Qiyao Deng
GAN-based Facial Attribute Manipulation
Oct 23, 2022



Abstract:Facial Attribute Manipulation (FAM) aims to aesthetically modify a given face image to render desired attributes, which has received significant attention due to its broad practical applications ranging from digital entertainment to biometric forensics. In the last decade, with the remarkable success of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in synthesizing realistic images, numerous GAN-based models have been proposed to solve FAM with various problem formulation approaches and guiding information representations. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of GAN-based FAM methods with a focus on summarizing their principal motivations and technical details. The main contents of this survey include: (i) an introduction to the research background and basic concepts related to FAM, (ii) a systematic review of GAN-based FAM methods in three main categories, and (iii) an in-depth discussion of important properties of FAM methods, open issues, and future research directions. This survey not only builds a good starting point for researchers new to this field but also serves as a reference for the vision community.
AnyFace: Free-style Text-to-Face Synthesis and Manipulation
Mar 29, 2022
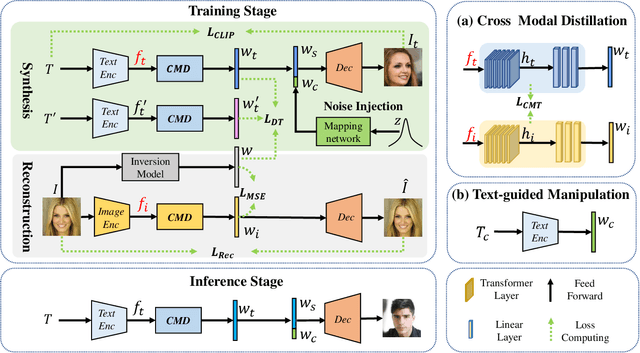
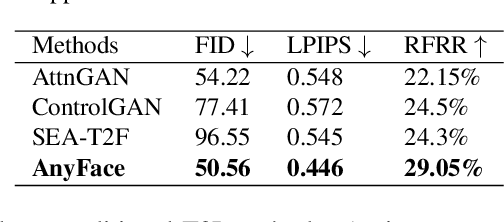
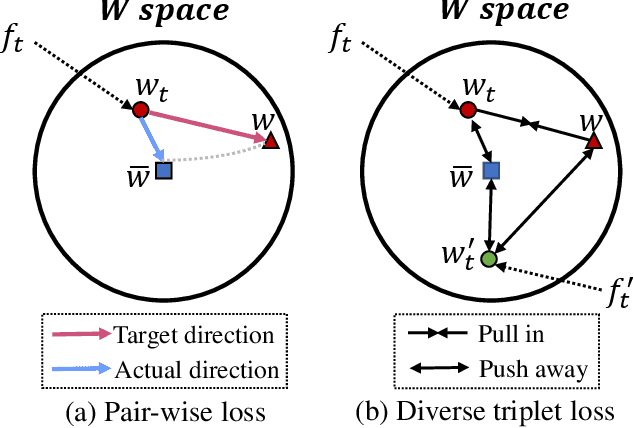
Abstract:Existing text-to-image synthesis methods generally are only applicable to words in the training dataset. However, human faces are so variable to be described with limited words. So this paper proposes the first free-style text-to-face method namely AnyFace enabling much wider open world applications such as metaverse, social media, cosmetics, forensics, etc. AnyFace has a novel two-stream framework for face image synthesis and manipulation given arbitrary descriptions of the human face. Specifically, one stream performs text-to-face generation and the other conducts face image reconstruction. Facial text and image features are extracted using the CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training) encoders. And a collaborative Cross Modal Distillation (CMD) module is designed to align the linguistic and visual features across these two streams. Furthermore, a Diverse Triplet Loss (DT loss) is developed to model fine-grained features and improve facial diversity. Extensive experiments on Multi-modal CelebA-HQ and CelebAText-HQ demonstrate significant advantages of AnyFace over state-of-the-art methods. AnyFace can achieve high-quality, high-resolution, and high-diversity face synthesis and manipulation results without any constraints on the number and content of input captions.
Reference Guided Face Component Editing
Jun 03, 2020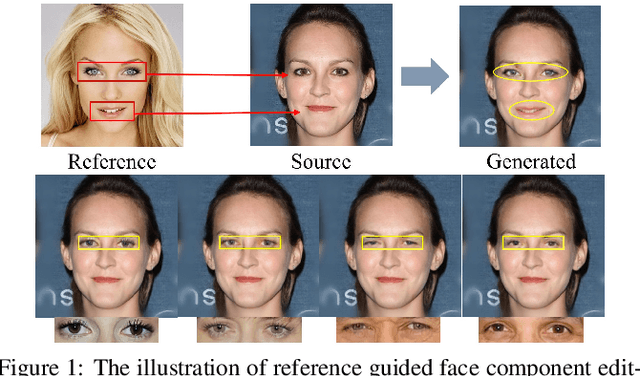
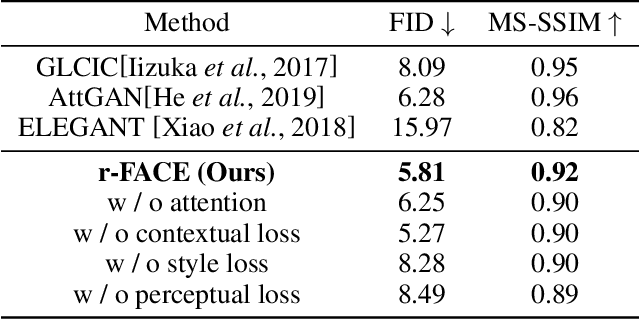
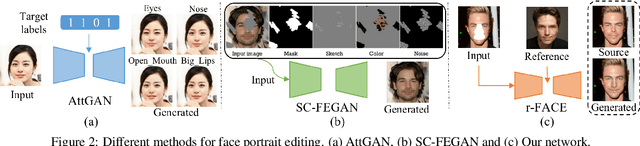
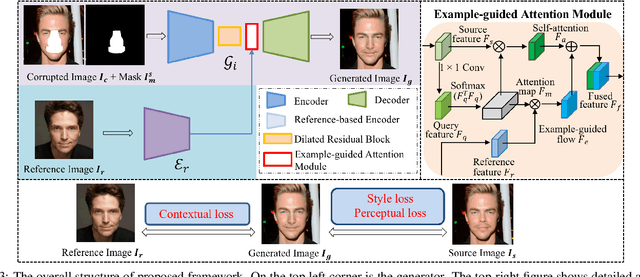
Abstract:Face portrait editing has achieved great progress in recent years. However, previous methods either 1) operate on pre-defined face attributes, lacking the flexibility of controlling shapes of high-level semantic facial components (e.g., eyes, nose, mouth), or 2) take manually edited mask or sketch as an intermediate representation for observable changes, but such additional input usually requires extra efforts to obtain. To break the limitations (e.g. shape, mask or sketch) of the existing methods, we propose a novel framework termed r-FACE (Reference Guided FAce Component Editing) for diverse and controllable face component editing with geometric changes. Specifically, r-FACE takes an image inpainting model as the backbone, utilizing reference images as conditions for controlling the shape of face components. In order to encourage the framework to concentrate on the target face components, an example-guided attention module is designed to fuse attention features and the target face component features extracted from the reference image. Both qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that our model is superior to existing literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge