Qianyang Wu
THOR: Text to Human-Object Interaction Diffusion via Relation Intervention
Mar 17, 2024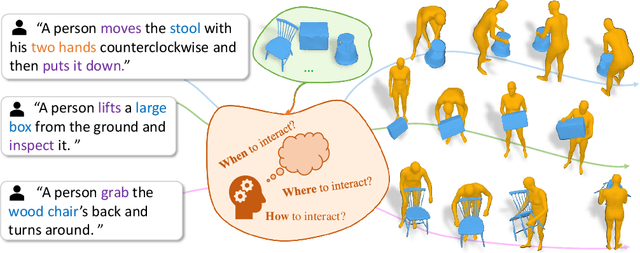


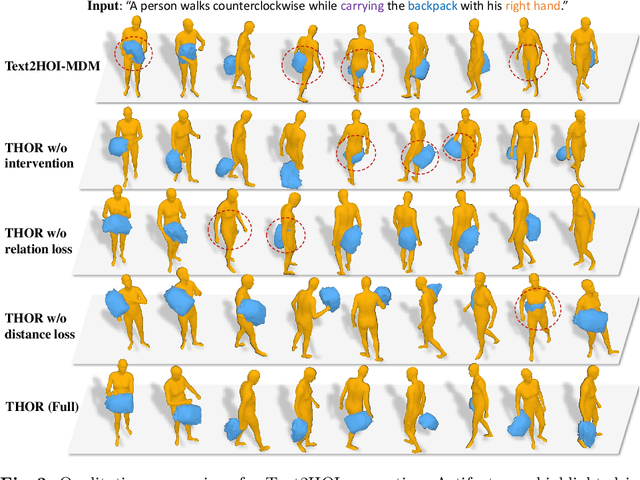
Abstract:This paper addresses new methodologies to deal with the challenging task of generating dynamic Human-Object Interactions from textual descriptions (Text2HOI). While most existing works assume interactions with limited body parts or static objects, our task involves addressing the variation in human motion, the diversity of object shapes, and the semantic vagueness of object motion simultaneously. To tackle this, we propose a novel Text-guided Human-Object Interaction diffusion model with Relation Intervention (THOR). THOR is a cohesive diffusion model equipped with a relation intervention mechanism. In each diffusion step, we initiate text-guided human and object motion and then leverage human-object relations to intervene in object motion. This intervention enhances the spatial-temporal relations between humans and objects, with human-centric interaction representation providing additional guidance for synthesizing consistent motion from text. To achieve more reasonable and realistic results, interaction losses is introduced at different levels of motion granularity. Moreover, we construct Text-BEHAVE, a Text2HOI dataset that seamlessly integrates textual descriptions with the currently largest publicly available 3D HOI dataset. Both quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model.
NeuralDome: A Neural Modeling Pipeline on Multi-View Human-Object Interactions
Dec 15, 2022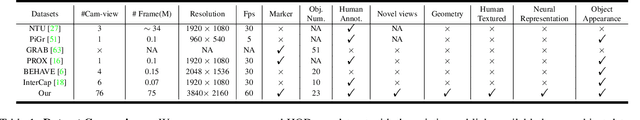
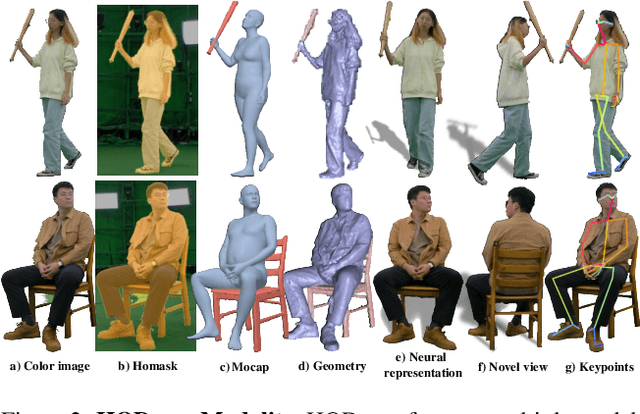
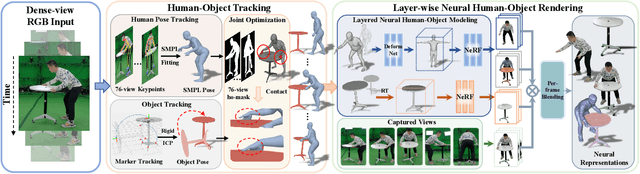
Abstract:Humans constantly interact with objects in daily life tasks. Capturing such processes and subsequently conducting visual inferences from a fixed viewpoint suffers from occlusions, shape and texture ambiguities, motions, etc. To mitigate the problem, it is essential to build a training dataset that captures free-viewpoint interactions. We construct a dense multi-view dome to acquire a complex human object interaction dataset, named HODome, that consists of $\sim$75M frames on 10 subjects interacting with 23 objects. To process the HODome dataset, we develop NeuralDome, a layer-wise neural processing pipeline tailored for multi-view video inputs to conduct accurate tracking, geometry reconstruction and free-view rendering, for both human subjects and objects. Extensive experiments on the HODome dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of NeuralDome on a variety of inference, modeling, and rendering tasks. Both the dataset and the NeuralDome tools will be disseminated to the community for further development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge