Rocío Cabrera Lozoya
Detecting Security Fixes in Open-Source Repositories using Static Code Analyzers
May 07, 2021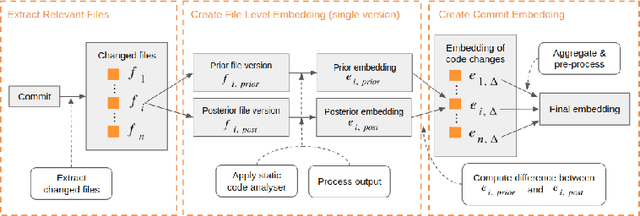
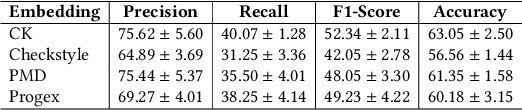
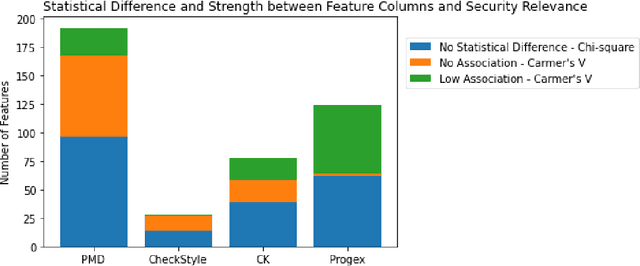
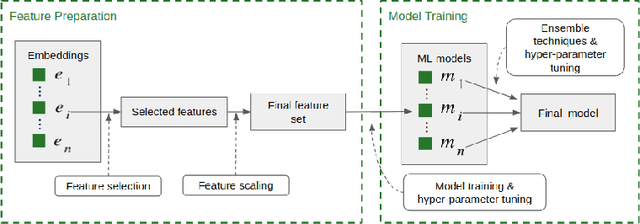
Abstract:The sources of reliable, code-level information about vulnerabilities that affect open-source software (OSS) are scarce, which hinders a broad adoption of advanced tools that provide code-level detection and assessment of vulnerable OSS dependencies. In this paper, we study the extent to which the output of off-the-shelf static code analyzers can be used as a source of features to represent commits in Machine Learning (ML) applications. In particular, we investigate how such features can be used to construct embeddings and train ML models to automatically identify source code commits that contain vulnerability fixes. We analyze such embeddings for security-relevant and non-security-relevant commits, and we show that, although in isolation they are not different in a statistically significant manner, it is possible to use them to construct a ML pipeline that achieves results comparable with the state of the art. We also found that the combination of our method with commit2vec represents a tangible improvement over the state of the art in the automatic identification of commits that fix vulnerabilities: the ML models we construct and commit2vec are complementary, the former being more generally applicable, albeit not as accurate.
Exploiting Token and Path-based Representations of Code for Identifying Security-Relevant Commits
Nov 15, 2019
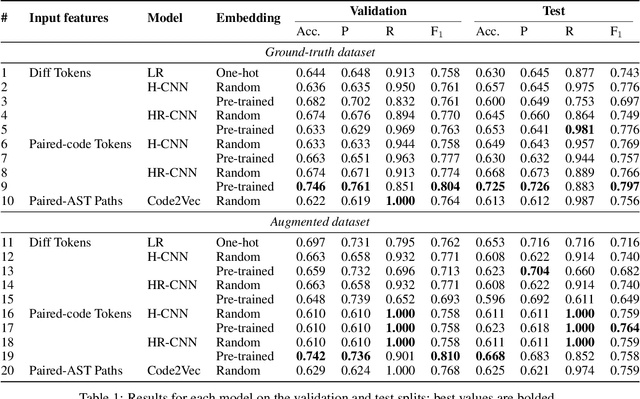
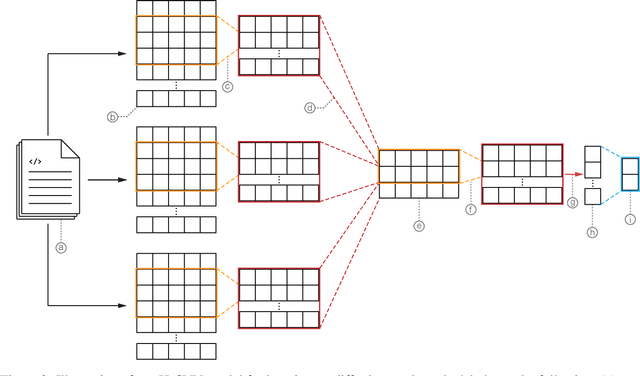
Abstract:Public vulnerability databases such as CVE and NVD account for only 60% of security vulnerabilities present in open-source projects, and are known to suffer from inconsistent quality. Over the last two years, there has been considerable growth in the number of known vulnerabilities across projects available in various repositories such as NPM and Maven Central. Such an increasing risk calls for a mechanism to infer the presence of security threats in a timely manner. We propose novel hierarchical deep learning models for the identification of security-relevant commits from either the commit diff or the source code for the Java classes. By comparing the performance of our model against code2vec, a state-of-the-art model that learns from path-based representations of code, and a logistic regression baseline, we show that deep learning models show promising results in identifying security-related commits. We also conduct a comparative analysis of how various deep learning models learn across different input representations and the effect of regularization on the generalization of our models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge