Piotr Wilczyński
Warsaw University of Technology
Fake or Real: The Impostor Hunt in Texts for Space Operations
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:The "Fake or Real" competition hosted on Kaggle (\href{https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/fake-or-real-the-impostor-hunt}{https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/fake-or-real-the-impostor-hunt}) is the second part of a series of follow-up competitions and hackathons related to the "Assurance for Space Domain AI Applications" project funded by the European Space Agency (\href{https://assurance-ai.space-codev.org/}{https://assurance-ai.space-codev.org/}). The competition idea is based on two real-life AI security threats identified within the project -- data poisoning and overreliance in Large Language Models. The task is to distinguish between the proper output from LLM and the output generated under malicious modification of the LLM. As this problem was not extensively researched, participants are required to develop new techniques to address this issue or adjust already existing ones to this problem's statement.
MASCOTS: Model-Agnostic Symbolic COunterfactual explanations for Time Series
Mar 28, 2025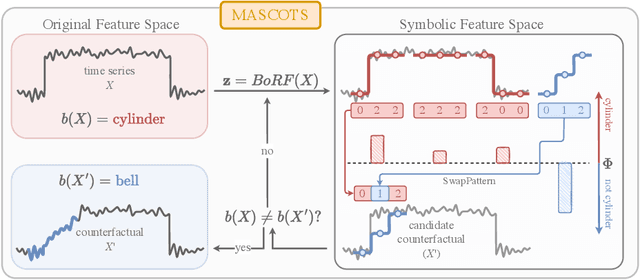
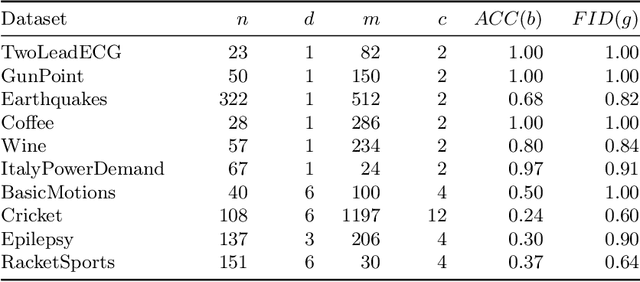
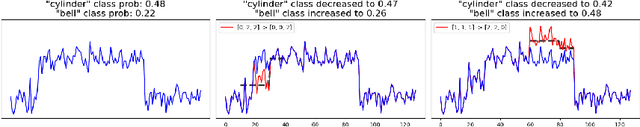
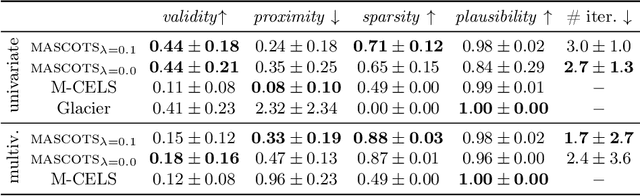
Abstract:Counterfactual explanations provide an intuitive way to understand model decisions by identifying minimal changes required to alter an outcome. However, applying counterfactual methods to time series models remains challenging due to temporal dependencies, high dimensionality, and the lack of an intuitive human-interpretable representation. We introduce MASCOTS, a method that leverages the Bag-of-Receptive-Fields representation alongside symbolic transformations inspired by Symbolic Aggregate Approximation. By operating in a symbolic feature space, it enhances interpretability while preserving fidelity to the original data and model. Unlike existing approaches that either depend on model structure or autoencoder-based sampling, MASCOTS directly generates meaningful and diverse counterfactual observations in a model-agnostic manner, operating on both univariate and multivariate data. We evaluate MASCOTS on univariate and multivariate benchmark datasets, demonstrating comparable validity, proximity, and plausibility to state-of-the-art methods, while significantly improving interpretability and sparsity. Its symbolic nature allows for explanations that can be expressed visually, in natural language, or through semantic representations, making counterfactual reasoning more accessible and actionable.
SeFNet: Bridging Tabular Datasets with Semantic Feature Nets
Jun 20, 2023Abstract:Machine learning applications cover a wide range of predictive tasks in which tabular datasets play a significant role. However, although they often address similar problems, tabular datasets are typically treated as standalone tasks. The possibilities of using previously solved problems are limited due to the lack of structured contextual information about their features and the lack of understanding of the relations between them. To overcome this limitation, we propose a new approach called Semantic Feature Net (SeFNet), capturing the semantic meaning of the analyzed tabular features. By leveraging existing ontologies and domain knowledge, SeFNet opens up new opportunities for sharing insights between diverse predictive tasks. One such opportunity is the Dataset Ontology-based Semantic Similarity (DOSS) measure, which quantifies the similarity between datasets using relations across their features. In this paper, we present an example of SeFNet prepared for a collection of predictive tasks in healthcare, with the features' relations derived from the SNOMED-CT ontology. The proposed SeFNet framework and the accompanying DOSS measure address the issue of limited contextual information in tabular datasets. By incorporating domain knowledge and establishing semantic relations between features, we enhance the potential for meta-learning and enable valuable insights to be shared across different predictive tasks.
HADES: Homologous Automated Document Exploration and Summarization
Feb 25, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces HADES, a novel tool for automatic comparative documents with similar structures. HADES is designed to streamline the work of professionals dealing with large volumes of documents, such as policy documents, legal acts, and scientific papers. The tool employs a multi-step pipeline that begins with processing PDF documents using topic modeling, summarization, and analysis of the most important words for each topic. The process concludes with an interactive web app with visualizations that facilitate the comparison of the documents. HADES has the potential to significantly improve the productivity of professionals dealing with high volumes of documents, reducing the time and effort required to complete tasks related to comparative document analysis. Our package is publically available on GitHub.
Climate Policy Tracker: Pipeline for automated analysis of public climate policies
Nov 10, 2022



Abstract:The number of standardized policy documents regarding climate policy and their publication frequency is significantly increasing. The documents are long and tedious for manual analysis, especially for policy experts, lawmakers, and citizens who lack access or domain expertise to utilize data analytics tools. Potential consequences of such a situation include reduced citizen governance and involvement in climate policies and an overall surge in analytics costs, rendering less accessibility for the public. In this work, we use a Latent Dirichlet Allocation-based pipeline for the automatic summarization and analysis of 10-years of national energy and climate plans (NECPs) for the period from 2021 to 2030, established by 27 Member States of the European Union. We focus on analyzing policy framing, the language used to describe specific issues, to detect essential nuances in the way governments frame their climate policies and achieve climate goals. The methods leverage topic modeling and clustering for the comparative analysis of policy documents across different countries. It allows for easier integration in potential user-friendly applications for the development of theories and processes of climate policy. This would further lead to better citizen governance and engagement over climate policies and public policy research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge