Diverse Hallucination Benchmark for Summarization by Modern LLMs
Oct 17, 2024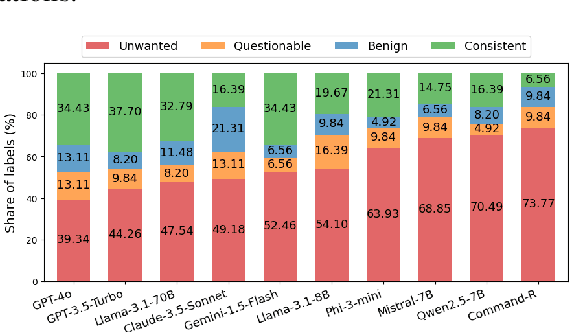
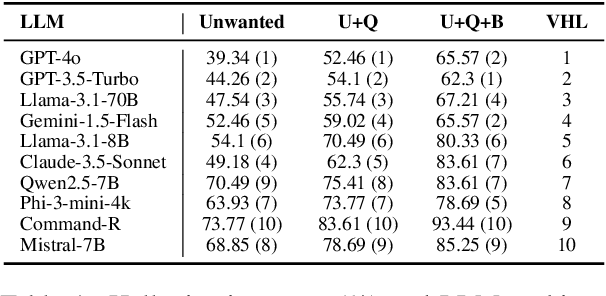
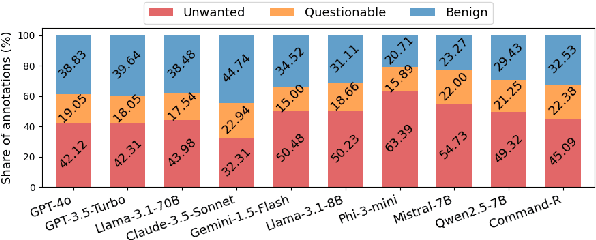
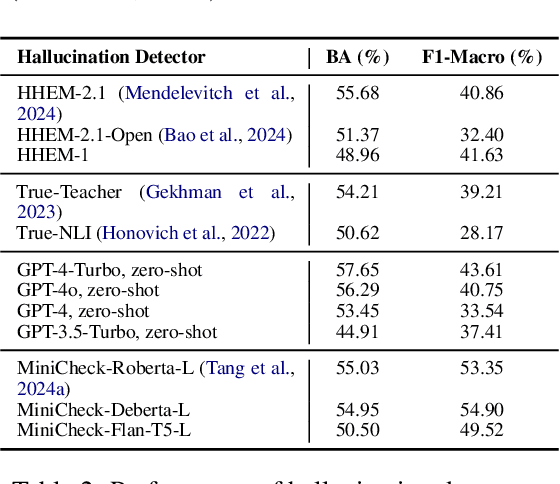
Abstract:Summarization is one of the most common tasks performed by large language models (LLMs), especially in applications like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). However, existing evaluations of hallucinations in LLM-generated summaries, and evaluations of hallucination detection models both suffer from a lack of diversity and recency in the LLM and LLM families considered. This paper introduces FaithBench, a summarization hallucination benchmark comprising challenging hallucinations made by 10 modern LLMs from 8 different families, with ground truth annotations by human experts. ``Challenging'' here means summaries on which popular, state-of-the-art hallucination detection models, including GPT-4o-as-a-judge, disagreed on. Our results show GPT-4o and GPT-3.5-Turbo produce the least hallucinations. However, even the best hallucination detection models have near 50\% accuracies on FaithBench, indicating lots of room for future improvement. The repo is https://github.com/vectara/FaithBench
Is Semantic Chunking Worth the Computational Cost?
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems have popularized semantic chunking, which aims to improve retrieval performance by dividing documents into semantically coherent segments. Despite its growing adoption, the actual benefits over simpler fixed-size chunking, where documents are split into consecutive, fixed-size segments, remain unclear. This study systematically evaluates the effectiveness of semantic chunking using three common retrieval-related tasks: document retrieval, evidence retrieval, and retrieval-based answer generation. The results show that the computational costs associated with semantic chunking are not justified by consistent performance gains. These findings challenge the previous assumptions about semantic chunking and highlight the need for more efficient chunking strategies in RAG systems.
DocAsRef: A Pilot Empirical Study on Repurposing Reference-Based Summary Quality Metrics Reference-Freely
Dec 20, 2022Abstract:Summary quality assessment metrics have two categories: reference-based and reference-free. Reference-based metrics are theoretically more accurate but are limited by the availability and quality of the human-written references, which are both difficulty to ensure. This inspires the development of reference-free metrics, which are independent from human-written references, in the past few years. However, existing reference-free metrics cannot be both zero-shot and accurate. In this paper, we propose a zero-shot but accurate reference-free approach in a sneaky way: feeding documents, based upon which summaries generated, as references into reference-based metrics. Experimental results show that this zero-shot approach can give us the best-performing reference-free metrics on nearly all aspects on several recently-released datasets, even beating reference-free metrics specifically trained for this task sometimes. We further investigate what reference-based metrics can benefit from such repurposing and whether our additional tweaks help.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge