Pushpak Bhattacharya
Is your LLM trapped in a Mental Set? Investigative study on how mental sets affect the reasoning capabilities of LLMs
Jan 21, 2025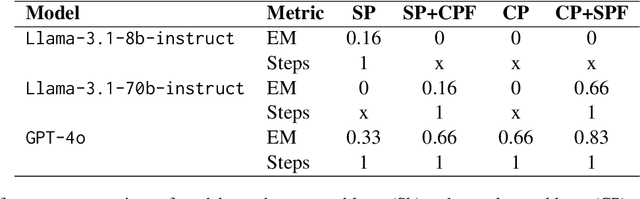
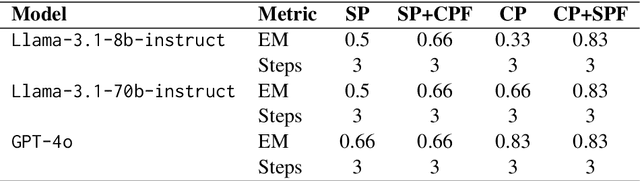
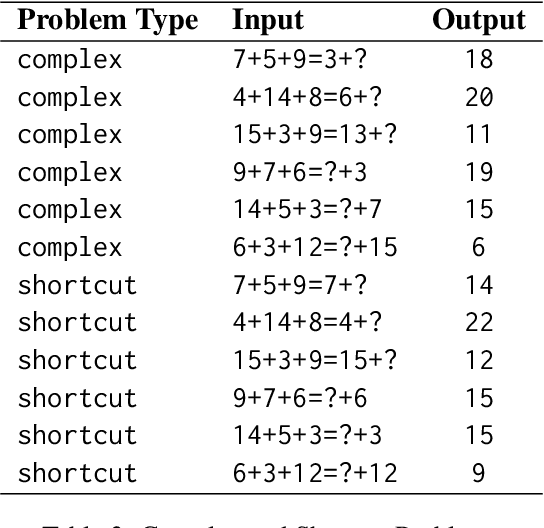
Abstract:In this paper, we present an investigative study on how Mental Sets influence the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. LLMs have excelled in diverse natural language processing (NLP) tasks, driven by advancements in parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) and emergent capabilities like in-context learning (ICL). For complex reasoning tasks, selecting the right model for PEFT or ICL is critical, often relying on scores on benchmarks such as MMLU, MATH, and GSM8K. However, current evaluation methods, based on metrics like F1 Score or reasoning chain assessments by larger models, overlook a key dimension: adaptability to unfamiliar situations and overcoming entrenched thinking patterns. In cognitive psychology, Mental Set refers to the tendency to persist with previously successful strategies, even when they become inefficient - a challenge for problem solving and reasoning. We compare the performance of LLM models like Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct, Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct and GPT-4o in the presence of mental sets. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to integrate cognitive psychology concepts into the evaluation of LLMs for complex reasoning tasks, providing deeper insights into their adaptability and problem-solving efficacy.
Technology Pipeline for Large Scale Cross-Lingual Dubbing of Lecture Videos into Multiple Indian Languages
Nov 01, 2022

Abstract:Cross-lingual dubbing of lecture videos requires the transcription of the original audio, correction and removal of disfluencies, domain term discovery, text-to-text translation into the target language, chunking of text using target language rhythm, text-to-speech synthesis followed by isochronous lipsyncing to the original video. This task becomes challenging when the source and target languages belong to different language families, resulting in differences in generated audio duration. This is further compounded by the original speaker's rhythm, especially for extempore speech. This paper describes the challenges in regenerating English lecture videos in Indian languages semi-automatically. A prototype is developed for dubbing lectures into 9 Indian languages. A mean-opinion-score (MOS) is obtained for two languages, Hindi and Tamil, on two different courses. The output video is compared with the original video in terms of MOS (1-5) and lip synchronisation with scores of 4.09 and 3.74, respectively. The human effort also reduces by 75%.
End-to-End Relation Extraction using Markov Logic Networks
Dec 04, 2017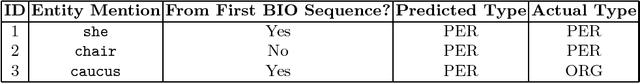
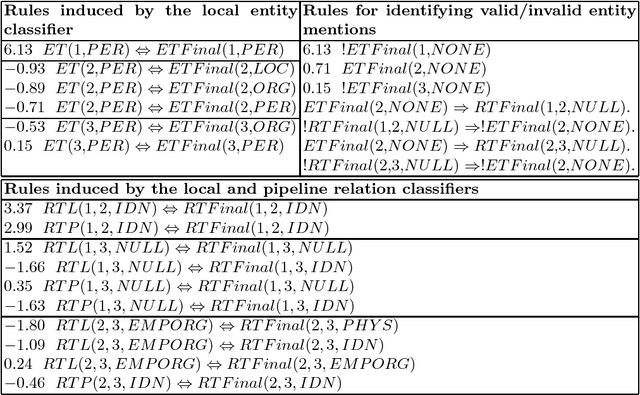
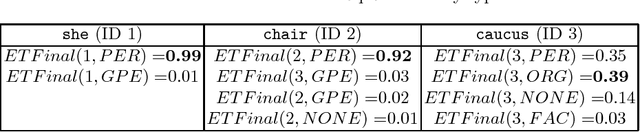
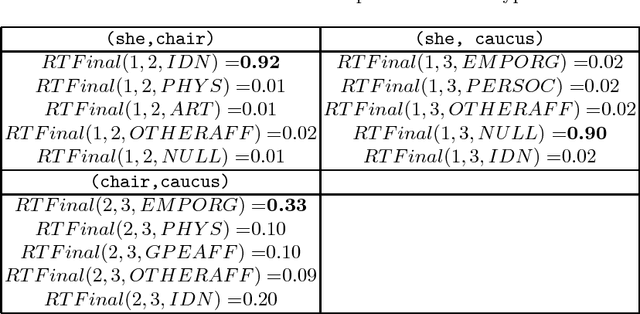
Abstract:The task of end-to-end relation extraction consists of two sub-tasks: i) identifying entity mentions along with their types and ii) recognizing semantic relations among the entity mention pairs. %Identifying entity mentions along with their types and recognizing semantic relations among the entity mentions, are two very important problems in Information Extraction. It has been shown that for better performance, it is necessary to address these two sub-tasks jointly. We propose an approach for simultaneous extraction of entity mentions and relations in a sentence, by using inference in Markov Logic Networks (MLN). We learn three different classifiers : i) local entity classifier, ii) local relation classifier and iii) "pipeline" relation classifier which uses predictions of the local entity classifier. Predictions of these classifiers may be inconsistent with each other. We represent these predictions along with some domain knowledge using weighted first-order logic rules in an MLN and perform joint inference over the MLN to obtain a global output with minimum inconsistencies. Experiments on the ACE (Automatic Content Extraction) 2004 dataset demonstrate that our approach of joint extraction using MLNs outperforms the baselines of individual classifiers. Our end-to-end relation extraction performance is better than 2 out of 3 previous results reported on the ACE 2004 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge