Qiqi Wan
RiemannGFM: Learning a Graph Foundation Model from Riemannian Geometry
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:The foundation model has heralded a new era in artificial intelligence, pretraining a single model to offer cross-domain transferability on different datasets. Graph neural networks excel at learning graph data, the omnipresent non-Euclidean structure, but often lack the generalization capacity. Hence, graph foundation model is drawing increasing attention, and recent efforts have been made to leverage Large Language Models. On the one hand, existing studies primarily focus on text-attributed graphs, while a wider range of real graphs do not contain fruitful textual attributes. On the other hand, the sequential graph description tailored for the Large Language Model neglects the structural complexity, which is a predominant characteristic of the graph. Such limitations motivate an important question: Can we go beyond Large Language Models, and pretrain a universal model to learn the structural knowledge for any graph? The answer in the language or vision domain is a shared vocabulary. We observe the fact that there also exist shared substructures underlying graph domain, and thereby open a new opportunity of graph foundation model with structural vocabulary. The key innovation is the discovery of a simple yet effective structural vocabulary of trees and cycles, and we explore its inherent connection to Riemannian geometry. Herein, we present a universal pretraining model, RiemannGFM. Concretely, we first construct a novel product bundle to incorporate the diverse geometries of the vocabulary. Then, on this constructed space, we stack Riemannian layers where the structural vocabulary, regardless of specific graph, is learned in Riemannian manifold offering cross-domain transferability. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of RiemannGFM on a diversity of real graphs.
Pioneer: Physics-informed Riemannian Graph ODE for Entropy-increasing Dynamics
Feb 05, 2025
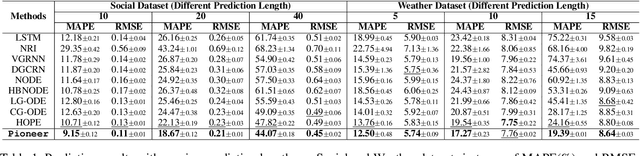
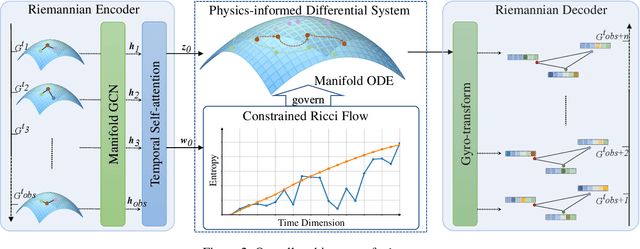
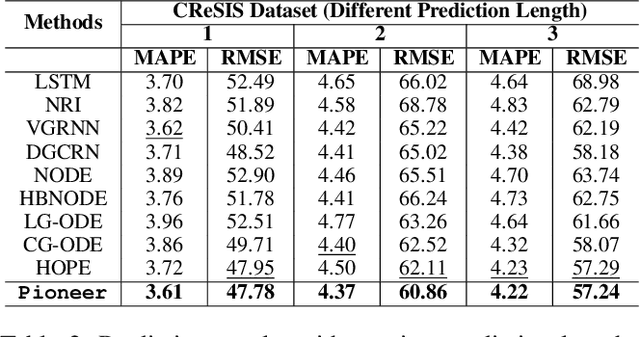
Abstract:Dynamic interacting system modeling is important for understanding and simulating real world systems. The system is typically described as a graph, where multiple objects dynamically interact with each other and evolve over time. In recent years, graph Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) receive increasing research attentions. While achieving encouraging results, existing solutions prioritize the traditional Euclidean space, and neglect the intrinsic geometry of the system and physics laws, e.g., the principle of entropy increasing. The limitations above motivate us to rethink the system dynamics from a fresh perspective of Riemannian geometry, and pose a more realistic problem of physics-informed dynamic system modeling, considering the underlying geometry and physics law for the first time. In this paper, we present a novel physics-informed Riemannian graph ODE for a wide range of entropy-increasing dynamic systems (termed as Pioneer). In particular, we formulate a differential system on the Riemannian manifold, where a manifold-valued graph ODE is governed by the proposed constrained Ricci flow, and a manifold preserving Gyro-transform aware of system geometry. Theoretically, we report the provable entropy non-decreasing of our formulation, obeying the physics laws. Empirical results show the superiority of Pioneer on real datasets.
Spiking Graph Neural Network on Riemannian Manifolds
Oct 23, 2024


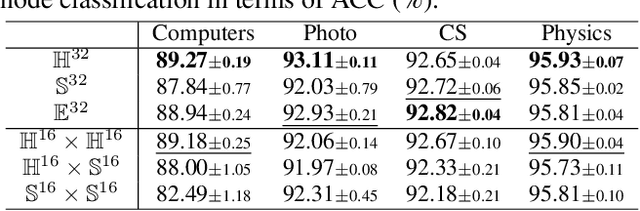
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have become the dominant solution for learning on graphs, the typical non-Euclidean structures. Conventional GNNs, constructed with the Artificial Neuron Network (ANN), have achieved impressive performance at the cost of high computation and energy consumption. In parallel, spiking GNNs with brain-like spiking neurons are drawing increasing research attention owing to the energy efficiency. So far, existing spiking GNNs consider graphs in Euclidean space, ignoring the structural geometry, and suffer from the high latency issue due to Back-Propagation-Through-Time (BPTT) with the surrogate gradient. In light of the aforementioned issues, we are devoted to exploring spiking GNN on Riemannian manifolds, and present a Manifold-valued Spiking GNN (MSG). In particular, we design a new spiking neuron on geodesically complete manifolds with the diffeomorphism, so that BPTT regarding the spikes is replaced by the proposed differentiation via manifold. Theoretically, we show that MSG approximates a solver of the manifold ordinary differential equation. Extensive experiments on common graphs show the proposed MSG achieves superior performance to previous spiking GNNs and energy efficiency to conventional GNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge