Richard Schwartz
BBN
Combining Word Embeddings and N-grams for Unsupervised Document Summarization
Apr 25, 2020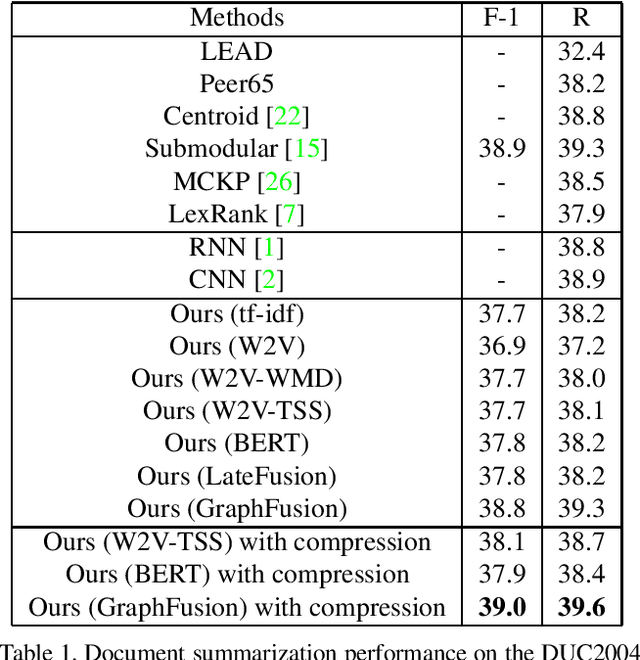
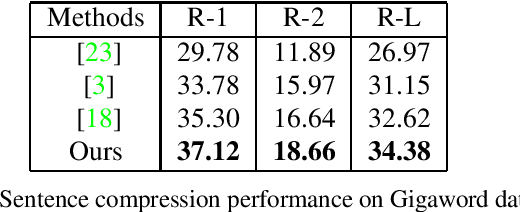
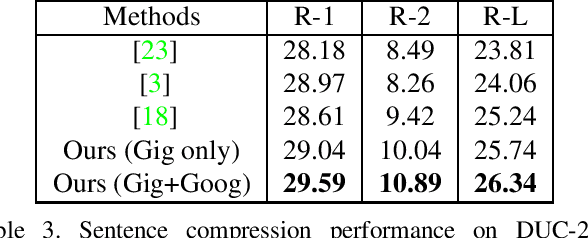
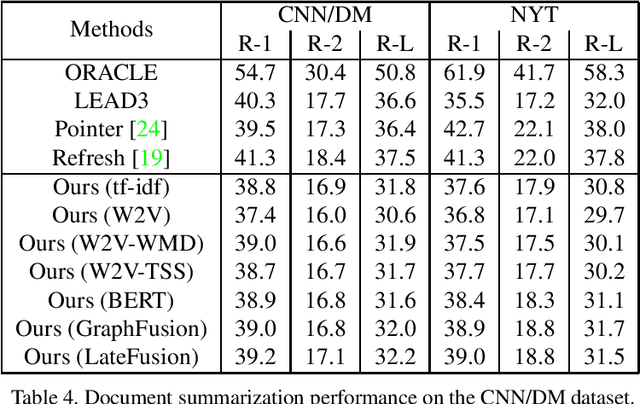
Abstract:Graph-based extractive document summarization relies on the quality of the sentence similarity graph. Bag-of-words or tf-idf based sentence similarity uses exact word matching, but fails to measure the semantic similarity between individual words or to consider the semantic structure of sentences. In order to improve the similarity measure between sentences, we employ off-the-shelf deep embedding features and tf-idf features, and introduce a new text similarity metric. An improved sentence similarity graph is built and used in a submodular objective function for extractive summarization, which consists of a weighted coverage term and a diversity term. A Transformer based compression model is developed for sentence compression to aid in document summarization. Our summarization approach is extractive and unsupervised. Experiments demonstrate that our approach can outperform the tf-idf based approach and achieve state-of-the-art performance on the DUC04 dataset, and comparable performance to the fully supervised learning methods on the CNN/DM and NYT datasets.
MEM_GE: a new maximum entropy method for image reconstruction from solar X-ray visibilities
Feb 18, 2020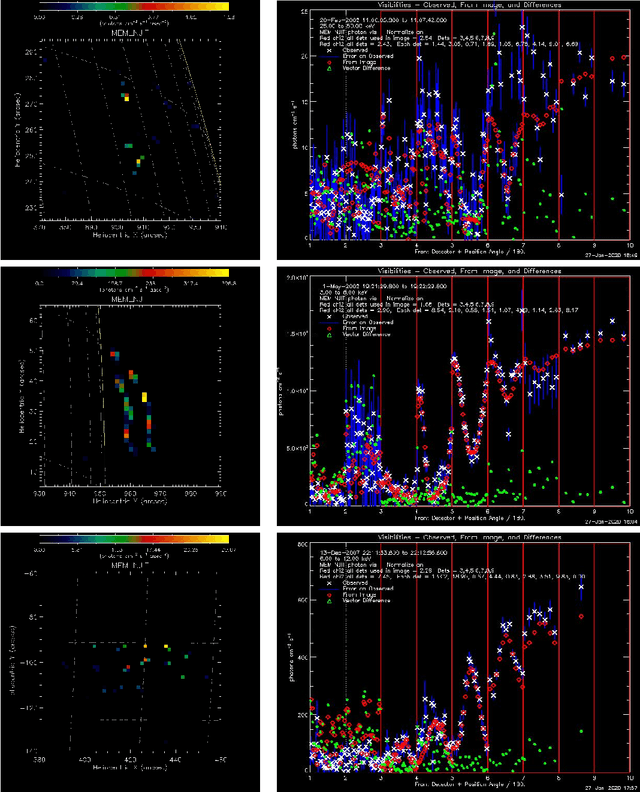
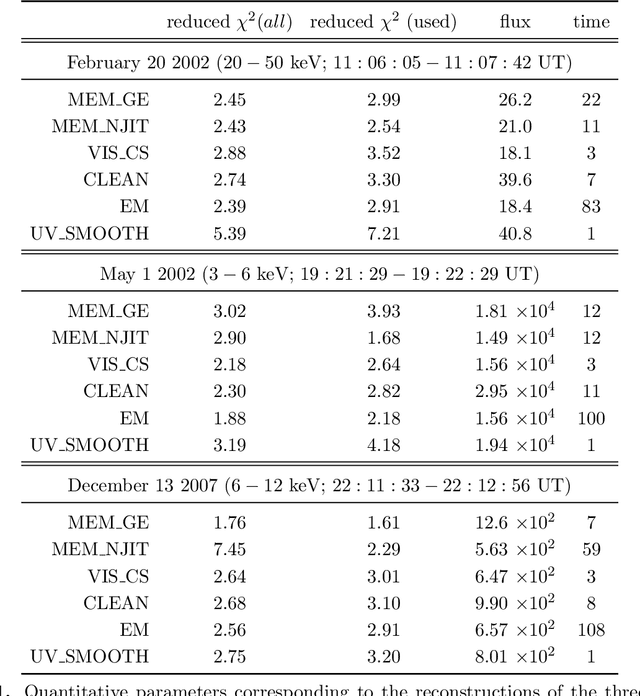

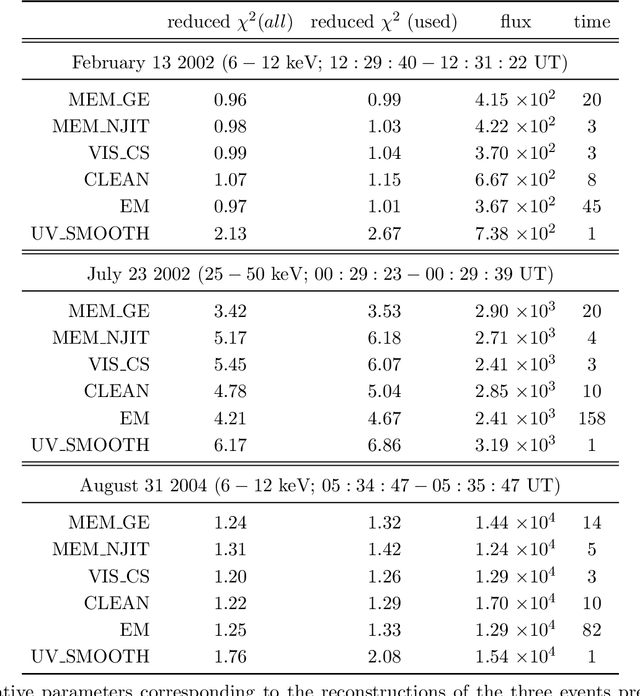
Abstract:Maximum Entropy is an image reconstruction method conceived to image a sparsely occupied field of view and therefore particularly appropriate to achieve super-resolution effects. Although widely used in image deconvolution, this method has been formulated in radio astronomy for the analysis of observations in the spatial frequency domain, and an Interactive Data Language (IDL) code has been implemented for image reconstruction from solar X-ray Fourier data. However, this code relies on a non-convex formulation of the constrained optimization problem addressed by the Maximum Entropy approach and this sometimes results in unreliable reconstructions characterized by unphysical shrinking effects. This paper introduces a new approach to Maximum Entropy based on the constrained minimization of a convex functional. In the case of observations recorded by the Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI), the resulting code provides the same super-resolution effects of the previous algorithm, while working properly also when that code produces unphysical reconstructions. Results are also provided of testing the algorithm with synthetic data simulating observations of the Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX) in Solar Orbiter. The new code is available in the {\em{HESSI}} folder of the Solar SoftWare (SSW)tree.
Desaturating EUV observations of solar flaring storms
Apr 08, 2019
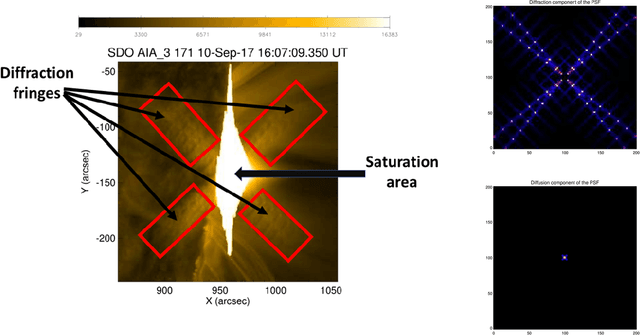
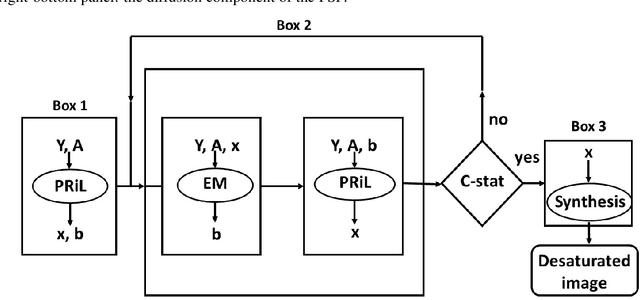
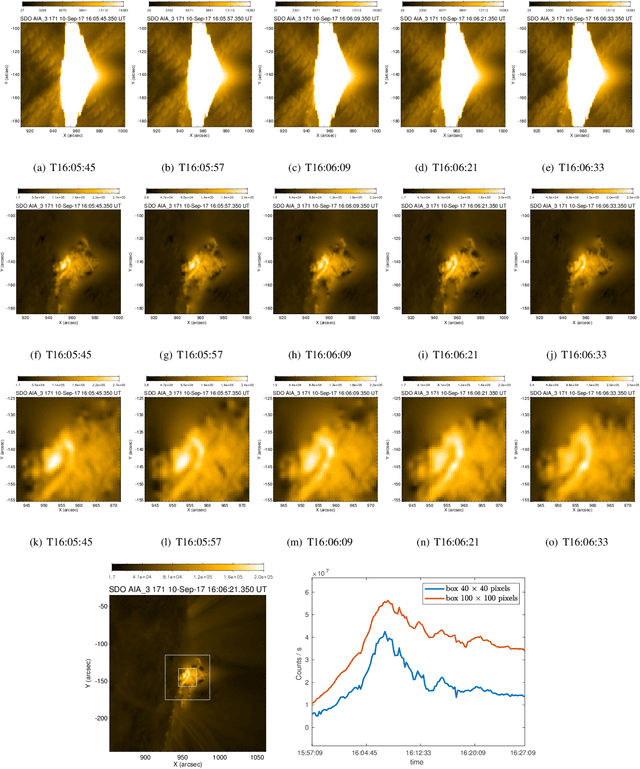
Abstract:Image saturation has been an issue for several instruments in solar astronomy, mainly at EUV wavelengths. However, with the launch of the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) as part of the payload of the Solar Dynamic Observatory (SDO) image saturation has become a big data issue, involving around 10^$ frames of the impressive dataset this beautiful telescope has been providing every year since February 2010. This paper introduces a novel desaturation method, which is able to recover the signal in the saturated region of any AIA image by exploiting no other information but the one contained in the image itself. This peculiar methodological property, jointly with the unprecedented statistical reliability of the desaturated images, could make this algorithm the perfect tool for the realization of a reconstruction pipeline for AIA data, able to work properly even in the case of long-lasting, very energetic flaring events.
Statistical Machine Translation Features with Multitask Tensor Networks
Jun 01, 2015
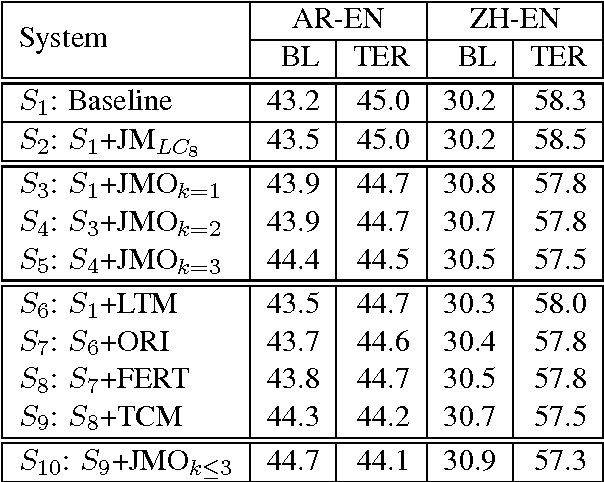
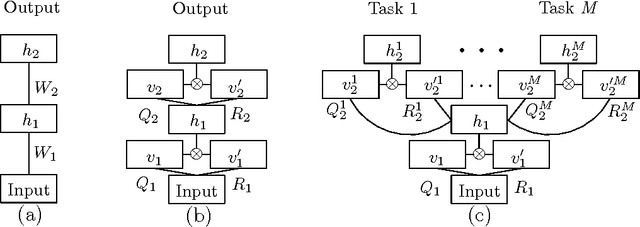
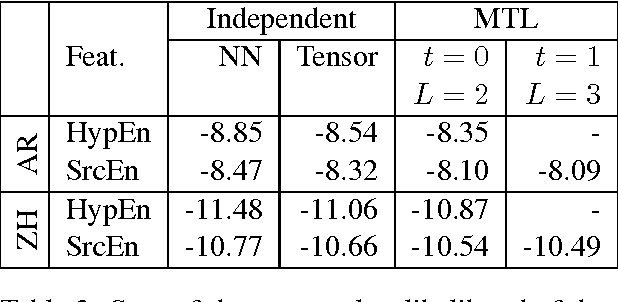
Abstract:We present a three-pronged approach to improving Statistical Machine Translation (SMT), building on recent success in the application of neural networks to SMT. First, we propose new features based on neural networks to model various non-local translation phenomena. Second, we augment the architecture of the neural network with tensor layers that capture important higher-order interaction among the network units. Third, we apply multitask learning to estimate the neural network parameters jointly. Each of our proposed methods results in significant improvements that are complementary. The overall improvement is +2.7 and +1.8 BLEU points for Arabic-English and Chinese-English translation over a state-of-the-art system that already includes neural network features.
Nymble: a High-Performance Learning Name-finder
Mar 27, 1998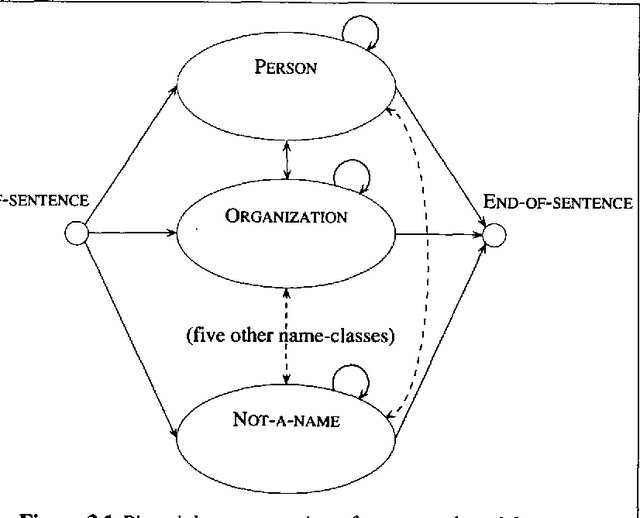
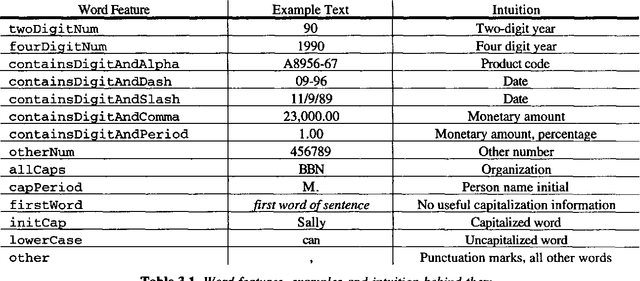
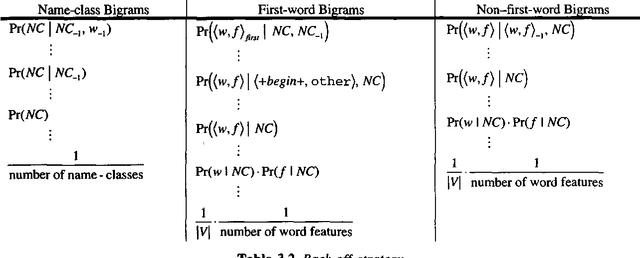
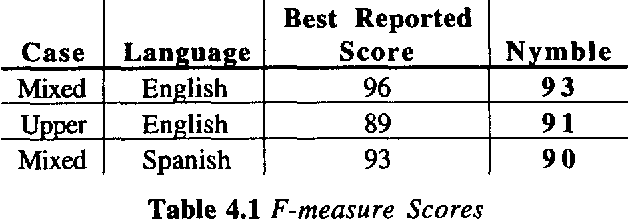
Abstract:This paper presents a statistical, learned approach to finding names and other non-recursive entities in text (as per the MUC-6 definition of the NE task), using a variant of the standard hidden Markov model. We present our justification for the problem and our approach, a detailed discussion of the model itself and finally the successful results of this new approach.
* Postscript only, 8 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge