Qiaosha Zou
Frequency Adaptive Normalization For Non-stationary Time Series Forecasting
Sep 30, 2024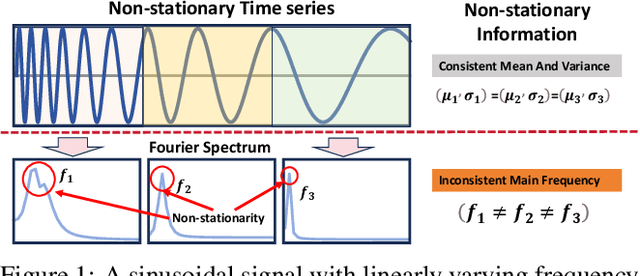
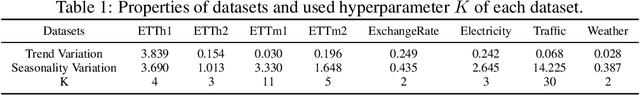
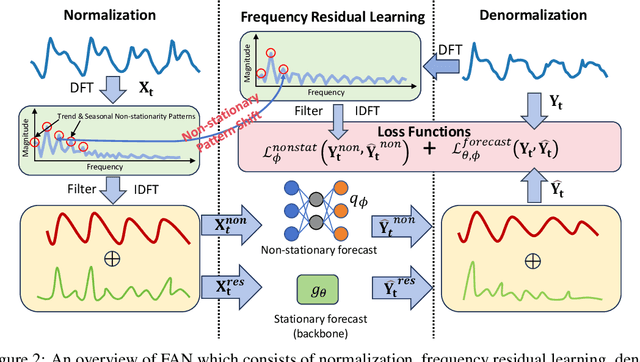
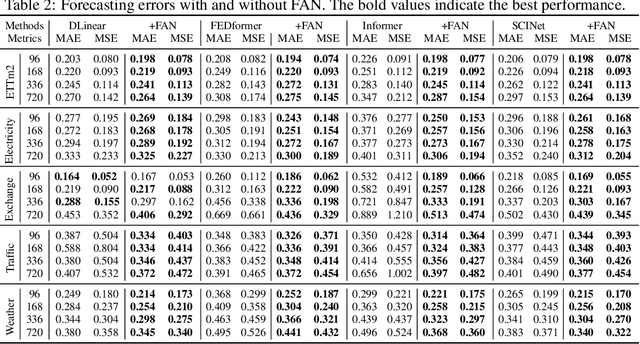
Abstract:Time series forecasting typically needs to address non-stationary data with evolving trend and seasonal patterns. To address the non-stationarity, reversible instance normalization has been recently proposed to alleviate impacts from the trend with certain statistical measures, e.g., mean and variance. Although they demonstrate improved predictive accuracy, they are limited to expressing basic trends and are incapable of handling seasonal patterns. To address this limitation, this paper proposes a new instance normalization solution, called frequency adaptive normalization (FAN), which extends instance normalization in handling both dynamic trend and seasonal patterns. Specifically, we employ the Fourier transform to identify instance-wise predominant frequent components that cover most non-stationary factors. Furthermore, the discrepancy of those frequency components between inputs and outputs is explicitly modeled as a prediction task with a simple MLP model. FAN is a model-agnostic method that can be applied to arbitrary predictive backbones. We instantiate FAN on four widely used forecasting models as the backbone and evaluate their prediction performance improvements on eight benchmark datasets. FAN demonstrates significant performance advancement, achieving 7.76% ~ 37.90% average improvements in MSE.
The Spike Gating Flow: A Hierarchical Structure Based Spiking Neural Network for Online Gesture Recognition
Jun 07, 2022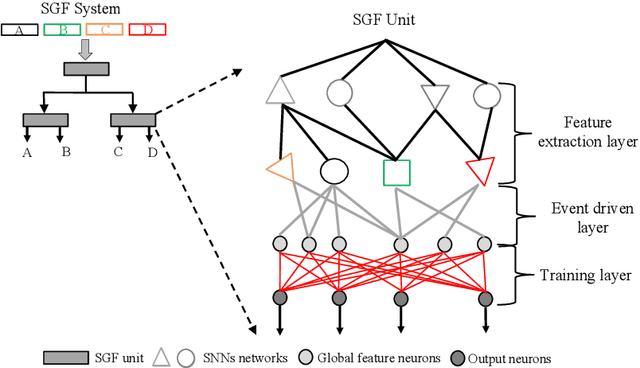
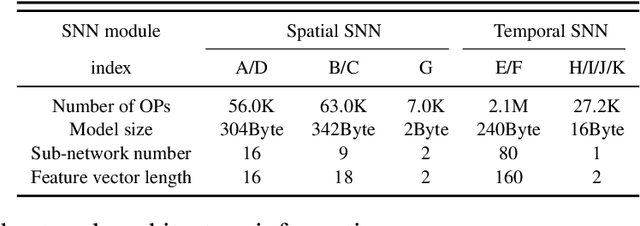
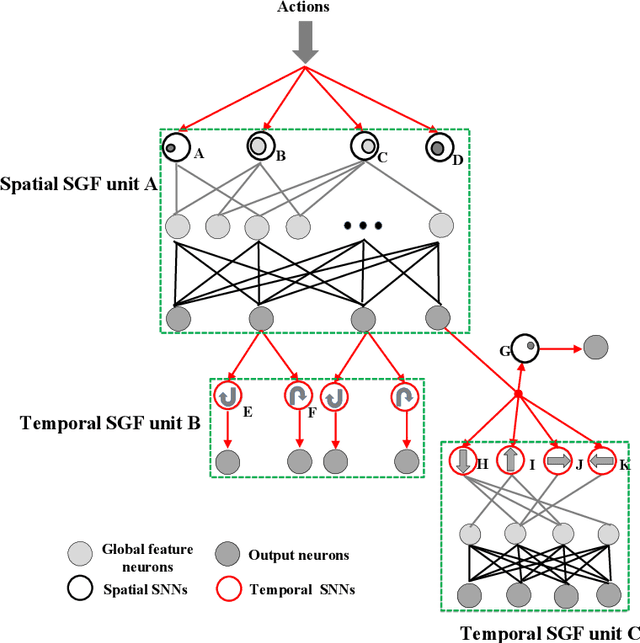
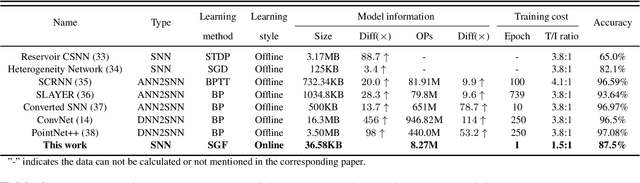
Abstract:Action recognition is an exciting research avenue for artificial intelligence since it may be a game changer in the emerging industrial fields such as robotic visions and automobiles. However, current deep learning faces major challenges for such applications because of the huge computational cost and the inefficient learning. Hence, we develop a novel brain-inspired Spiking Neural Network (SNN) based system titled Spiking Gating Flow (SGF) for online action learning. The developed system consists of multiple SGF units which assembled in a hierarchical manner. A single SGF unit involves three layers: a feature extraction layer, an event-driven layer and a histogram-based training layer. To demonstrate the developed system capabilities, we employ a standard Dynamic Vision Sensor (DVS) gesture classification as a benchmark. The results indicate that we can achieve 87.5% accuracy which is comparable with Deep Learning (DL), but at smaller training/inference data number ratio 1.5:1. And only a single training epoch is required during the learning process. Meanwhile, to the best of our knowledge, this is the highest accuracy among the non-backpropagation algorithm based SNNs. At last, we conclude the few-shot learning paradigm of the developed network: 1) a hierarchical structure-based network design involves human prior knowledge; 2) SNNs for content based global dynamic feature detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge