Paolo Massa
PRESOL: a web-based computational setting for feature-based flare forecasting
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Solar flares are the most explosive phenomena in the solar system and the main trigger of the events' chain that starts from Coronal Mass Ejections and leads to geomagnetic storms with possible impacts on the infrastructures at Earth. Data-driven solar flare forecasting relies on either deep learning approaches, which are operationally promising but with a low explainability degree, or machine learning algorithms, which can provide information on the physical descriptors that mostly impact the prediction. This paper describes a web-based technological platform for the execution of a computational pipeline of feature-based machine learning methods that provide predictions of the flare occurrence, feature ranking information, and assessment of the prediction performances.
Enhancing Image Resolution of Solar Magnetograms: A Latent Diffusion Model Approach
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The spatial properties of the solar magnetic field are crucial to decoding the physical processes in the solar interior and their interplanetary effects. However, observations from older instruments, such as the Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI), have limited spatial or temporal resolution, which hinders the ability to study small-scale solar features in detail. Super resolving these older datasets is essential for uniform analysis across different solar cycles, enabling better characterization of solar flares, active regions, and magnetic network dynamics. In this work, we introduce a novel diffusion model approach for Super-Resolution and we apply it to MDI magnetograms to match the higher-resolution capabilities of the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI). By training a Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) with residuals on downscaled HMI data and fine-tuning it with paired MDI/HMI data, we can enhance the resolution of MDI observations from 2"/pixel to 0.5"/pixel. We evaluate the quality of the reconstructed images by means of classical metrics (e.g., PSNR, SSIM, FID and LPIPS) and we check if physical properties, such as the unsigned magnetic flux or the size of an active region, are preserved. We compare our model with different variations of LDM and Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic models (DDPMs), but also with two deterministic architectures already used in the past for performing the Super-Resolution task. Furthermore, we show with an analysis in the Fourier domain that the LDM with residuals can resolve features smaller than 2", and due to the probabilistic nature of the LDM, we can asses their reliability, in contrast with the deterministic models. Future studies aim to super-resolve the temporal scale of the solar MDI instrument so that we can also have a better overview of the dynamics of the old events.
AI-FLARES: Artificial Intelligence for the Analysis of Solar Flares Data
Jan 02, 2024Abstract:AI-FLARES (Artificial Intelligence for the Analysis of Solar Flares Data) is a research project funded by the Agenzia Spaziale Italiana and by the Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica within the framework of the ``Attivit\`a di Studio per la Comunit\`a Scientifica Nazionale Sole, Sistema Solare ed Esopianeti'' program. The topic addressed by this project was the development and use of computational methods for the analysis of remote sensing space data associated to solar flare emission. This paper overviews the main results obtained by the project, with specific focus on solar flare forecasting, reconstruction of morphologies of the flaring sources, and interpretation of acceleration mechanisms triggered by solar flares.
Visibility Interpolation in Solar Hard X-ray Imaging: Application to RHESSI and STIX
Dec 27, 2020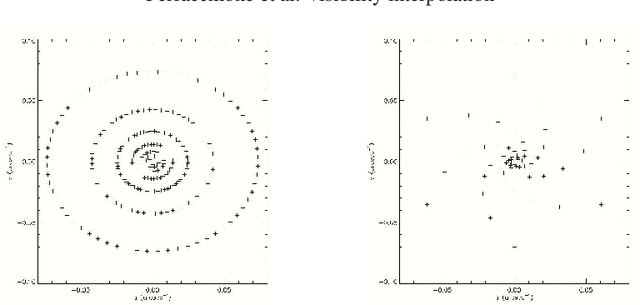
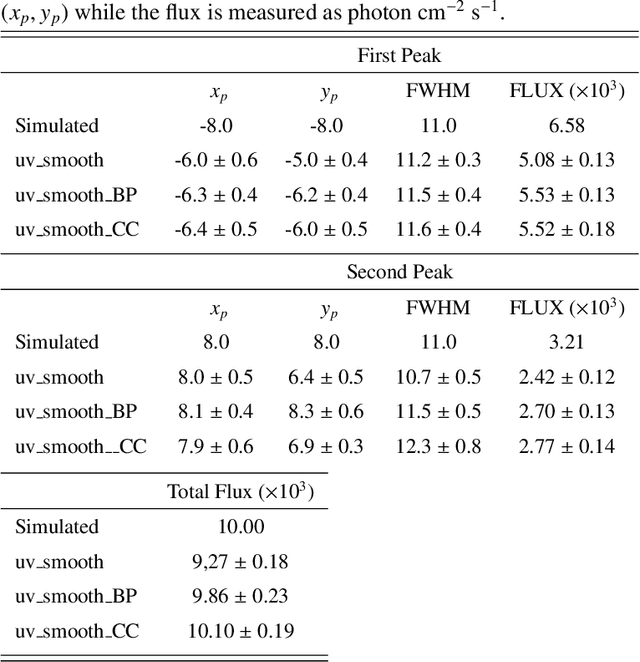
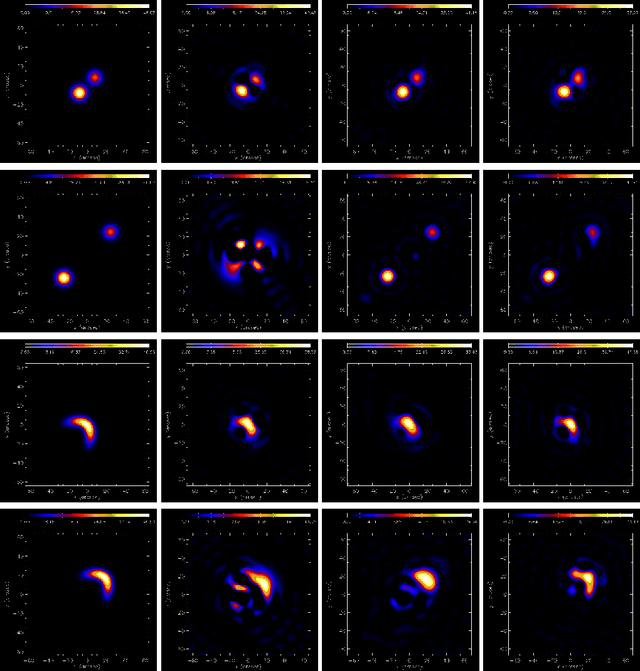
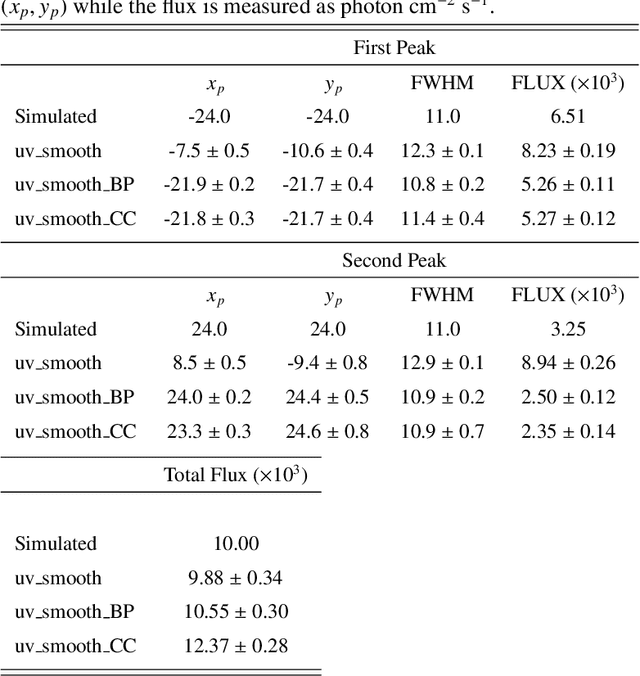
Abstract:Space telescopes for solar hard X-ray imaging provide observations made of sampled Fourier components of the incoming photon flux. The aim of this study is to design an image reconstruction method relying on enhanced visibility interpolation in the Fourier domain. % methods heading (mandatory) The interpolation-based method is applied on synthetic visibilities generated by means of the simulation software implemented within the framework of the Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX) mission on board Solar Orbiter. An application to experimental visibilities observed by the Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI) is also considered. In order to interpolate these visibility data we have utilized an approach based on Variably Scaled Kernels (VSKs), which are able to realize feature augmentation by exploiting prior information on the flaring source and which are used here, for the first time, for image reconstruction purposes.} % results heading (mandatory) When compared to an interpolation-based reconstruction algorithm previously introduced for RHESSI, VSKs offer significantly better performances, particularly in the case of STIX imaging, which is characterized by a notably sparse sampling of the Fourier domain. In the case of RHESSI data, this novel approach is particularly reliable when either the flaring sources are characterized by narrow, ribbon-like shapes or high-resolution detectors are utilized for observations. % conclusions heading (optional), leave it empty if necessary The use of VSKs for interpolating hard X-ray visibilities allows a notable image reconstruction accuracy when the information on the flaring source is encoded by a small set of scattered Fourier data and when the visibility surface is affected by significant oscillations in the frequency domain.
MEM_GE: a new maximum entropy method for image reconstruction from solar X-ray visibilities
Feb 18, 2020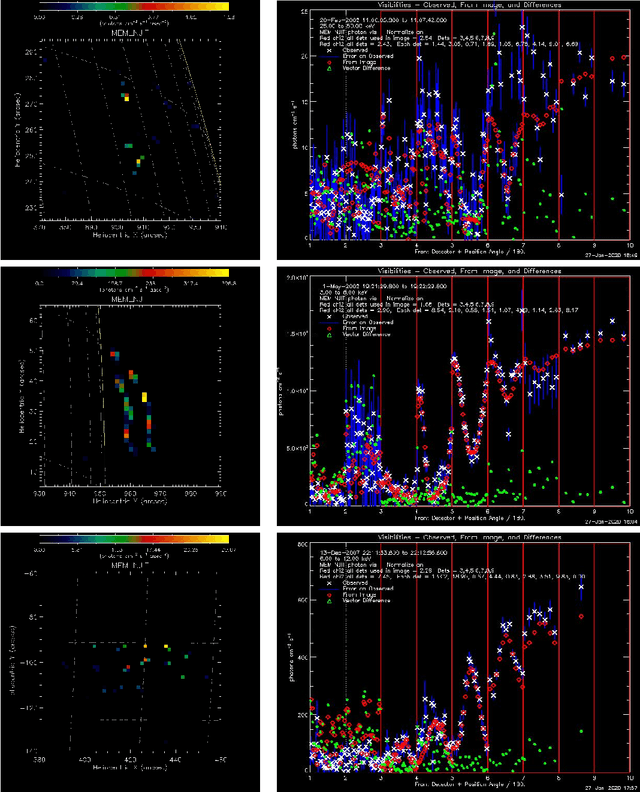
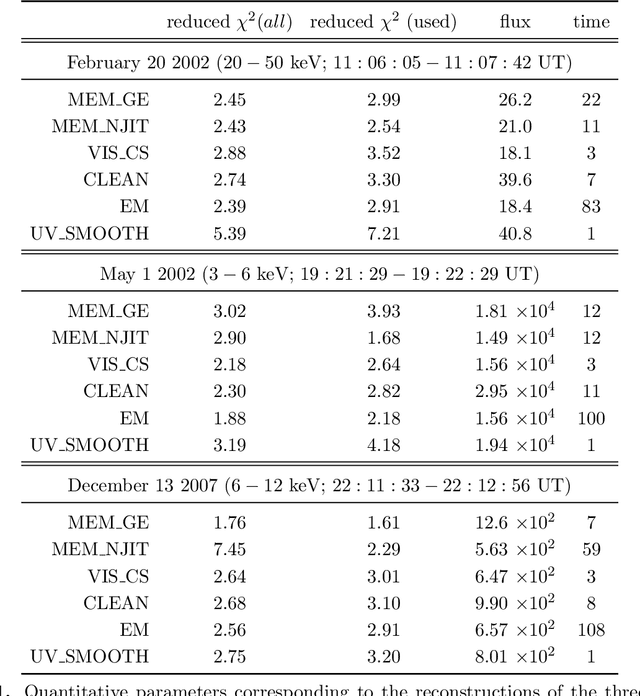

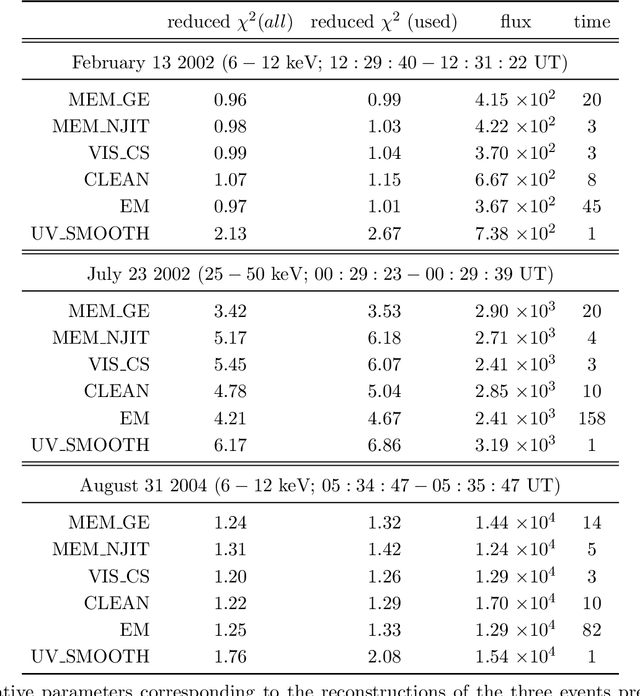
Abstract:Maximum Entropy is an image reconstruction method conceived to image a sparsely occupied field of view and therefore particularly appropriate to achieve super-resolution effects. Although widely used in image deconvolution, this method has been formulated in radio astronomy for the analysis of observations in the spatial frequency domain, and an Interactive Data Language (IDL) code has been implemented for image reconstruction from solar X-ray Fourier data. However, this code relies on a non-convex formulation of the constrained optimization problem addressed by the Maximum Entropy approach and this sometimes results in unreliable reconstructions characterized by unphysical shrinking effects. This paper introduces a new approach to Maximum Entropy based on the constrained minimization of a convex functional. In the case of observations recorded by the Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI), the resulting code provides the same super-resolution effects of the previous algorithm, while working properly also when that code produces unphysical reconstructions. Results are also provided of testing the algorithm with synthetic data simulating observations of the Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX) in Solar Orbiter. The new code is available in the {\em{HESSI}} folder of the Solar SoftWare (SSW)tree.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge