Randy Gomez
Ain't Misbehavin' -- Using LLMs to Generate Expressive Robot Behavior in Conversations with the Tabletop Robot Haru
Feb 18, 2024Abstract:Social robots aim to establish long-term bonds with humans through engaging conversation. However, traditional conversational approaches, reliant on scripted interactions, often fall short in maintaining engaging conversations. This paper addresses this limitation by integrating large language models (LLMs) into social robots to achieve more dynamic and expressive conversations. We introduce a fully-automated conversation system that leverages LLMs to generate robot responses with expressive behaviors, congruent with the robot's personality. We incorporate robot behavior with two modalities: 1) a text-to-speech (TTS) engine capable of various delivery styles, and 2) a library of physical actions for the robot. We develop a custom, state-of-the-art emotion recognition model to dynamically select the robot's tone of voice and utilize emojis from LLM output as cues for generating robot actions. A demo of our system is available here. To illuminate design and implementation issues, we conduct a pilot study where volunteers chat with a social robot using our proposed system, and we analyze their feedback, conducting a rigorous error analysis of chat transcripts. Feedback was overwhelmingly positive, with participants commenting on the robot's empathy, helpfulness, naturalness, and entertainment. Most negative feedback was due to automatic speech recognition (ASR) errors which had limited impact on conversations. However, we observed a small class of errors, such as the LLM repeating itself or hallucinating fictitious information and human responses, that have the potential to derail conversations, raising important issues for LLM application.
* Accepted as Late Breaking Report (LBR) at the 19th Annual ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human Robot Interaction (HRI '24)
Developing Autonomous Robot-Mediated Behavior Coaching Sessions with Haru
Feb 18, 2024


Abstract:This study presents an empirical investigation into the design and impact of autonomous dialogues in human-robot interaction for behavior change coaching. We focus on the use of Haru, a tabletop social robot, and explore the implementation of the Tiny Habits method for fostering positive behavior change. The core of our study lies in developing a fully autonomous dialogue system that maximizes Haru's emotional expressiveness and unique personality. Our methodology involved iterative design and extensive testing of the dialogue system, ensuring it effectively embodied the principles of the Tiny Habits method while also incorporating strategies for trust-raising and trust-dampening. The effectiveness of the final version of the dialogue was evaluated in an experimental study with human participants (N=12). The results indicated a significant improvement in perceptions of Haru's liveliness, interactivity, and neutrality. Additionally, our study contributes to the broader understanding of dialogue design in social robotics, offering practical insights for future developments in the field.
* Accepted as Late Breaking Report (LBR) at the 19th Annual ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human Robot Interaction (HRI '24)
A Study on Social Robot Behavior in Group Conversation
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:Recently, research in human-robot interaction began to consider a robot's influence at the group level. Despite the recent growth in research investigating the effects of robots within groups of people, our overall understanding of what happens when robots are placed within groups or teams of people is still limited. This paper investigates several key problems for social robots that manage conversations in a group setting, where the number of participants is more than two. In a group setting, the conversation dynamics are a lot more complicated than the conventional one-to-one conversation, thus, there are more challenges need to be solved.
Social Robot Mediator for Multiparty Interaction
Oct 20, 2023


Abstract:A social robot acting as a 'mediator' can enhance interactions between humans, for example, in fields such as education and healthcare. A particularly promising area of research is the use of a social robot mediator in a multiparty setting, which tends to be the most applicable in real-world scenarios. However, research in social robot mediation for multiparty interactions is still emerging and faces numerous challenges. This paper provides an overview of social robotics and mediation research by highlighting relevant literature and some of the ongoing problems. The importance of incorporating relevant psychological principles for developing social robot mediators is also presented. Additionally, the potential of implementing a Theory of Mind in a social robot mediator is explored, given how such a framework could greatly improve mediation by reading the individual and group mental states to interact effectively.
GAN-Based Interactive Reinforcement Learning from Demonstration and Human Evaluative Feedback
Apr 14, 2021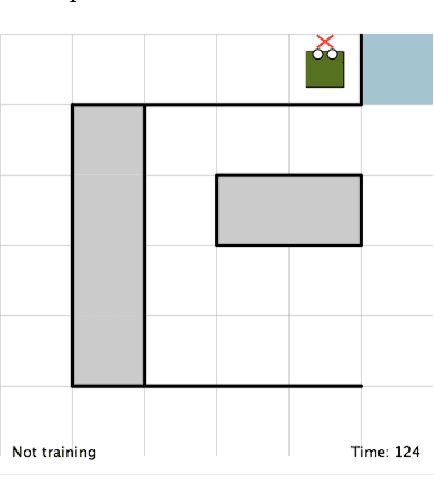
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has achieved great successes in many simulated tasks. The sample inefficiency problem makes applying traditional DRL methods to real-world robots a great challenge. Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning (GAIL) -- a general model-free imitation learning method, allows robots to directly learn policies from expert trajectories in large environments. However, GAIL shares the limitation of other imitation learning methods that they can seldom surpass the performance of demonstrations. In this paper, to address the limit of GAIL, we propose GAN-Based Interactive Reinforcement Learning (GAIRL) from demonstration and human evaluative feedback by combining the advantages of GAIL and interactive reinforcement learning. We tested our proposed method in six physics-based control tasks, ranging from simple low-dimensional control tasks -- Cart Pole and Mountain Car, to difficult high-dimensional tasks -- Inverted Double Pendulum, Lunar Lander, Hopper and HalfCheetah. Our results suggest that with both optimal and suboptimal demonstrations, a GAIRL agent can always learn a more stable policy with optimal or close to optimal performance, while the performance of the GAIL agent is upper bounded by the performance of demonstrations or even worse than it. In addition, our results indicate the reason that GAIRL is superior over GAIL is the complementary effect of demonstrations and human evaluative feedback.
Collaborative Storytelling with Large-scale Neural Language Models
Nov 20, 2020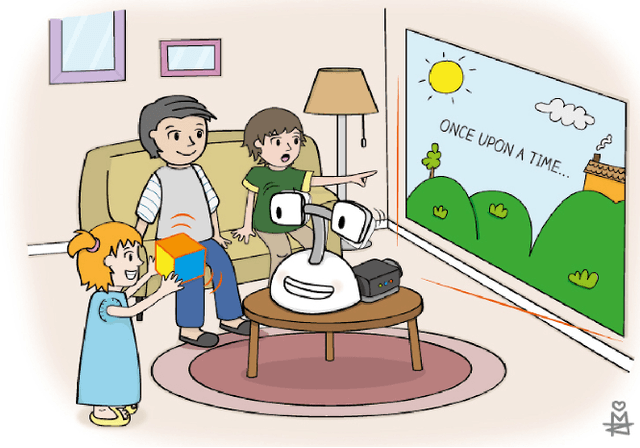
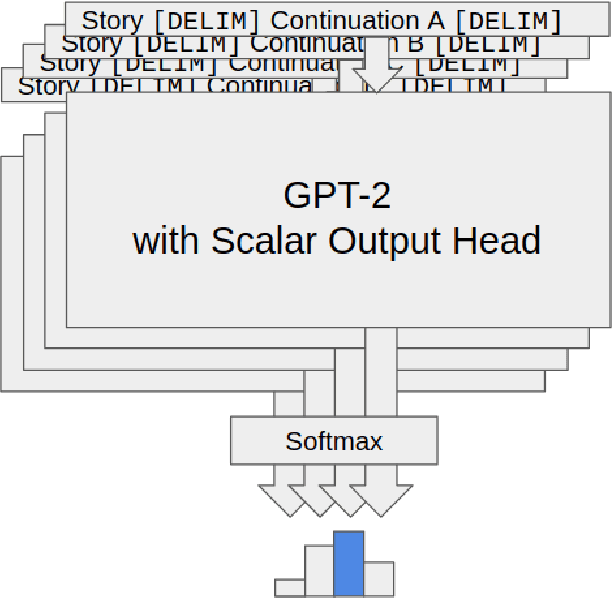
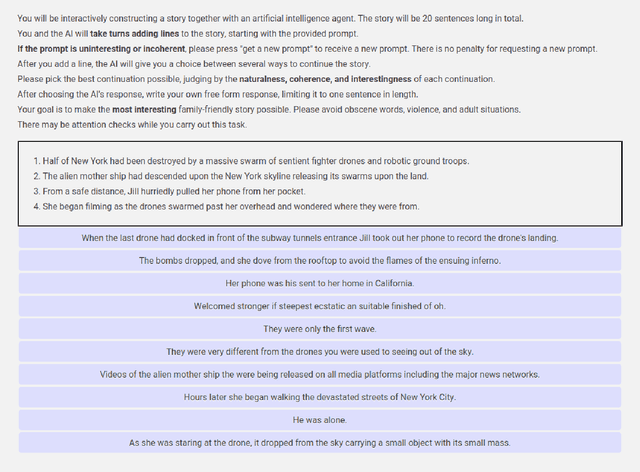

Abstract:Storytelling plays a central role in human socializing and entertainment. However, much of the research on automatic storytelling generation assumes that stories will be generated by an agent without any human interaction. In this paper, we introduce the task of collaborative storytelling, where an artificial intelligence agent and a person collaborate to create a unique story by taking turns adding to it. We present a collaborative storytelling system which works with a human storyteller to create a story by generating new utterances based on the story so far. We constructed the storytelling system by tuning a publicly-available large scale language model on a dataset of writing prompts and their accompanying fictional works. We identify generating sufficiently human-like utterances to be an important technical issue and propose a sample-and-rank approach to improve utterance quality. Quantitative evaluation shows that our approach outperforms a baseline, and we present qualitative evaluation of our system's capabilities.
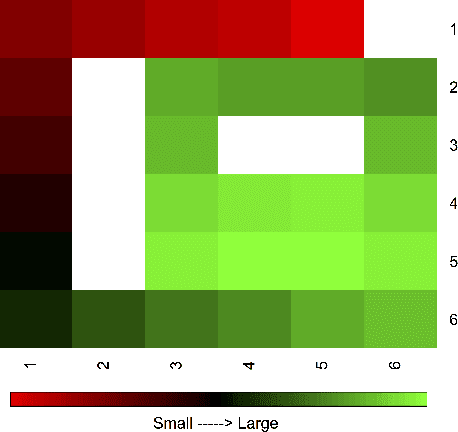
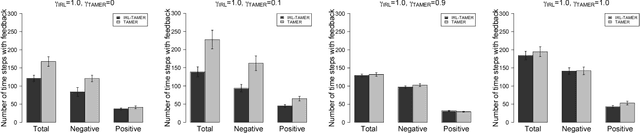
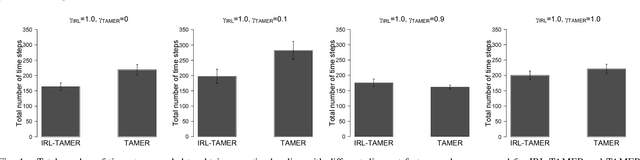
Improving Interactive Reinforcement Agent Planning with Human Demonstration
Apr 18, 2019
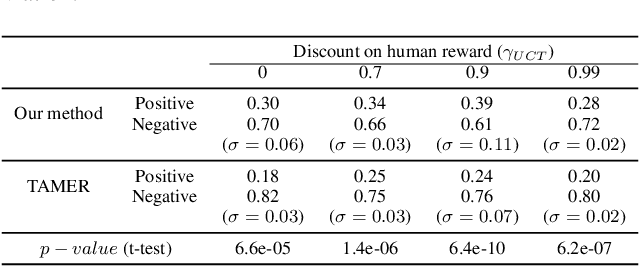
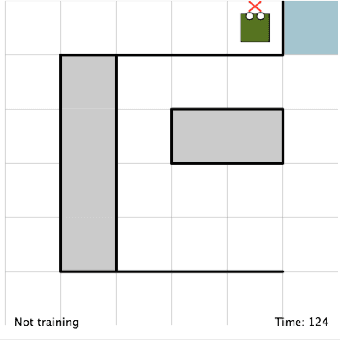
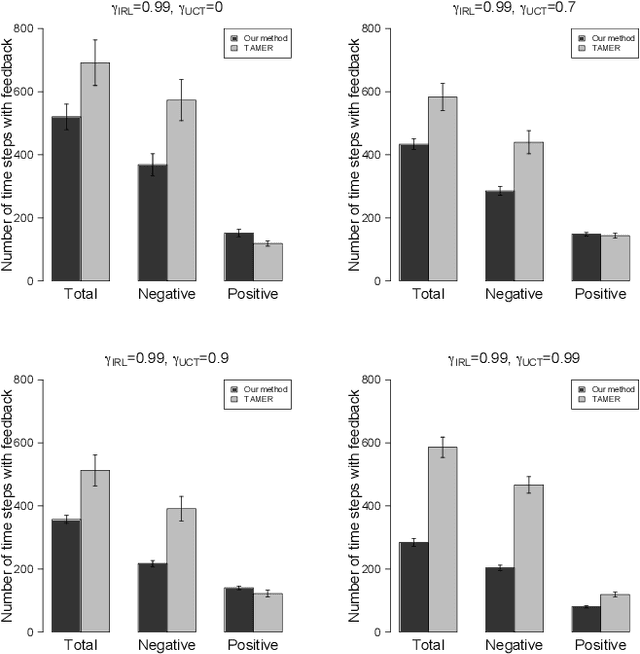
Abstract:TAMER has proven to be a powerful interactive reinforcement learning method for allowing ordinary people to teach and personalize autonomous agents' behavior by providing evaluative feedback. However, a TAMER agent planning with UCT---a Monte Carlo Tree Search strategy, can only update states along its path and might induce high learning cost especially for a physical robot. In this paper, we propose to drive the agent's exploration along the optimal path and reduce the learning cost by initializing the agent's reward function via inverse reinforcement learning from demonstration. We test our proposed method in the RL benchmark domain---Grid World---with different discounts on human reward. Our results show that learning from demonstration can allow a TAMER agent to learn a roughly optimal policy up to the deepest search and encourage the agent to explore along the optimal path. In addition, we find that learning from demonstration can improve the learning efficiency by reducing total feedback, the number of incorrect actions and increasing the ratio of correct actions to obtain an optimal policy, allowing a TAMER agent to converge faster.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge