Ruixiao Xu
Bayesian Robust Financial Trading with Adversarial Synthetic Market Data
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Algorithmic trading relies on machine learning models to make trading decisions. Despite strong in-sample performance, these models often degrade when confronted with evolving real-world market regimes, which can shift dramatically due to macroeconomic changes-e.g., monetary policy updates or unanticipated fluctuations in participant behavior. We identify two challenges that perpetuate this mismatch: (1) insufficient robustness in existing policy against uncertainties in high-level market fluctuations, and (2) the absence of a realistic and diverse simulation environment for training, leading to policy overfitting. To address these issues, we propose a Bayesian Robust Framework that systematically integrates a macro-conditioned generative model with robust policy learning. On the data side, to generate realistic and diverse data, we propose a macro-conditioned GAN-based generator that leverages macroeconomic indicators as primary control variables, synthesizing data with faithful temporal, cross-instrument, and macro correlations. On the policy side, to learn robust policy against market fluctuations, we cast the trading process as a two-player zero-sum Bayesian Markov game, wherein an adversarial agent simulates shifting regimes by perturbing macroeconomic indicators in the macro-conditioned generator, while the trading agent-guided by a quantile belief network-maintains and updates its belief over hidden market states. The trading agent seeks a Robust Perfect Bayesian Equilibrium via Bayesian neural fictitious self-play, stabilizing learning under adversarial market perturbations. Extensive experiments on 9 financial instruments demonstrate that our framework outperforms 9 state-of-the-art baselines. In extreme events like the COVID, our method shows improved profitability and risk management, offering a reliable solution for trading under uncertain and shifting market dynamics.
Vulnerable Agent Identification in Large-Scale Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Partial agent failure becomes inevitable when systems scale up, making it crucial to identify the subset of agents whose compromise would most severely degrade overall performance. In this paper, we study this Vulnerable Agent Identification (VAI) problem in large-scale multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). We frame VAI as a Hierarchical Adversarial Decentralized Mean Field Control (HAD-MFC), where the upper level involves an NP-hard combinatorial task of selecting the most vulnerable agents, and the lower level learns worst-case adversarial policies for these agents using mean-field MARL. The two problems are coupled together, making HAD-MFC difficult to solve. To solve this, we first decouple the hierarchical process by Fenchel-Rockafellar transform, resulting a regularized mean-field Bellman operator for upper level that enables independent learning at each level, thus reducing computational complexity. We then reformulate the upper-level combinatorial problem as a MDP with dense rewards from our regularized mean-field Bellman operator, enabling us to sequentially identify the most vulnerable agents by greedy and RL algorithms. This decomposition provably preserves the optimal solution of the original HAD-MFC. Experiments show our method effectively identifies more vulnerable agents in large-scale MARL and the rule-based system, fooling system into worse failures, and learns a value function that reveals the vulnerability of each agent.
MIR2: Towards Provably Robust Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning by Mutual Information Regularization
Oct 15, 2023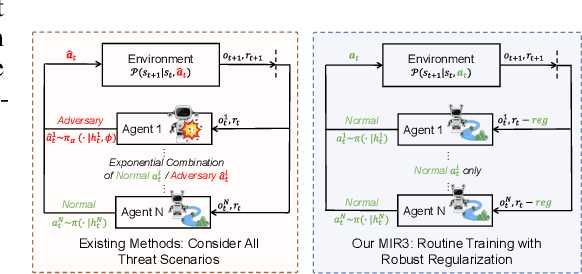


Abstract:Robust multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) necessitates resilience to uncertain or worst-case actions by unknown allies. Existing max-min optimization techniques in robust MARL seek to enhance resilience by training agents against worst-case adversaries, but this becomes intractable as the number of agents grows, leading to exponentially increasing worst-case scenarios. Attempts to simplify this complexity often yield overly pessimistic policies, inadequate robustness across scenarios and high computational demands. Unlike these approaches, humans naturally learn adaptive and resilient behaviors without the necessity of preparing for every conceivable worst-case scenario. Motivated by this, we propose MIR2, which trains policy in routine scenarios and minimize Mutual Information as Robust Regularization. Theoretically, we frame robustness as an inference problem and prove that minimizing mutual information between histories and actions implicitly maximizes a lower bound on robustness under certain assumptions. Further analysis reveals that our proposed approach prevents agents from overreacting to others through an information bottleneck and aligns the policy with a robust action prior. Empirically, our MIR2 displays even greater resilience against worst-case adversaries than max-min optimization in StarCraft II, Multi-agent Mujoco and rendezvous. Our superiority is consistent when deployed in challenging real-world robot swarm control scenario. See code and demo videos in Supplementary Materials.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge