David Brosset
Leveraging Siamese Networks for One-Shot Intrusion Detection Model
Jun 27, 2020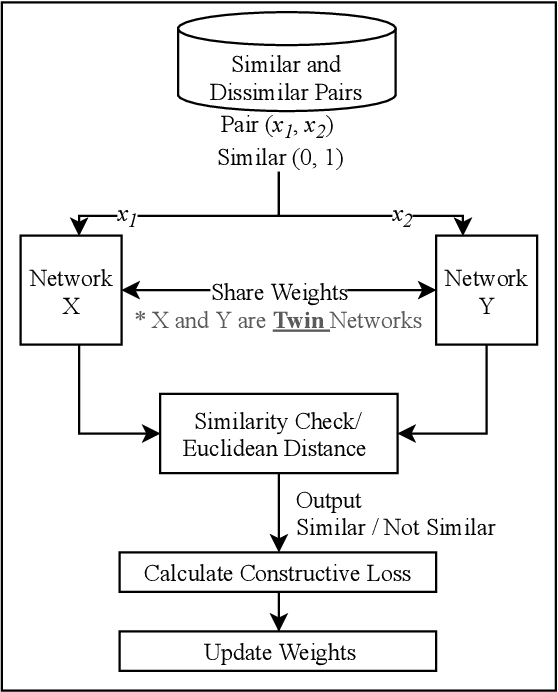

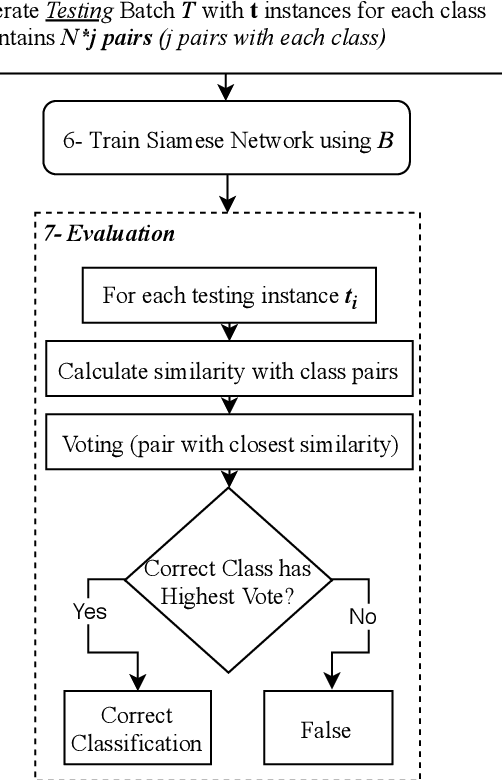
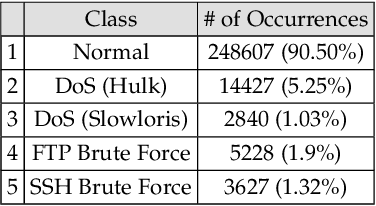
Abstract:The use of supervised Machine Learning (ML) to enhance Intrusion Detection Systems has been the subject of significant research. Supervised ML is based upon learning by example, demanding significant volumes of representative instances for effective training and the need to re-train the model for every unseen cyber-attack class. However, retraining the models in-situ renders the network susceptible to attacks owing to the time-window required to acquire a sufficient volume of data. Although anomaly detection systems provide a coarse-grained defence against unseen attacks, these approaches are significantly less accurate and suffer from high false-positive rates. Here, a complementary approach referred to as 'One-Shot Learning', whereby a limited number of examples of a new attack-class is used to identify a new attack-class (out of many) is detailed. The model grants a new cyber-attack classification without retraining. A Siamese Network is trained to differentiate between classes based on pairs similarities, rather than features, allowing to identify new and previously unseen attacks. The performance of a pre-trained model to classify attack-classes based only on one example is evaluated using three datasets. Results confirm the adaptability of the model in classifying unseen attacks and the trade-off between performance and the need for distinctive class representation.
Improving SIEM for Critical SCADA Water Infrastructures Using Machine Learning
Mar 06, 2019



Abstract:Network Control Systems (NAC) have been used in many industrial processes. They aim to reduce the human factor burden and efficiently handle the complex process and communication of those systems. Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems are used in industrial, infrastructure and facility processes (e.g. manufacturing, fabrication, oil and water pipelines, building ventilation, etc.) Like other Internet of Things (IoT) implementations, SCADA systems are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, therefore, a robust anomaly detection is a major requirement. However, having an accurate anomaly detection system is not an easy task, due to the difficulty to differentiate between cyber-attacks and system internal failures (e.g. hardware failures). In this paper, we present a model that detects anomaly events in a water system controlled by SCADA. Six Machine Learning techniques have been used in building and evaluating the model. The model classifies different anomaly events including hardware failures (e.g. sensor failures), sabotage and cyber-attacks (e.g. DoS and Spoofing). Unlike other detection systems, our proposed work focuses on notifying the operator when an anomaly occurs with a probability of the event occurring. This additional information helps in accelerating the mitigation process. The model is trained and tested using a real-world dataset.
* 17 pages, 8 figures, 4 tables. In the proceeding of International Workshop on the Security of Industrial Control Systems and Cyber-Physical Systems CyberICPS, In Conjunction With ESORICS 2018
A Taxonomy and Survey of Intrusion Detection System Design Techniques, Network Threats and Datasets
Jun 09, 2018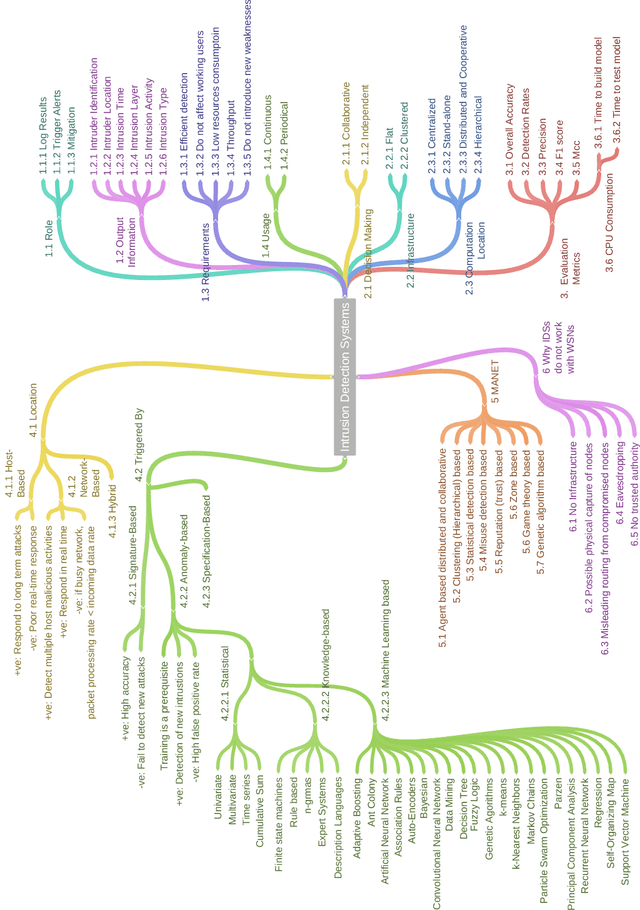
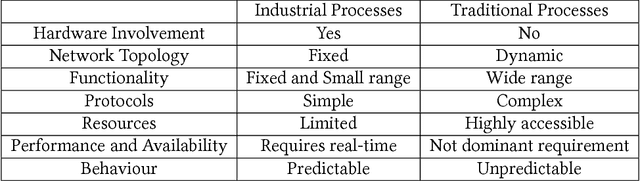
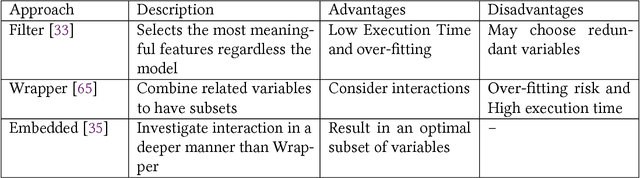
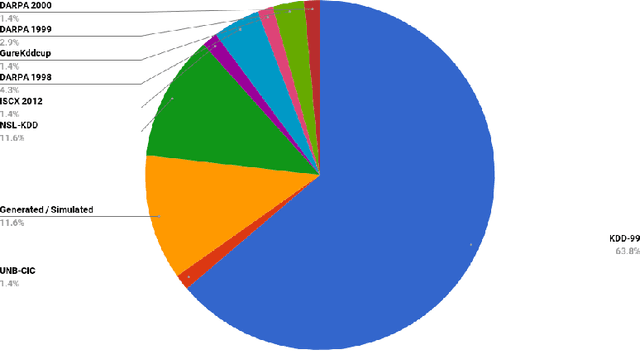
Abstract:With the world moving towards being increasingly dependent on computers and automation, one of the main challenges in the current decade has been to build secure applications, systems and networks. Alongside these challenges, the number of threats is rising exponentially due to the attack surface increasing through numerous interfaces offered for each service. To alleviate the impact of these threats, researchers have proposed numerous solutions; however, current tools often fail to adapt to ever-changing architectures, associated threats and 0-days. This manuscript aims to provide researchers with a taxonomy and survey of current dataset composition and current Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) capabilities and assets. These taxonomies and surveys aim to improve both the efficiency of IDS and the creation of datasets to build the next generation IDS as well as to reflect networks threats more accurately in future datasets. To this end, this manuscript also provides a taxonomy and survey or network threats and associated tools. The manuscript highlights that current IDS only cover 25% of our threat taxonomy, while current datasets demonstrate clear lack of real-network threats and attack representation, but rather include a large number of deprecated threats, hence limiting the accuracy of current machine learning IDS. Moreover, the taxonomies are open-sourced to allow public contributions through a Github repository.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge