Roger Gassert
Differentiable Biomechanics for Markerless Motion Capture in Upper Limb Stroke Rehabilitation: A Comparison with Optical Motion Capture
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:Marker-based Optical Motion Capture (OMC) paired with biomechanical modeling is currently considered the most precise and accurate method for measuring human movement kinematics. However, combining differentiable biomechanical modeling with Markerless Motion Capture (MMC) offers a promising approach to motion capture in clinical settings, requiring only minimal equipment, such as synchronized webcams, and minimal effort for data collection. This study compares key kinematic outcomes from biomechanically modeled MMC and OMC data in 15 stroke patients performing the drinking task, a functional task recommended for assessing upper limb movement quality. We observed a high level of agreement in kinematic trajectories between MMC and OMC, as indicated by high correlations (median r above 0.95 for the majority of kinematic trajectories) and median RMSE values ranging from 2-5 degrees for joint angles, 0.04 m/s for end-effector velocity, and 6 mm for trunk displacement. Trial-to-trial biases between OMC and MMC were consistent within participant sessions, with interquartile ranges of bias around 1-3 degrees for joint angles, 0.01 m/s in end-effector velocity, and approximately 3mm for trunk displacement. Our findings indicate that our MMC for arm tracking is approaching the accuracy of marker-based methods, supporting its potential for use in clinical settings. MMC could provide valuable insights into movement rehabilitation in stroke patients, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of rehabilitation strategies.
In the Arms of a Robot: Designing Autonomous Hugging Robots with Intra-Hug Gestures
Feb 20, 2022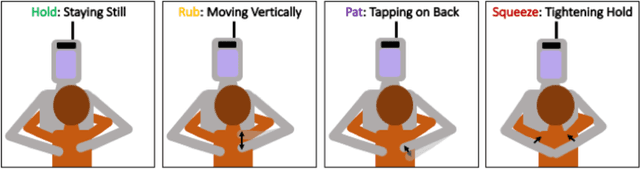
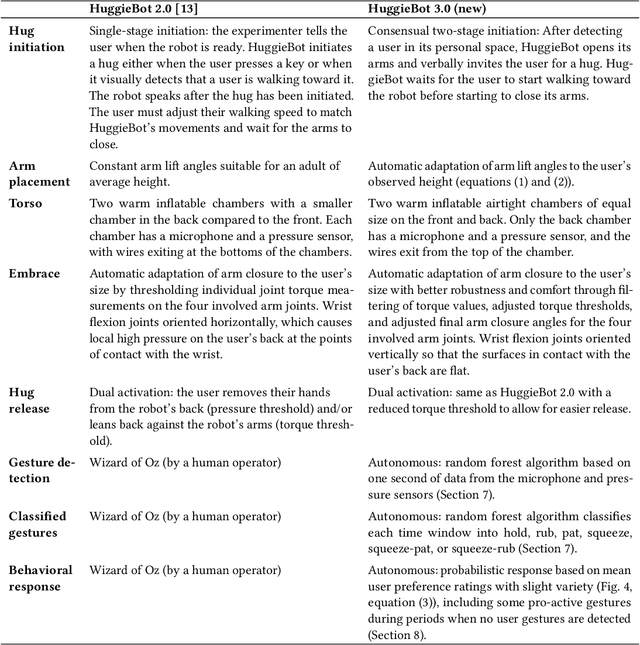
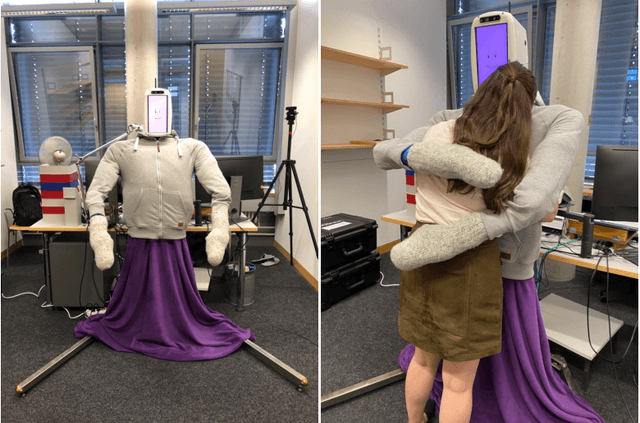
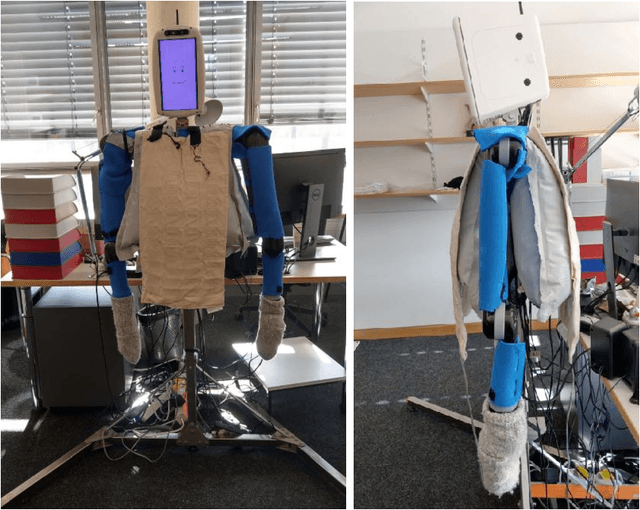
Abstract:Hugs are complex affective interactions that often include gestures like squeezes. We present six new guidelines for designing interactive hugging robots, which we validate through two studies with our custom robot. To achieve autonomy, we investigated robot responses to four human intra-hug gestures: holding, rubbing, patting, and squeezing. Thirty-two users each exchanged and rated sixteen hugs with an experimenter-controlled HuggieBot 2.0. The robot's inflated torso's microphone and pressure sensor collected data of the subjects' demonstrations that were used to develop a perceptual algorithm that classifies user actions with 88\% accuracy. Users enjoyed robot squeezes, regardless of their performed action, they valued variety in the robot response, and they appreciated robot-initiated intra-hug gestures. From average user ratings, we created a probabilistic behavior algorithm that chooses robot responses in real time. We implemented improvements to the robot platform to create HuggieBot 3.0 and then validated its gesture perception system and behavior algorithm with sixteen users. The robot's responses and proactive gestures were greatly enjoyed. Users found the robot more natural, enjoyable, and intelligent in the last phase of the experiment than in the first. After the study, they felt more understood by the robot and thought robots were nicer to hug.
The Six Hug Commandments: Design and Evaluation of a Human-Sized Hugging Robot with Visual and Haptic Perception
Jan 19, 2021


Abstract:Receiving a hug is one of the best ways to feel socially supported, and the lack of social touch can have severe negative effects on an individual's well-being. Based on previous research both within and outside of HRI, we propose six tenets ("commandments") of natural and enjoyable robotic hugging: a hugging robot should be soft, be warm, be human sized, visually perceive its user, adjust its embrace to the user's size and position, and reliably release when the user wants to end the hug. Prior work validated the first two tenets, and the final four are new. We followed all six tenets to create a new robotic platform, HuggieBot 2.0, that has a soft, warm, inflated body (HuggieChest) and uses visual and haptic sensing to deliver closed-loop hugging. We first verified the outward appeal of this platform in comparison to the previous PR2-based HuggieBot 1.0 via an online video-watching study involving 117 users. We then conducted an in-person experiment in which 32 users each exchanged eight hugs with HuggieBot 2.0, experiencing all combinations of visual hug initiation, haptic sizing, and haptic releasing. The results show that adding haptic reactivity definitively improves user perception a hugging robot, largely verifying our four new tenets and illuminating several interesting opportunities for further improvement.
Exoskeleton Knee Compliance Improves Gait Velocity and Stability in a Spinal Cord Injured User: A Case Report
Oct 31, 2019
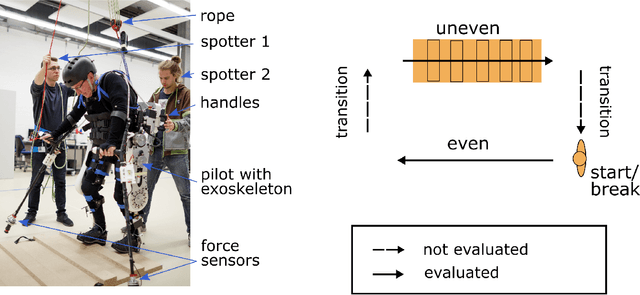


Abstract:Spinal cord injuries frequently impair the ability to walk. Powered lower limb exoskeletons offer a promising solution to restore walking ability. However, they are currently restricted to even ground. We hypothesized that compliant exoskeleton knees could decrease required effort to maneuver on uneven terrain, and increase gait velocity and stability. We describe a case study of a motor-complete spinal cord injury user (AIS A, Th12) walking with a powered exoskeleton on even and uneven ground over multiple sessions after extensive training. Measurements with compliant or rigid exoskeleton knee joints were performed on three different days for each configuration. Body motion and crutch ground interaction forces were recorded to assess gait performance. We observed higher walking speeds with a compliant exoskeleton knee configuration (mean: 0.116 m/s on uneven and 0.145 m/s on even ground) compared to a rigid configuration (mean: 0.083 m/s and 0.100 m/s). Crutch force impulse was significantly reduced in the compliant configuration. Lastly, gait was more symmetric when the knee joints were compliant. In conclusion, compliant exoskeleton knee joints can help maneuver uneven ground faster and with less user effort than rigid joints. Based on our findings, exoskeleton designers should consider introducing compliance into their design to increase gait robustness and performance, and render exoskeletons more suitable for daily life use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge