Ruixuan Sun
Large Language Models as Conversational Movie Recommenders: A User Study
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:This paper explores the effectiveness of using large language models (LLMs) for personalized movie recommendations from users' perspectives in an online field experiment. Our study involves a combination of between-subject prompt and historic consumption assessments, along with within-subject recommendation scenario evaluations. By examining conversation and survey response data from 160 active users, we find that LLMs offer strong recommendation explainability but lack overall personalization, diversity, and user trust. Our results also indicate that different personalized prompting techniques do not significantly affect user-perceived recommendation quality, but the number of movies a user has watched plays a more significant role. Furthermore, LLMs show a greater ability to recommend lesser-known or niche movies. Through qualitative analysis, we identify key conversational patterns linked to positive and negative user interaction experiences and conclude that providing personal context and examples is crucial for obtaining high-quality recommendations from LLMs.
What Are We Optimizing For? A Human-centric Evaluation Of Deep Learning-based Recommender Systems
Jan 21, 2024Abstract:Deep learning-based (DL) models in recommender systems (RecSys) have gained significant recognition for their remarkable accuracy in predicting user preferences. However, their performance often lacks a comprehensive evaluation from a human-centric perspective, which encompasses various dimensions beyond simple interest matching. In this work, we have developed a robust human-centric evaluation framework that incorporates seven diverse metrics to assess the quality of recommendations generated by five recent open-sourced DL models. Our evaluation datasets consist of both offline benchmark data and personalized online recommendation feedback collected from 445 real users. We find that (1) different DL models have different pros and cons in the multi-dimensional metrics that we test with; (2) users generally want a combination of accuracy with at least one another human values in the recommendation; (3) the degree of combination of different values needs to be carefully experimented to user preferred level.
Less Can Be More: Exploring Population Rating Dispositions with Partitioned Models in Recommender Systems
Jun 20, 2023



Abstract:In this study, we partition users by rating disposition - looking first at their percentage of negative ratings, and then at the general use of the rating scale. We hypothesize that users with different rating dispositions may use the recommender system differently and therefore the agreement with their past ratings may be less predictive of the future agreement. We use data from a large movie rating website to explore whether users should be grouped by disposition, focusing on identifying their various rating distributions that may hurt recommender effectiveness. We find that such partitioning not only improves computational efficiency but also improves top-k performance and predictive accuracy. Though such effects are largest for the user-based KNN CF, smaller for item-based KNN CF, and smallest for latent factor algorithms such as SVD.
Getting the Most from Eye-Tracking: User-Interaction Based Reading Region Estimation Dataset and Models
Jun 12, 2023



Abstract:A single digital newsletter usually contains many messages (regions). Users' reading time spent on, and read level (skip/skim/read-in-detail) of each message is important for platforms to understand their users' interests, personalize their contents, and make recommendations. Based on accurate but expensive-to-collect eyetracker-recorded data, we built models that predict per-region reading time based on easy-to-collect Javascript browser tracking data. With eye-tracking, we collected 200k ground-truth datapoints on participants reading news on browsers. Then we trained machine learning and deep learning models to predict message-level reading time based on user interactions like mouse position, scrolling, and clicking. We reached 27\% percentage error in reading time estimation with a two-tower neural network based on user interactions only, against the eye-tracking ground truth data, while the heuristic baselines have around 46\% percentage error. We also discovered the benefits of replacing per-session models with per-timestamp models, and adding user pattern features. We concluded with suggestions on developing message-level reading estimation techniques based on available data.
* Ruoyan Kong, Ruixuan Sun, Charles Chuankai Zhang, Chen Chen, Sneha Patri, Gayathri Gajjela, and Joseph A. Konstan. Getting the most from eyetracking: User-interaction based reading region estimation dataset and models. In Proceedings of the 2023 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, ETRA 23, New York, NY, USA, 2023. Association for Computing Machinery
We Are in This Together: Quantifying Community Subjective Wellbeing and Resilience
Aug 23, 2022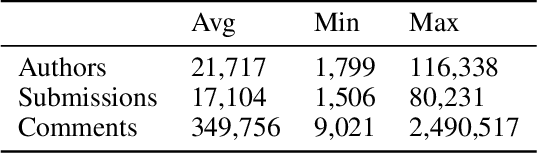
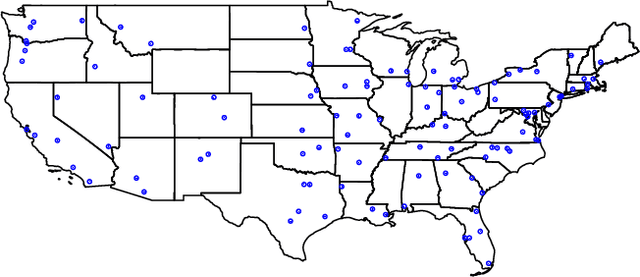
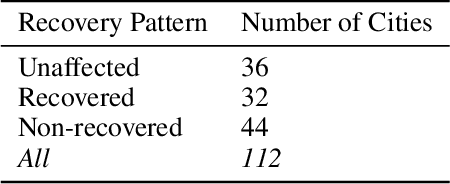
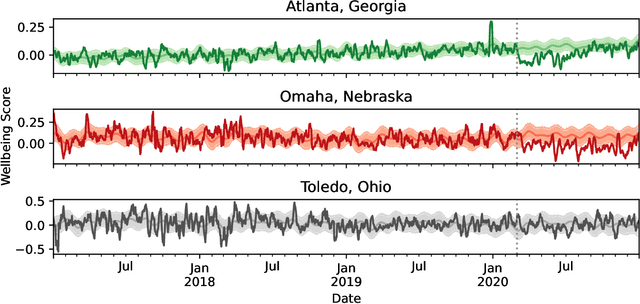
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted everyone's life across the world. In this work, we characterize the subjective wellbeing patterns of 112 cities across the United States during the pandemic prior to vaccine availability, as exhibited in subreddits corresponding to the cities. We quantify subjective wellbeing using positive and negative affect. We then measure the pandemic's impact by comparing a community's observed wellbeing with its expected wellbeing, as forecasted by time series models derived from prior to the pandemic.We show that general community traits reflected in language can be predictive of community resilience. We predict how the pandemic would impact the wellbeing of each community based on linguistic and interaction features from normal times \textit{before} the pandemic. We find that communities with interaction characteristics corresponding to more closely connected users and higher engagement were less likely to be significantly impacted. Notably, we find that communities that talked more about social ties normally experienced in-person, such as friends, family, and affiliations, were actually more likely to be impacted. Additionally, we use the same features to also predict how quickly each community would recover after the initial onset of the pandemic. We similarly find that communities that talked more about family, affiliations, and identifying as part of a group had a slower recovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge