Rihao Chang
Organ-Agents: Virtual Human Physiology Simulator via LLMs
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled new possibilities in simulating complex physiological systems. We introduce Organ-Agents, a multi-agent framework that simulates human physiology via LLM-driven agents. Each Simulator models a specific system (e.g., cardiovascular, renal, immune). Training consists of supervised fine-tuning on system-specific time-series data, followed by reinforcement-guided coordination using dynamic reference selection and error correction. We curated data from 7,134 sepsis patients and 7,895 controls, generating high-resolution trajectories across 9 systems and 125 variables. Organ-Agents achieved high simulation accuracy on 4,509 held-out patients, with per-system MSEs <0.16 and robustness across SOFA-based severity strata. External validation on 22,689 ICU patients from two hospitals showed moderate degradation under distribution shifts with stable simulation. Organ-Agents faithfully reproduces critical multi-system events (e.g., hypotension, hyperlactatemia, hypoxemia) with coherent timing and phase progression. Evaluation by 15 critical care physicians confirmed realism and physiological plausibility (mean Likert ratings 3.9 and 3.7). Organ-Agents also enables counterfactual simulations under alternative sepsis treatment strategies, generating trajectories and APACHE II scores aligned with matched real-world patients. In downstream early warning tasks, classifiers trained on synthetic data showed minimal AUROC drops (<0.04), indicating preserved decision-relevant patterns. These results position Organ-Agents as a credible, interpretable, and generalizable digital twin for precision diagnosis, treatment simulation, and hypothesis testing in critical care.
Causal Disentanglement Hidden Markov Model for Fault Diagnosis
Aug 06, 2023

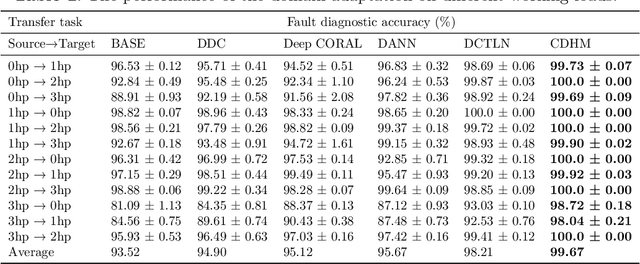

Abstract:In modern industries, fault diagnosis has been widely applied with the goal of realizing predictive maintenance. The key issue for the fault diagnosis system is to extract representative characteristics of the fault signal and then accurately predict the fault type. In this paper, we propose a Causal Disentanglement Hidden Markov model (CDHM) to learn the causality in the bearing fault mechanism and thus, capture their characteristics to achieve a more robust representation. Specifically, we make full use of the time-series data and progressively disentangle the vibration signal into fault-relevant and fault-irrelevant factors. The ELBO is reformulated to optimize the learning of the causal disentanglement Markov model. Moreover, to expand the scope of the application, we adopt unsupervised domain adaptation to transfer the learned disentangled representations to other working environments. Experiments were conducted on the CWRU dataset and IMS dataset. Relevant results validate the superiority of the proposed method.
3D Shape Knowledge Graph for Cross-domain and Cross-modal 3D Shape Retrieval
Oct 27, 2022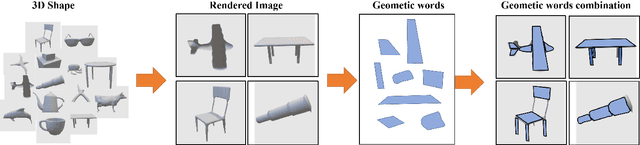

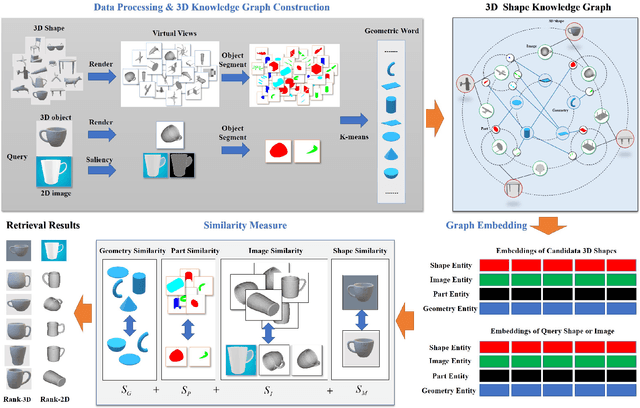

Abstract:With the development of 3D modeling and fabrication, 3D shape retrieval has become a hot topic. In recent years, several strategies have been put forth to address this retrieval issue. However, it is difficult for them to handle cross-modal 3D shape retrieval because of the natural differences between modalities. In this paper, we propose an innovative concept, namely, geometric words, which is regarded as the basic element to represent any 3D or 2D entity by combination, and assisted by which, we can simultaneously handle cross-domain or cross-modal retrieval problems. First, to construct the knowledge graph, we utilize the geometric word as the node, and then use the category of the 3D shape as well as the attribute of the geometry to bridge the nodes. Second, based on the knowledge graph, we provide a unique way for learning each entity's embedding. Finally, we propose an effective similarity measure to handle the cross-domain and cross-modal 3D shape retrieval. Specifically, every 3D or 2D entity could locate its geometric terms in the 3D knowledge graph, which serve as a link between cross-domain and cross-modal data. Thus, our approach can achieve the cross-domain and cross-modal 3D shape retrieval at the same time. We evaluated our proposed method on the ModelNet40 dataset and ShapeNetCore55 dataset for both the 3D shape retrieval task and cross-domain 3D shape retrieval task. The classic cross-modal dataset (MI3DOR) is utilized to evaluate cross-modal 3D shape retrieval. Experimental results and comparisons with state-of-the-art methods illustrate the superiority of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge