Eric Nichols
Ain't Misbehavin' -- Using LLMs to Generate Expressive Robot Behavior in Conversations with the Tabletop Robot Haru
Feb 18, 2024Abstract:Social robots aim to establish long-term bonds with humans through engaging conversation. However, traditional conversational approaches, reliant on scripted interactions, often fall short in maintaining engaging conversations. This paper addresses this limitation by integrating large language models (LLMs) into social robots to achieve more dynamic and expressive conversations. We introduce a fully-automated conversation system that leverages LLMs to generate robot responses with expressive behaviors, congruent with the robot's personality. We incorporate robot behavior with two modalities: 1) a text-to-speech (TTS) engine capable of various delivery styles, and 2) a library of physical actions for the robot. We develop a custom, state-of-the-art emotion recognition model to dynamically select the robot's tone of voice and utilize emojis from LLM output as cues for generating robot actions. A demo of our system is available here. To illuminate design and implementation issues, we conduct a pilot study where volunteers chat with a social robot using our proposed system, and we analyze their feedback, conducting a rigorous error analysis of chat transcripts. Feedback was overwhelmingly positive, with participants commenting on the robot's empathy, helpfulness, naturalness, and entertainment. Most negative feedback was due to automatic speech recognition (ASR) errors which had limited impact on conversations. However, we observed a small class of errors, such as the LLM repeating itself or hallucinating fictitious information and human responses, that have the potential to derail conversations, raising important issues for LLM application.
* Accepted as Late Breaking Report (LBR) at the 19th Annual ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human Robot Interaction (HRI '24)
Developing Autonomous Robot-Mediated Behavior Coaching Sessions with Haru
Feb 18, 2024


Abstract:This study presents an empirical investigation into the design and impact of autonomous dialogues in human-robot interaction for behavior change coaching. We focus on the use of Haru, a tabletop social robot, and explore the implementation of the Tiny Habits method for fostering positive behavior change. The core of our study lies in developing a fully autonomous dialogue system that maximizes Haru's emotional expressiveness and unique personality. Our methodology involved iterative design and extensive testing of the dialogue system, ensuring it effectively embodied the principles of the Tiny Habits method while also incorporating strategies for trust-raising and trust-dampening. The effectiveness of the final version of the dialogue was evaluated in an experimental study with human participants (N=12). The results indicated a significant improvement in perceptions of Haru's liveliness, interactivity, and neutrality. Additionally, our study contributes to the broader understanding of dialogue design in social robotics, offering practical insights for future developments in the field.
* Accepted as Late Breaking Report (LBR) at the 19th Annual ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human Robot Interaction (HRI '24)
A Study on Social Robot Behavior in Group Conversation
Dec 21, 2023Abstract:Recently, research in human-robot interaction began to consider a robot's influence at the group level. Despite the recent growth in research investigating the effects of robots within groups of people, our overall understanding of what happens when robots are placed within groups or teams of people is still limited. This paper investigates several key problems for social robots that manage conversations in a group setting, where the number of participants is more than two. In a group setting, the conversation dynamics are a lot more complicated than the conventional one-to-one conversation, thus, there are more challenges need to be solved.
Collaborative Storytelling with Large-scale Neural Language Models
Nov 20, 2020
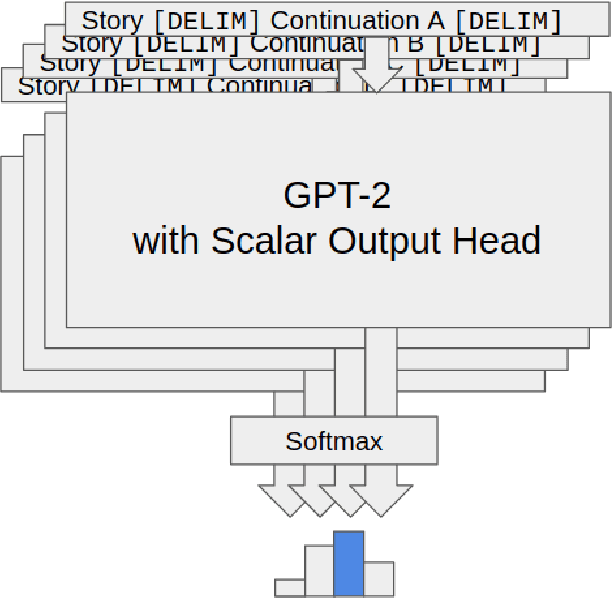
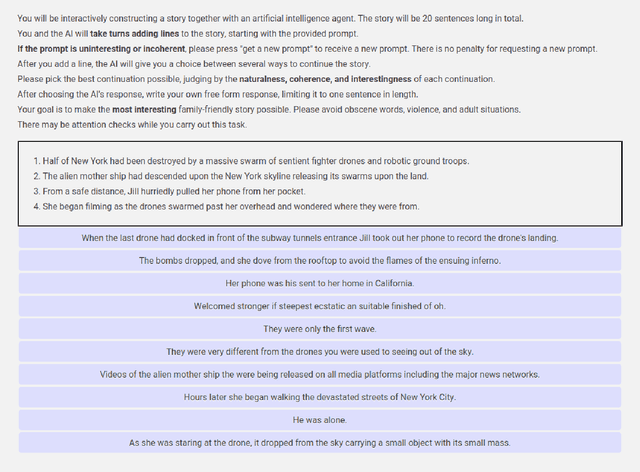

Abstract:Storytelling plays a central role in human socializing and entertainment. However, much of the research on automatic storytelling generation assumes that stories will be generated by an agent without any human interaction. In this paper, we introduce the task of collaborative storytelling, where an artificial intelligence agent and a person collaborate to create a unique story by taking turns adding to it. We present a collaborative storytelling system which works with a human storyteller to create a story by generating new utterances based on the story so far. We constructed the storytelling system by tuning a publicly-available large scale language model on a dataset of writing prompts and their accompanying fictional works. We identify generating sufficiently human-like utterances to be an important technical issue and propose a sample-and-rank approach to improve utterance quality. Quantitative evaluation shows that our approach outperforms a baseline, and we present qualitative evaluation of our system's capabilities.
Multi-label Sound Event Retrieval Using a Deep Learning-based Siamese Structure with a Pairwise Presence Matrix
Feb 20, 2020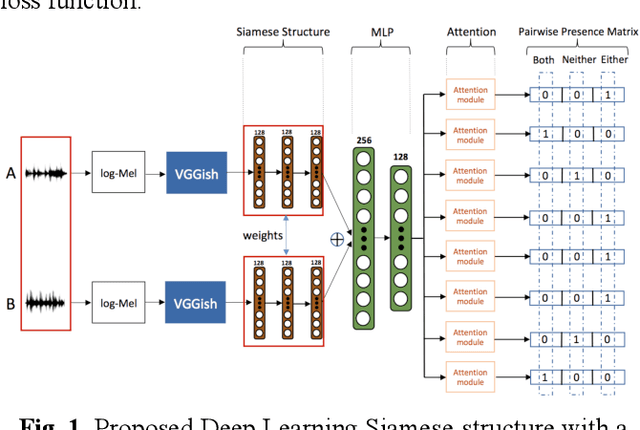
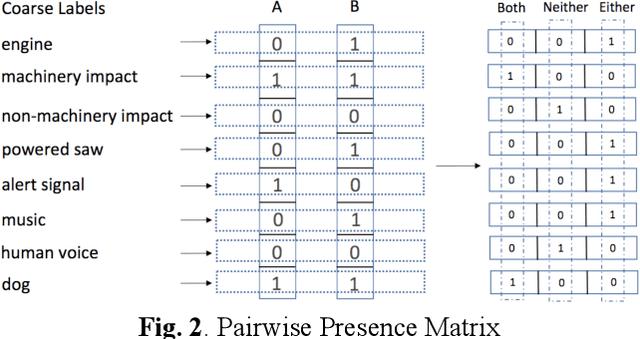
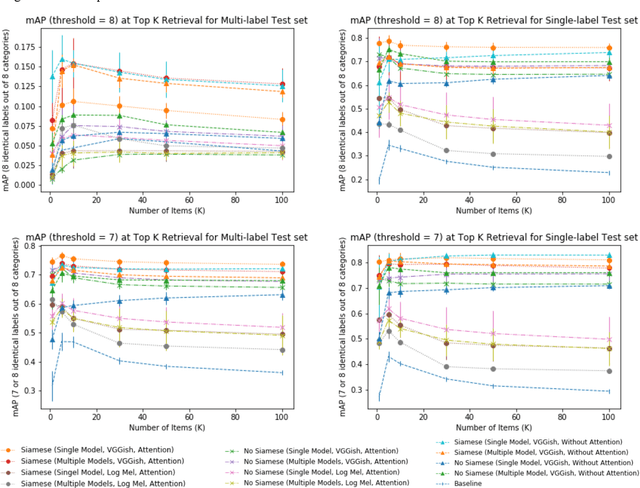
Abstract:Realistic recordings of soundscapes often have multiple sound events co-occurring, such as car horns, engine and human voices. Sound event retrieval is a type of content-based search aiming at finding audio samples, similar to an audio query based on their acoustic or semantic content. State of the art sound event retrieval models have focused on single-label audio recordings, with only one sound event occurring, rather than on multi-label audio recordings (i.e., multiple sound events occur in one recording). To address this latter problem, we propose different Deep Learning architectures with a Siamese-structure and a Pairwise Presence Matrix. The networks are trained and evaluated using the SONYC-UST dataset containing both single- and multi-label soundscape recordings. The performance results show the effectiveness of our proposed model.
Named Entity Recognition with Bidirectional LSTM-CNNs
Jul 19, 2016Abstract:Named entity recognition is a challenging task that has traditionally required large amounts of knowledge in the form of feature engineering and lexicons to achieve high performance. In this paper, we present a novel neural network architecture that automatically detects word- and character-level features using a hybrid bidirectional LSTM and CNN architecture, eliminating the need for most feature engineering. We also propose a novel method of encoding partial lexicon matches in neural networks and compare it to existing approaches. Extensive evaluation shows that, given only tokenized text and publicly available word embeddings, our system is competitive on the CoNLL-2003 dataset and surpasses the previously reported state of the art performance on the OntoNotes 5.0 dataset by 2.13 F1 points. By using two lexicons constructed from publicly-available sources, we establish new state of the art performance with an F1 score of 91.62 on CoNLL-2003 and 86.28 on OntoNotes, surpassing systems that employ heavy feature engineering, proprietary lexicons, and rich entity linking information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge