Rachel Wong
on behalf of the N3C Consortium
Enhancing Clinical Predictive Modeling through Model Complexity-Driven Class Proportion Tuning for Class Imbalanced Data: An Empirical Study on Opioid Overdose Prediction
May 09, 2023Abstract:Class imbalance problems widely exist in the medical field and heavily deteriorates performance of clinical predictive models. Most techniques to alleviate the problem rebalance class proportions and they predominantly assume the rebalanced proportions should be a function of the original data and oblivious to the model one uses. This work challenges this prevailing assumption and proposes that links the optimal class proportions to the model complexity, thereby tuning the class proportions per model. Our experiments on the opioid overdose prediction problem highlight the performance gain of tuning class proportions. Rigorous regression analysis also confirms the advantages of the theoretical framework proposed and the statistically significant correlation between the hyperparameters controlling the model complexity and the optimal class proportions.
A Multimodal Transformer: Fusing Clinical Notes with Structured EHR Data for Interpretable In-Hospital Mortality Prediction
Aug 09, 2022
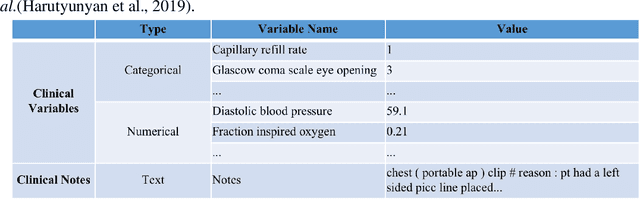
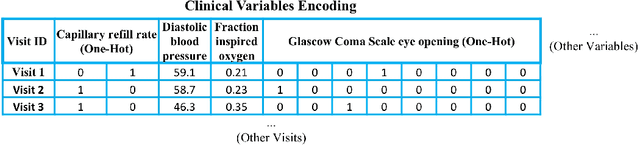
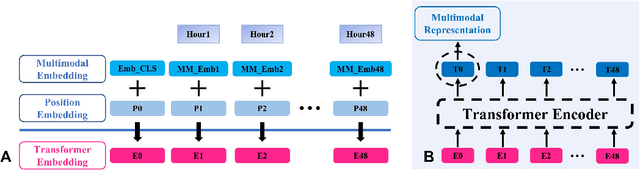
Abstract:Deep-learning-based clinical decision support using structured electronic health records (EHR) has been an active research area for predicting risks of mortality and diseases. Meanwhile, large amounts of narrative clinical notes provide complementary information, but are often not integrated into predictive models. In this paper, we provide a novel multimodal transformer to fuse clinical notes and structured EHR data for better prediction of in-hospital mortality. To improve interpretability, we propose an integrated gradients (IG) method to select important words in clinical notes and discover the critical structured EHR features with Shapley values. These important words and clinical features are visualized to assist with interpretation of the prediction outcomes. We also investigate the significance of domain adaptive pretraining and task adaptive fine-tuning on the Clinical BERT, which is used to learn the representations of clinical notes. Experiments demonstrated that our model outperforms other methods (AUCPR: 0.538, AUCROC: 0.877, F1:0.490).
A Methodological Framework for the Comparative Evaluation of Multiple Imputation Methods: Multiple Imputation of Race, Ethnicity and Body Mass Index in the U.S. National COVID Cohort Collaborative
Jun 13, 2022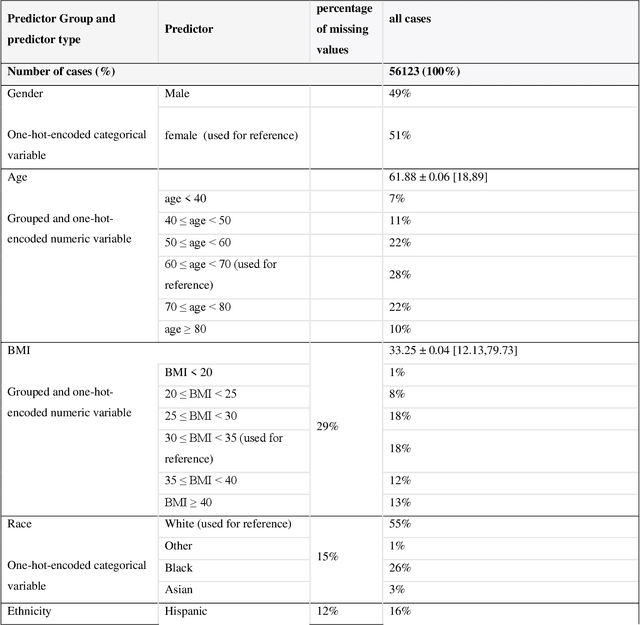
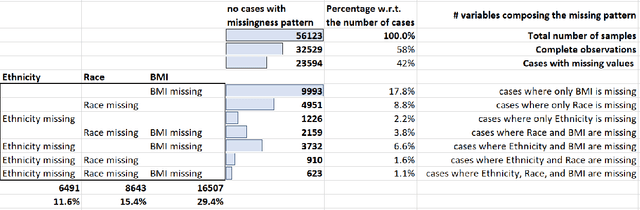
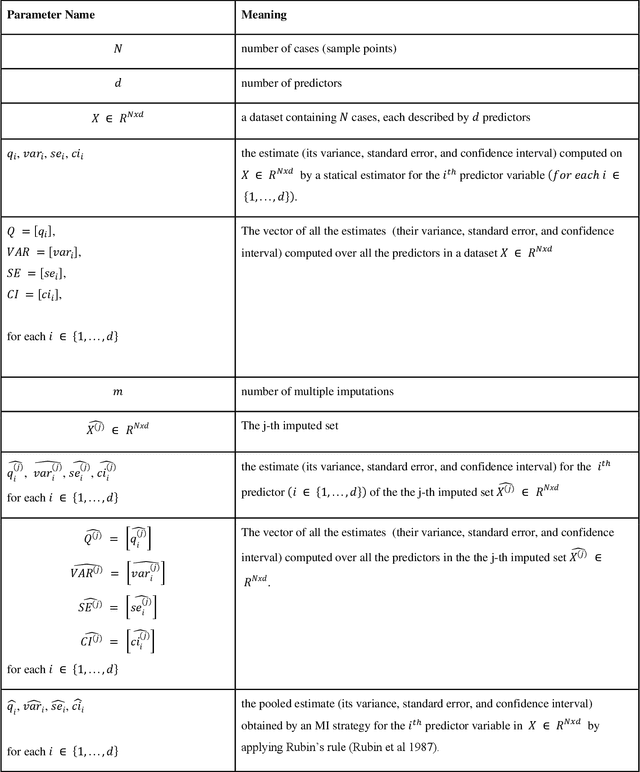
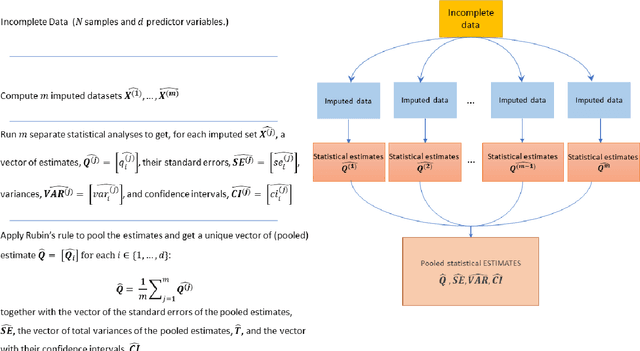
Abstract:While electronic health records are a rich data source for biomedical research, these systems are not implemented uniformly across healthcare settings and significant data may be missing due to healthcare fragmentation and lack of interoperability between siloed electronic health records. Considering that the deletion of cases with missing data may introduce severe bias in the subsequent analysis, several authors prefer applying a multiple imputation strategy to recover the missing information. Unfortunately, although several literature works have documented promising results by using any of the different multiple imputation algorithms that are now freely available for research, there is no consensus on which MI algorithm works best. Beside the choice of the MI strategy, the choice of the imputation algorithm and its application settings are also both crucial and challenging. In this paper, inspired by the seminal works of Rubin and van Buuren, we propose a methodological framework that may be applied to evaluate and compare several multiple imputation techniques, with the aim to choose the most valid for computing inferences in a clinical research work. Our framework has been applied to validate, and extend on a larger cohort, the results we presented in a previous literature study, where we evaluated the influence of crucial patients' descriptors and COVID-19 severity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus whose data is provided by the National COVID Cohort Collaborative Enclave.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge