Robert Atkinson
A Novel Contrastive Loss for Zero-Day Network Intrusion Detection
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Machine learning has achieved state-of-the-art results in network intrusion detection; however, its performance significantly degrades when confronted by a new attack class -- a zero-day attack. In simple terms, classical machine learning-based approaches are adept at identifying attack classes on which they have been previously trained, but struggle with those not included in their training data. One approach to addressing this shortcoming is to utilise anomaly detectors which train exclusively on benign data with the goal of generalising to all attack classes -- both known and zero-day. However, this comes at the expense of a prohibitively high false positive rate. This work proposes a novel contrastive loss function which is able to maintain the advantages of other contrastive learning-based approaches (robustness to imbalanced data) but can also generalise to zero-day attacks. Unlike anomaly detectors, this model learns the distributions of benign traffic using both benign and known malign samples, i.e. other well-known attack classes (not including the zero-day class), and consequently, achieves significant performance improvements. The proposed approach is experimentally verified on the Lycos2017 dataset where it achieves an AUROC improvement of .000065 and .060883 over previous models in known and zero-day attack detection, respectively. Finally, the proposed method is extended to open-set recognition achieving OpenAUC improvements of .170883 over existing approaches.
* Published in: IEEE Transactions on Network Service and Management (TNSM), 2026. Official version: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11340750 Code: https://github.com/jackwilkie/CLOSR
Non-invasive Diver Respiration Rate Monitoring in Hyperbaric Lifeboat Environments using Short-Range Radar
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:The monitoring of diver health during emergency events is crucial to ensuring the safety of personnel. A non-invasive system continuously providing a measure of the respiration rate of individual divers is exceedingly beneficial in this context. The paper reports on the application of short-range radar to record the respiration rate of divers within hyperbaric lifeboat environments. Results demonstrate that the respiratory motion can be extracted from the radar return signal applying routine signal processing. Further, evidence is provided that the radar-based approach yields a more accurate measure of respiration rate than an audio signal from a headset microphone. The system promotes an improvement in evacuation protocols under critical operational scenarios.
Detecting Cloud Presence in Satellite Images Using the RGB-based CLIP Vision-Language Model
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:This work explores capabilities of the pre-trained CLIP vision-language model to identify satellite images affected by clouds. Several approaches to using the model to perform cloud presence detection are proposed and evaluated, including a purely zero-shot operation with text prompts and several fine-tuning approaches. Furthermore, the transferability of the methods across different datasets and sensor types (Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8) is tested. The results that CLIP can achieve non-trivial performance on the cloud presence detection task with apparent capability to generalise across sensing modalities and sensing bands. It is also found that a low-cost fine-tuning stage leads to a strong increase in true negative rate. The results demonstrate that the representations learned by the CLIP model can be useful for satellite image processing tasks involving clouds.
Neural Weight Step Video Compression
Dec 02, 2021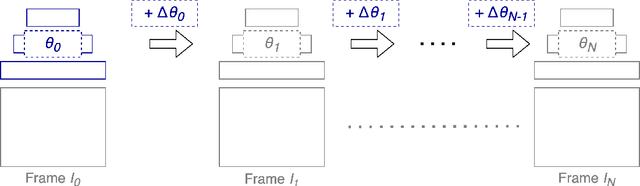
Abstract:A variety of compression methods based on encoding images as weights of a neural network have been recently proposed. Yet, the potential of similar approaches for video compression remains unexplored. In this work, we suggest a set of experiments for testing the feasibility of compressing video using two architectural paradigms, coordinate-based MLP (CbMLP) and convolutional network. Furthermore, we propose a novel technique of neural weight stepping, where subsequent frames of a video are encoded as low-entropy parameter updates. To assess the feasibility of the considered approaches, we will test the video compression performance on several high-resolution video datasets and compare against existing conventional and neural compression techniques.
Neural Knitworks: Patched Neural Implicit Representation Networks
Sep 29, 2021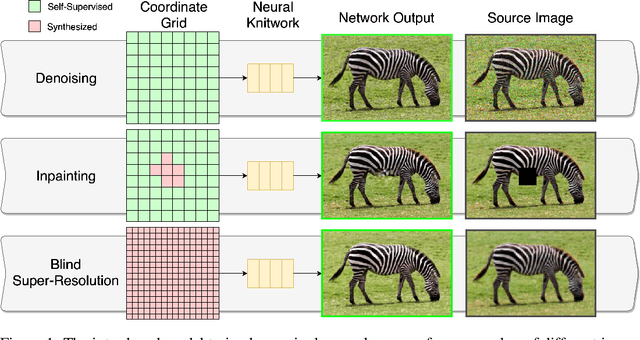
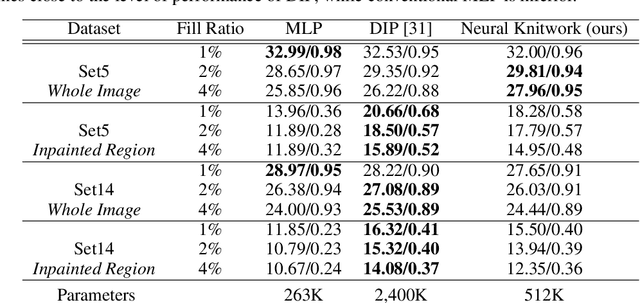
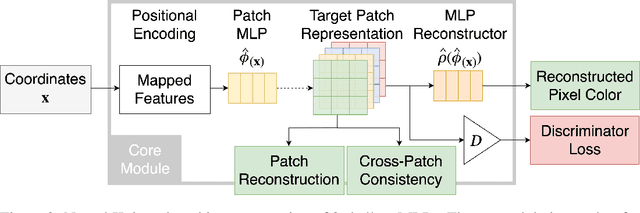
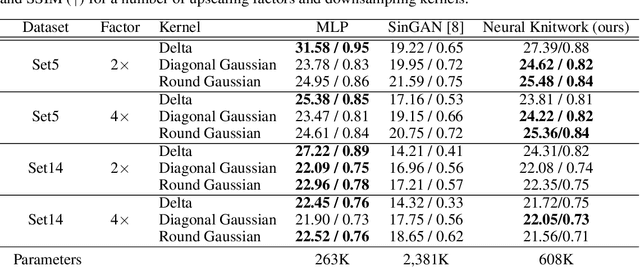
Abstract:Coordinate-based Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) networks, despite being capable of learning neural implicit representations, are not performant for internal image synthesis applications. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are typically used instead for a variety of internal generative tasks, at the cost of a larger model. We propose Neural Knitwork, an architecture for neural implicit representation learning of natural images that achieves image synthesis by optimizing the distribution of image patches in an adversarial manner and by enforcing consistency between the patch predictions. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first implementation of a coordinate-based MLP tailored for synthesis tasks such as image inpainting, super-resolution, and denoising. We demonstrate the utility of the proposed technique by training on these three tasks. The results show that modeling natural images using patches, rather than pixels, produces results of higher fidelity. The resulting model requires 80% fewer parameters than alternative CNN-based solutions while achieving comparable performance and training time.
Utilising Flow Aggregation to Classify Benign Imitating Attacks
Mar 06, 2021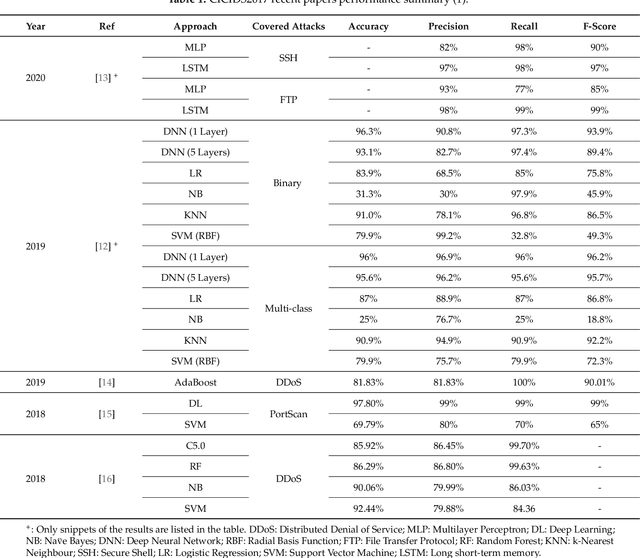
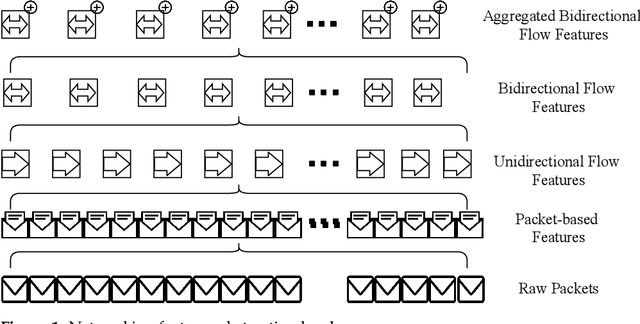
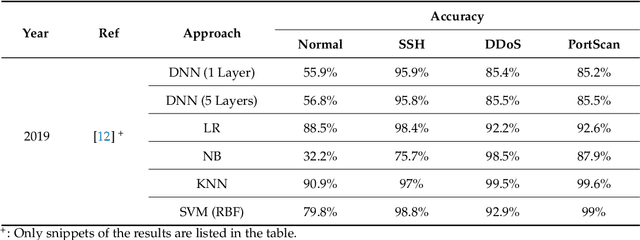
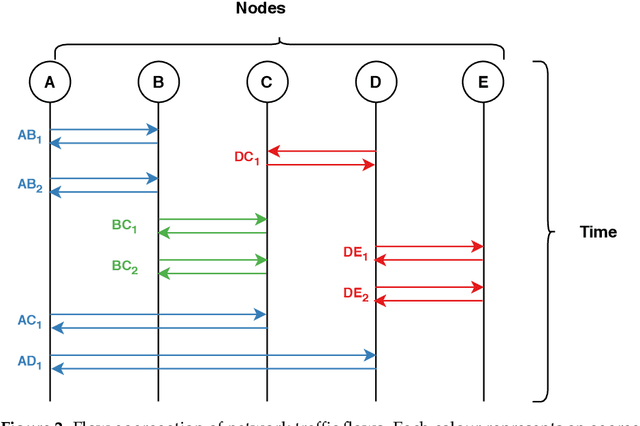
Abstract:Cyber-attacks continue to grow, both in terms of volume and sophistication. This is aided by an increase in available computational power, expanding attack surfaces, and advancements in the human understanding of how to make attacks undetectable. Unsurprisingly, machine learning is utilised to defend against these attacks. In many applications, the choice of features is more important than the choice of model. A range of studies have, with varying degrees of success, attempted to discriminate between benign traffic and well-known cyber-attacks. The features used in these studies are broadly similar and have demonstrated their effectiveness in situations where cyber-attacks do not imitate benign behaviour. To overcome this barrier, in this manuscript, we introduce new features based on a higher level of abstraction of network traffic. Specifically, we perform flow aggregation by grouping flows with similarities. This additional level of feature abstraction benefits from cumulative information, thus qualifying the models to classify cyber-attacks that mimic benign traffic. The performance of the new features is evaluated using the benchmark CICIDS2017 dataset, and the results demonstrate their validity and effectiveness. This novel proposal will improve the detection accuracy of cyber-attacks and also build towards a new direction of feature extraction for complex ones.
* 21 pages, 6 figures
Leveraging Siamese Networks for One-Shot Intrusion Detection Model
Jun 27, 2020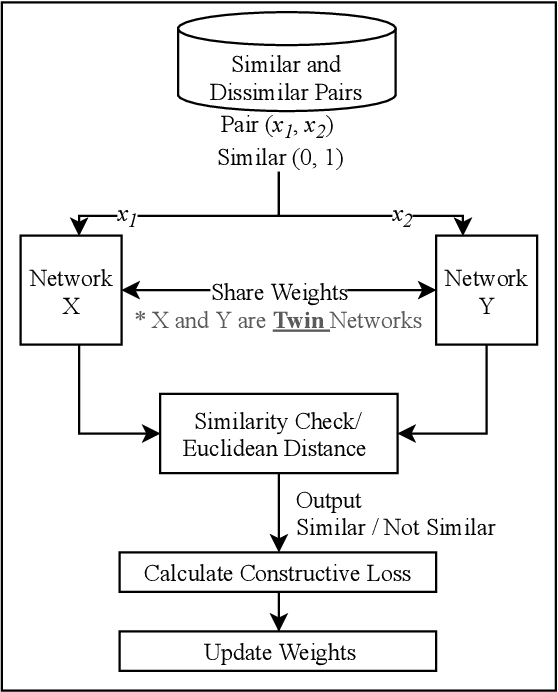

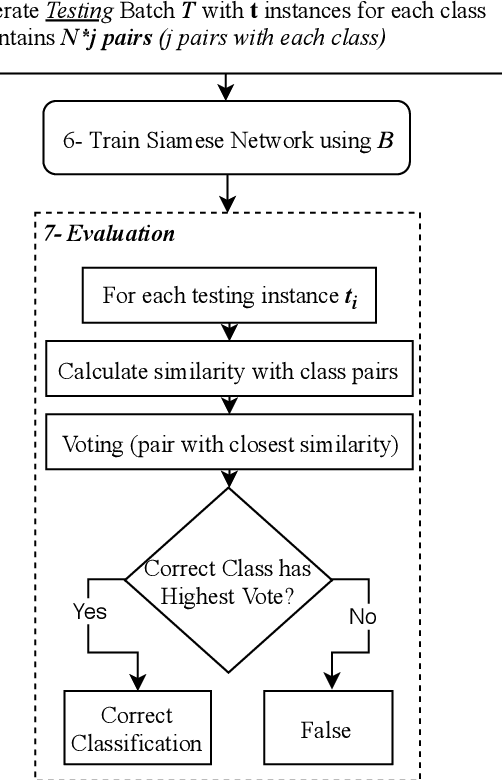
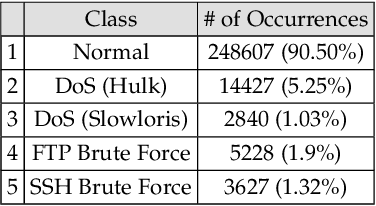
Abstract:The use of supervised Machine Learning (ML) to enhance Intrusion Detection Systems has been the subject of significant research. Supervised ML is based upon learning by example, demanding significant volumes of representative instances for effective training and the need to re-train the model for every unseen cyber-attack class. However, retraining the models in-situ renders the network susceptible to attacks owing to the time-window required to acquire a sufficient volume of data. Although anomaly detection systems provide a coarse-grained defence against unseen attacks, these approaches are significantly less accurate and suffer from high false-positive rates. Here, a complementary approach referred to as 'One-Shot Learning', whereby a limited number of examples of a new attack-class is used to identify a new attack-class (out of many) is detailed. The model grants a new cyber-attack classification without retraining. A Siamese Network is trained to differentiate between classes based on pairs similarities, rather than features, allowing to identify new and previously unseen attacks. The performance of a pre-trained model to classify attack-classes based only on one example is evaluated using three datasets. Results confirm the adaptability of the model in classifying unseen attacks and the trade-off between performance and the need for distinctive class representation.
A Taxonomy and Survey of Intrusion Detection System Design Techniques, Network Threats and Datasets
Jun 09, 2018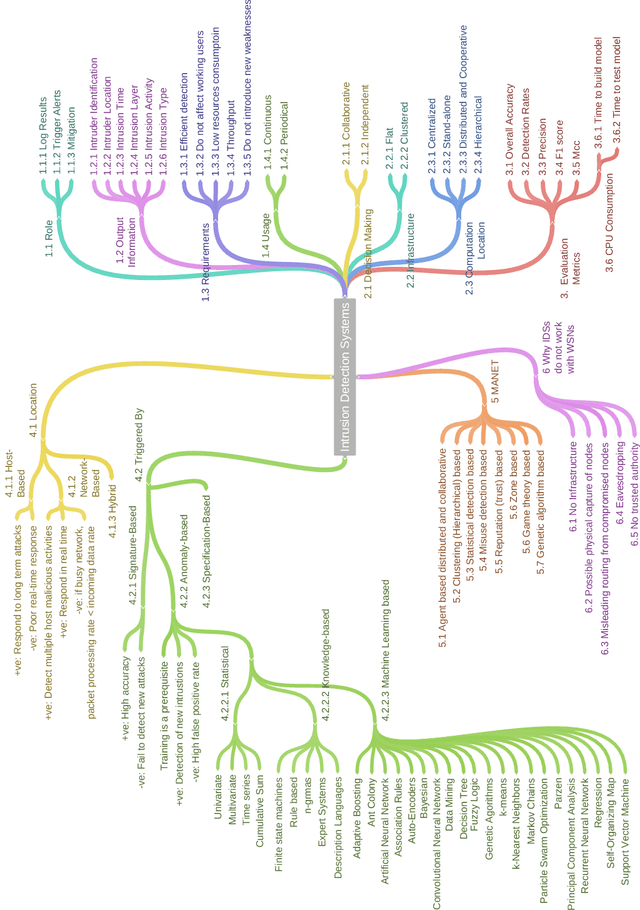
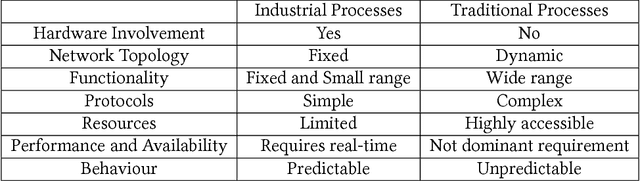
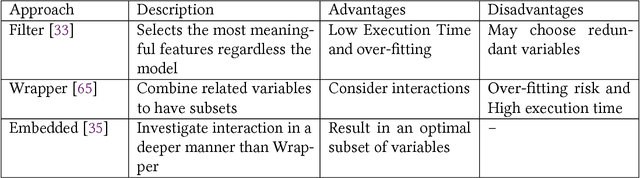
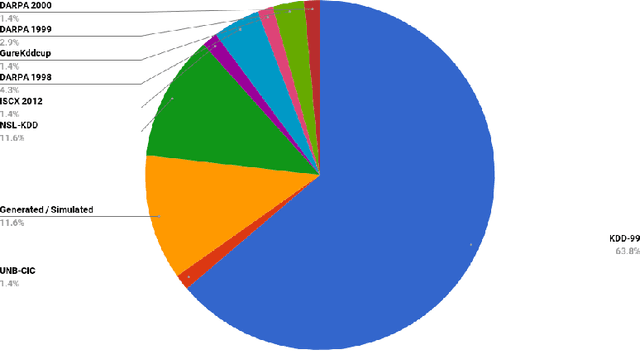
Abstract:With the world moving towards being increasingly dependent on computers and automation, one of the main challenges in the current decade has been to build secure applications, systems and networks. Alongside these challenges, the number of threats is rising exponentially due to the attack surface increasing through numerous interfaces offered for each service. To alleviate the impact of these threats, researchers have proposed numerous solutions; however, current tools often fail to adapt to ever-changing architectures, associated threats and 0-days. This manuscript aims to provide researchers with a taxonomy and survey of current dataset composition and current Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) capabilities and assets. These taxonomies and surveys aim to improve both the efficiency of IDS and the creation of datasets to build the next generation IDS as well as to reflect networks threats more accurately in future datasets. To this end, this manuscript also provides a taxonomy and survey or network threats and associated tools. The manuscript highlights that current IDS only cover 25% of our threat taxonomy, while current datasets demonstrate clear lack of real-network threats and attack representation, but rather include a large number of deprecated threats, hence limiting the accuracy of current machine learning IDS. Moreover, the taxonomies are open-sourced to allow public contributions through a Github repository.
Machine Learning Approach for Detection of nonTor Traffic
Aug 29, 2017
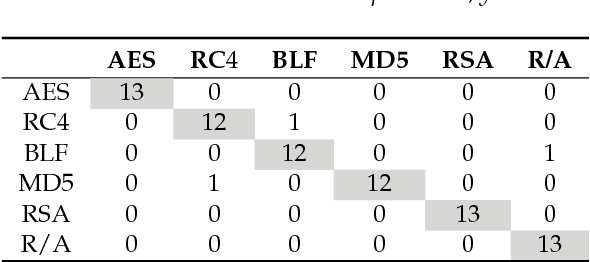
Abstract:Intrusion detection has attracted a considerable interest from researchers and industries. After many years of research the community still faces the problem of building reliable and efficient intrusion detection systems (IDS) capable of handling large quantities of data with changing patterns in real time situations. The Tor network is popular in providing privacy and security to end user by anonymising the identity of internet users connecting through a series of tunnels and nodes. This work focuses on the classification of Tor traffic and nonTor traffic to expose the activities within Tor traffic that minimizes the protection of users. A study to compare the reliability and efficiency of Artificial Neural Network and Support vector machine in detecting nonTor traffic in UNB-CIC Tor Network Traffic dataset is presented in this paper. The results are analysed based on the overall accuracy, detection rate and false positive rate of the two algorithms. Experimental results show that both algorithms could detect nonTor traffic in the dataset. A hybrid Artificial neural network proved a better classifier than SVM in detecting nonTor traffic in UNB-CIC Tor Network Traffic dataset.
* 6 pages, 4 figures, Accepted and Presented in ARES '17 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security
Threat analysis of IoT networks Using Artificial Neural Network Intrusion Detection System
Apr 07, 2017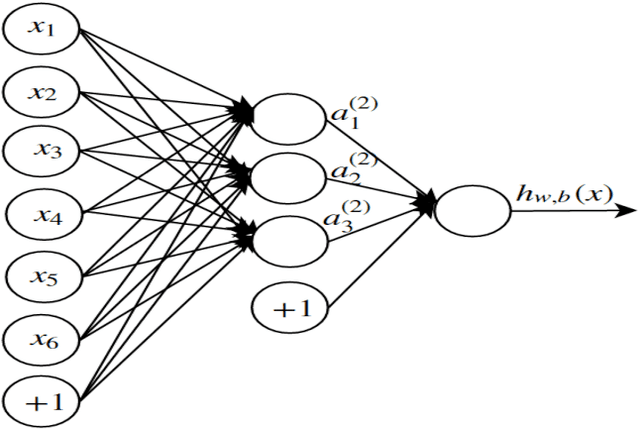
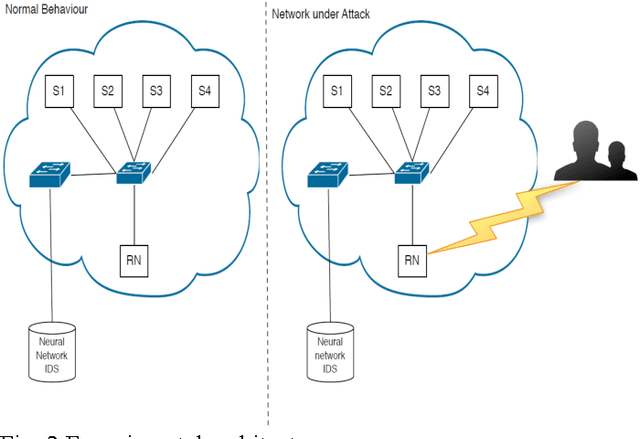
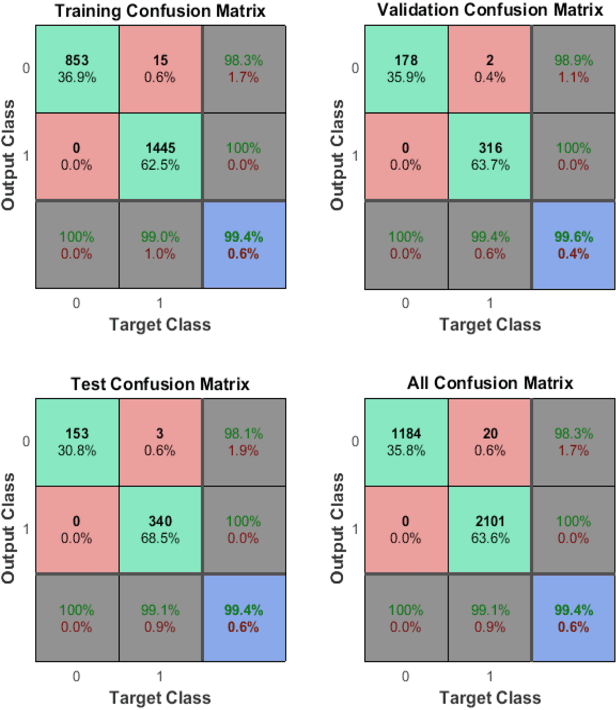
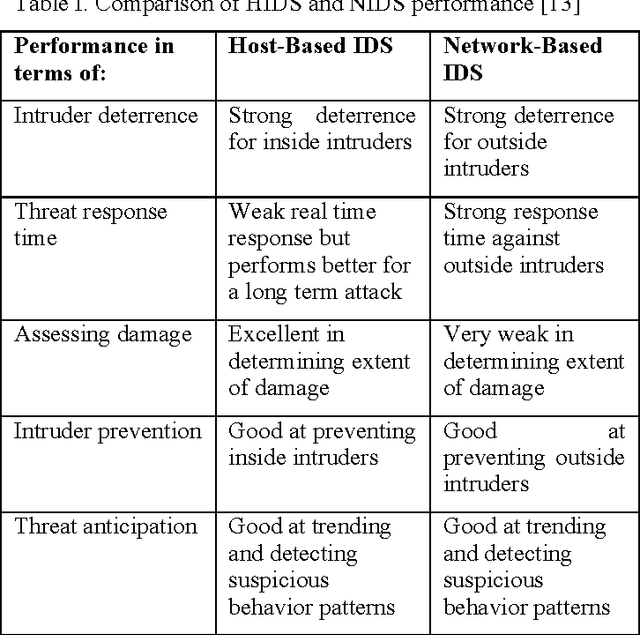
Abstract:The Internet of things (IoT) is still in its infancy and has attracted much interest in many industrial sectors including medical fields, logistics tracking, smart cities and automobiles. However as a paradigm, it is susceptible to a range of significant intrusion threats. This paper presents a threat analysis of the IoT and uses an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) to combat these threats. A multi-level perceptron, a type of supervised ANN, is trained using internet packet traces, then is assessed on its ability to thwart Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS/DoS) attacks. This paper focuses on the classification of normal and threat patterns on an IoT Network. The ANN procedure is validated against a simulated IoT network. The experimental results demonstrate 99.4% accuracy and can successfully detect various DDoS/DoS attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge