Prajwal K R
Sub-word Level Lip Reading With Visual Attention
Oct 14, 2021



Abstract:The goal of this paper is to learn strong lip reading models that can recognise speech in silent videos. Most prior works deal with the open-set visual speech recognition problem by adapting existing automatic speech recognition techniques on top of trivially pooled visual features. Instead, in this paper we focus on the unique challenges encountered in lip reading and propose tailored solutions. To that end we make the following contributions: (1) we propose an attention-based pooling mechanism to aggregate visual speech representations; (2) we use sub-word units for lip reading for the first time and show that this allows us to better model the ambiguities of the task; (3) we propose a training pipeline that balances the lip reading performance with other key factors such as data and compute efficiency. Following the above, we obtain state-of-the-art results on the challenging LRS2 and LRS3 benchmarks when training on public datasets, and even surpass models trained on large-scale industrial datasets by using an order of magnitude less data. Our best model achieves 22.6% word error rate on the LRS2 dataset, a performance unprecedented for lip reading models, significantly reducing the performance gap between lip reading and automatic speech recognition.
Towards Automatic Face-to-Face Translation
Mar 01, 2020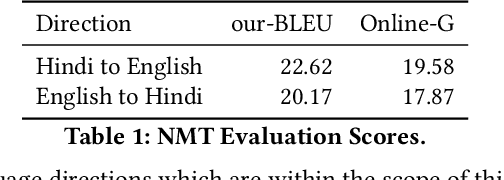
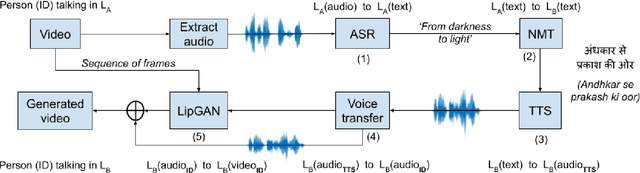

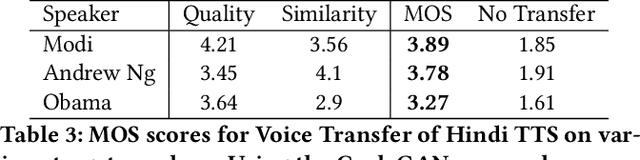
Abstract:In light of the recent breakthroughs in automatic machine translation systems, we propose a novel approach that we term as "Face-to-Face Translation". As today's digital communication becomes increasingly visual, we argue that there is a need for systems that can automatically translate a video of a person speaking in language A into a target language B with realistic lip synchronization. In this work, we create an automatic pipeline for this problem and demonstrate its impact on multiple real-world applications. First, we build a working speech-to-speech translation system by bringing together multiple existing modules from speech and language. We then move towards "Face-to-Face Translation" by incorporating a novel visual module, LipGAN for generating realistic talking faces from the translated audio. Quantitative evaluation of LipGAN on the standard LRW test set shows that it significantly outperforms existing approaches across all standard metrics. We also subject our Face-to-Face Translation pipeline, to multiple human evaluations and show that it can significantly improve the overall user experience for consuming and interacting with multimodal content across languages. Code, models and demo video are made publicly available. Demo video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aHG6Oei8jF0 Code and models: https://github.com/Rudrabha/LipGAN
* 9 pages (including references), 5 figures, Published in ACM Multimedia, 2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge