Qichen Sun
Any-to-Any Learning in Computational Pathology via Triplet Multimodal Pretraining
May 19, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in computational pathology and artificial intelligence have significantly enhanced the utilization of gigapixel whole-slide images and and additional modalities (e.g., genomics) for pathological diagnosis. Although deep learning has demonstrated strong potential in pathology, several key challenges persist: (1) fusing heterogeneous data types requires sophisticated strategies beyond simple concatenation due to high computational costs; (2) common scenarios of missing modalities necessitate flexible strategies that allow the model to learn robustly in the absence of certain modalities; (3) the downstream tasks in CPath are diverse, ranging from unimodal to multimodal, cnecessitating a unified model capable of handling all modalities. To address these challenges, we propose ALTER, an any-to-any tri-modal pretraining framework that integrates WSIs, genomics, and pathology reports. The term "any" emphasizes ALTER's modality-adaptive design, enabling flexible pretraining with any subset of modalities, and its capacity to learn robust, cross-modal representations beyond WSI-centric approaches. We evaluate ALTER across extensive clinical tasks including survival prediction, cancer subtyping, gene mutation prediction, and report generation, achieving superior or comparable performance to state-of-the-art baselines.
Comprehensive Manuscript Assessment with Text Summarization Using 69707 articles
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Rapid and efficient assessment of the future impact of research articles is a significant concern for both authors and reviewers. The most common standard for measuring the impact of academic papers is the number of citations. In recent years, numerous efforts have been undertaken to predict citation counts within various citation windows. However, most of these studies focus solely on a specific academic field or require early citation counts for prediction, rendering them impractical for the early-stage evaluation of papers. In this work, we harness Scopus to curate a significantly comprehensive and large-scale dataset of information from 69707 scientific articles sourced from 99 journals spanning multiple disciplines. We propose a deep learning methodology for the impact-based classification tasks, which leverages semantic features extracted from the manuscripts and paper metadata. To summarize the semantic features, such as titles and abstracts, we employ a Transformer-based language model to encode semantic features and design a text fusion layer to capture shared information between titles and abstracts. We specifically focus on the following impact-based prediction tasks using information of scientific manuscripts in pre-publication stage: (1) The impact of journals in which the manuscripts will be published. (2) The future impact of manuscripts themselves. Extensive experiments on our datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed model for impact-based prediction tasks. We also demonstrate potentials in generating manuscript's feedback and improvement suggestions.
Context Matters: Query-aware Dynamic Long Sequence Modeling of Gigapixel Images
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:Whole slide image (WSI) analysis presents significant computational challenges due to the massive number of patches in gigapixel images. While transformer architectures excel at modeling long-range correlations through self-attention, their quadratic computational complexity makes them impractical for computational pathology applications. Existing solutions like local-global or linear self-attention reduce computational costs but compromise the strong modeling capabilities of full self-attention. In this work, we propose Querent, i.e., the query-aware long contextual dynamic modeling framework, which maintains the expressive power of full self-attention while achieving practical efficiency. Our method adaptively predicts which surrounding regions are most relevant for each patch, enabling focused yet unrestricted attention computation only with potentially important contexts. By using efficient region-wise metadata computation and importance estimation, our approach dramatically reduces computational overhead while preserving global perception to model fine-grained patch correlations. Through comprehensive experiments on biomarker prediction, gene mutation prediction, cancer subtyping, and survival analysis across over 10 WSI datasets, our method demonstrates superior performance compared to the state-of-the-art approaches. Code will be made available at https://github.com/dddavid4real/Querent.
FOCUS: Knowledge-enhanced Adaptive Visual Compression for Few-shot Whole Slide Image Classification
Nov 22, 2024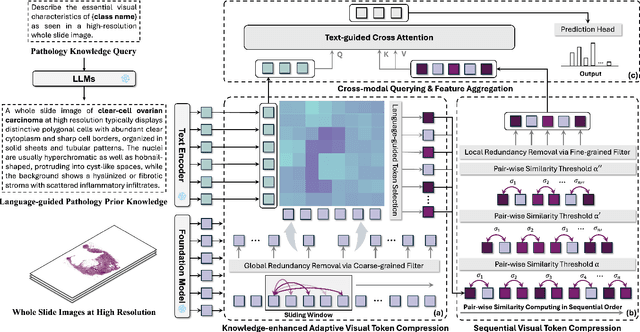
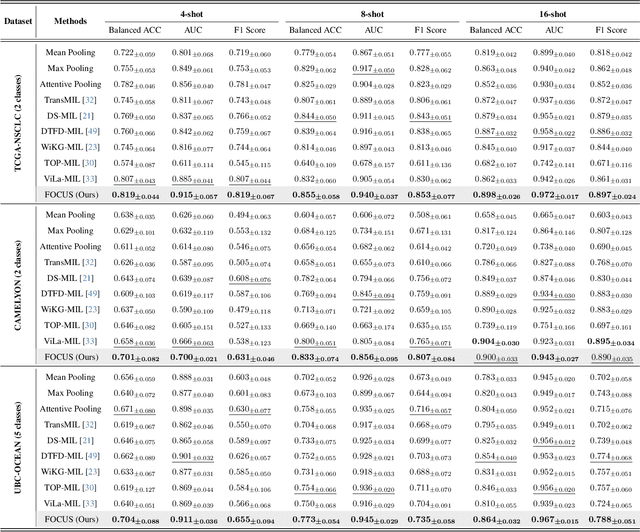
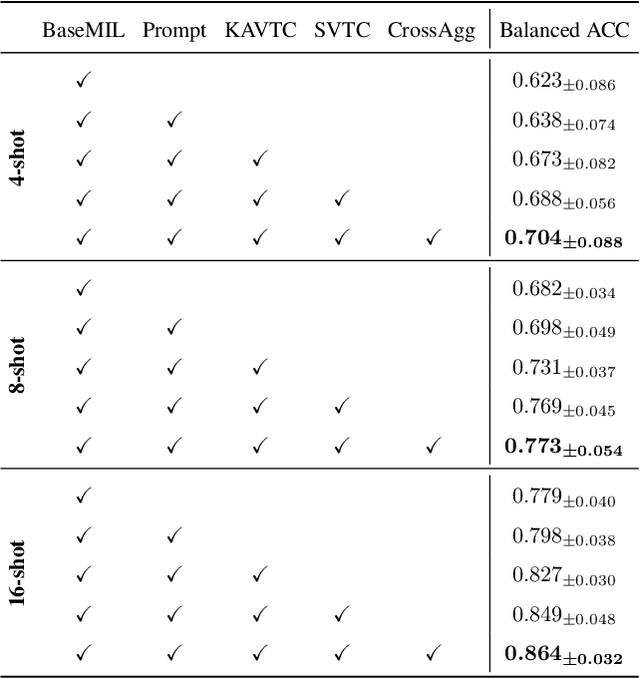
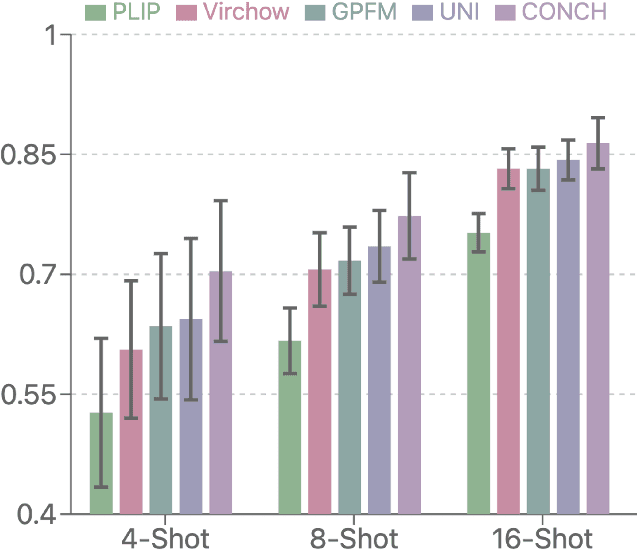
Abstract:Few-shot learning presents a critical solution for cancer diagnosis in computational pathology (CPath), addressing fundamental limitations in data availability, particularly the scarcity of expert annotations and patient privacy constraints. A key challenge in this paradigm stems from the inherent disparity between the limited training set of whole slide images (WSIs) and the enormous number of contained patches, where a significant portion of these patches lacks diagnostically relevant information, potentially diluting the model's ability to learn and focus on critical diagnostic features. While recent works attempt to address this by incorporating additional knowledge, several crucial gaps hinder further progress: (1) despite the emergence of powerful pathology foundation models (FMs), their potential remains largely untapped, with most approaches limiting their use to basic feature extraction; (2) current language guidance mechanisms attempt to align text prompts with vast numbers of WSI patches all at once, struggling to leverage rich pathological semantic information. To this end, we introduce the knowledge-enhanced adaptive visual compression framework, dubbed FOCUS, which uniquely combines pathology FMs with language prior knowledge to enable a focused analysis of diagnostically relevant regions by prioritizing discriminative WSI patches. Our approach implements a progressive three-stage compression strategy: we first leverage FMs for global visual redundancy elimination, and integrate compressed features with language prompts for semantic relevance assessment, then perform neighbor-aware visual token filtering while preserving spatial coherence. Extensive experiments on pathological datasets spanning breast, lung, and ovarian cancers demonstrate its superior performance in few-shot pathology diagnosis. Code will be made available at https://github.com/dddavid4real/FOCUS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge