Richard D. Souza
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianopolis, Brazil
Sense-then-Charge: Wireless Power Transfer to Unresponsive Devices with Unknown Location
Apr 29, 2025



Abstract:This paper explores a multi-antenna dual-functional radio frequency (RF) wireless power transfer (WPT) and radar system to charge multiple unresponsive devices. We formulate a beamforming problem to maximize the minimum received power at the devices without prior location and channel state information (CSI) knowledge. We propose dividing transmission blocks into sensing and charging phases. First, the location of the devices is estimated by sending sensing signals and performing multiple signal classification and least square estimation on the received echo. Then, the estimations are used for CSI prediction and RF-WPT beamforming. Simulation results reveal that there is an optimal number of blocks allocated for sensing and charging depending on the system setup. Our sense-then-charge (STC) protocol can outperform CSI-free benchmarks and achieve near-optimal performance with a sufficient number of receive antennas and transmit power. However, STC struggles if using insufficient antennas or power as device numbers grow.
Energy Beamforming for RF Wireless Power Transfer with Dynamic Metasurface Antennas
Jul 03, 2023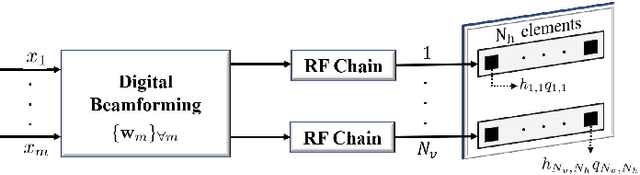
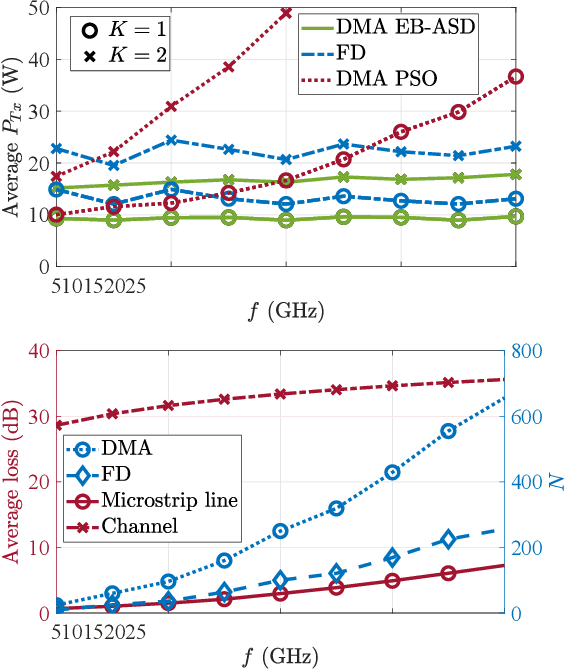
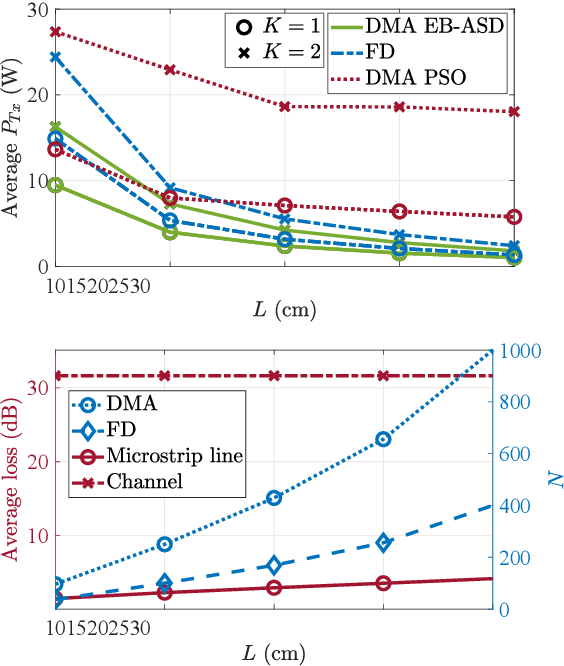
Abstract:Radio frequency (RF) wireless power transfer (WPT) is a promising technology for Internet of Things networks. However, RF-WPT is still energy inefficient, calling for advances in waveform optimization, distributed antenna, and energy beamforming (EB). In particular, EB can compensate for the severe propagation loss by directing beams toward the devices. The EB flexibility depends on the transmitter architecture, existing a trade-off between cost/complexity and degrees of freedom. Thus, simpler architectures such as dynamic metasurface antennas (DMAs) are gaining attention. Herein, we consider an RF-WPT system with a transmit DMA for meeting the EH requirements of multiple devices and formulate an optimization problem for the minimum-power design. First, we provide a mathematical model to capture the frequency-dependant signal propagation effect in the DMA architecture. Next, we propose a solution based on semi-definite programming and alternating optimization. Results show that a DMA-based implementation can outperform a fully-digital structure and that utilizing a larger antenna array can reduce the required transmit power, while the operation frequency does not influence much the performance.
Massive Wireless Energy Transfer with Multiple Power Beacons for very large Internet of Things
Jun 24, 2021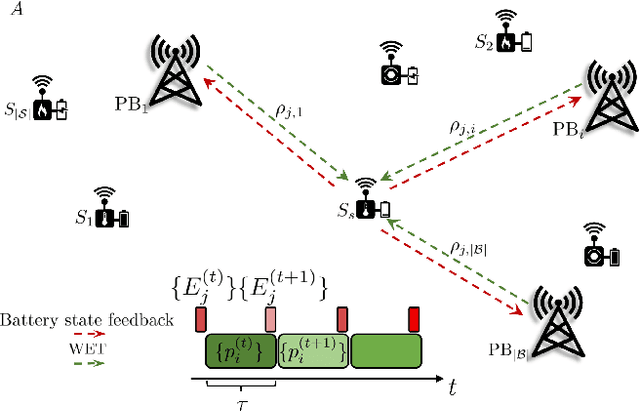
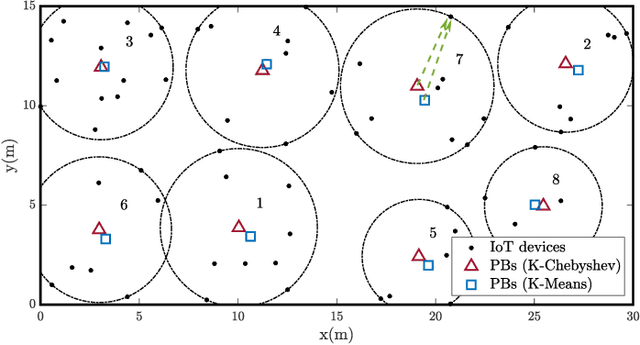
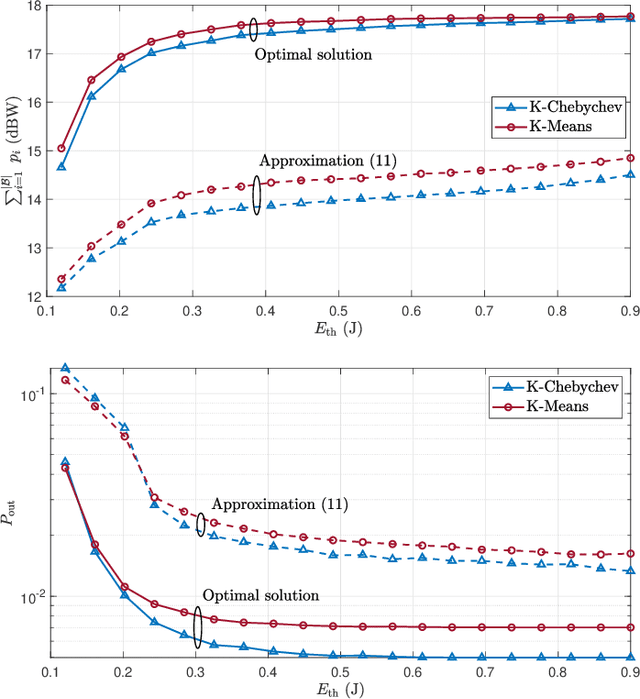
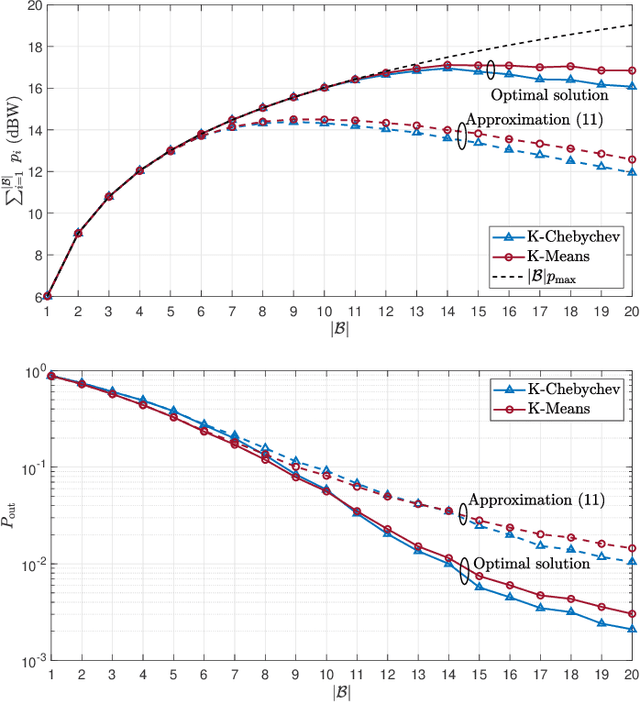
Abstract:The Internet of Things (IoT) comprises an increasing number of low-power and low-cost devices that autonomously interact with the surrounding environment. As a consequence of their popularity, future IoT deployments will be massive, which demands energy-efficient systems to extend their lifetime and improve the user experience. Radio frequency wireless energy transfer has the potential of powering massive IoT networks, thus eliminating the need for frequent battery replacement by using the so-called power beacons (PBs). In this paper, we provide a framework for minimizing the sum transmit power of the PBs using devices' positions information and their current battery state. Our strategy aims to reduce the PBs' power consumption and to mitigate the possible impact of the electromagnetic radiation on human health. We also present analytical insights for the case of very distant clusters and evaluate their applicability. Numerical results show that our proposed framework reduces the outage probability as the number of PBs and/or the energy demands increase.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge